Strain SiGe square-in-square type channel NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) integrated device and preparation method thereof
An integrated device and channel direction technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc. Devices and circuits, restricting the development of the semiconductor industry and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
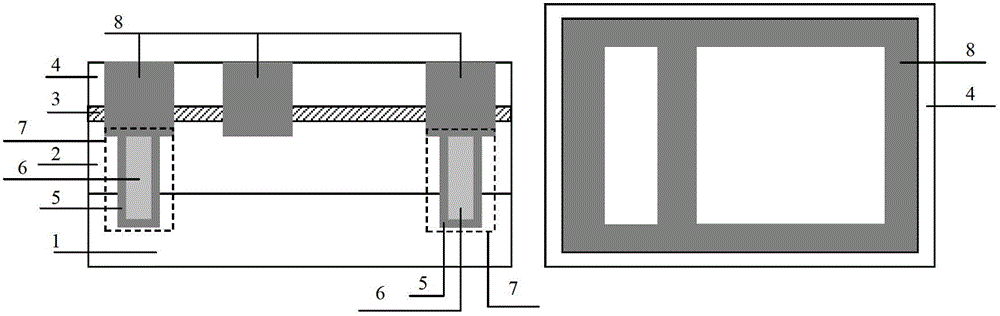
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
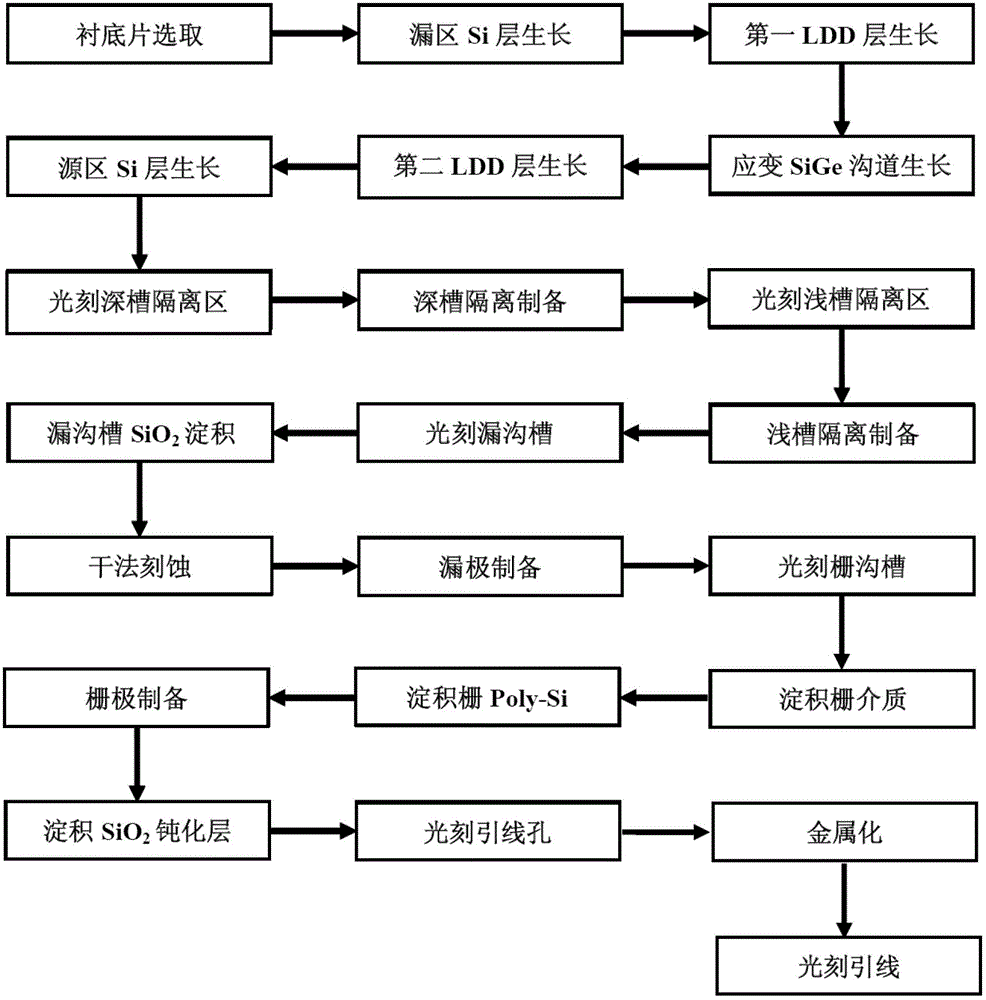
[0075] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the strained SiGe back channel NMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 45nm, the specific steps are as follows:
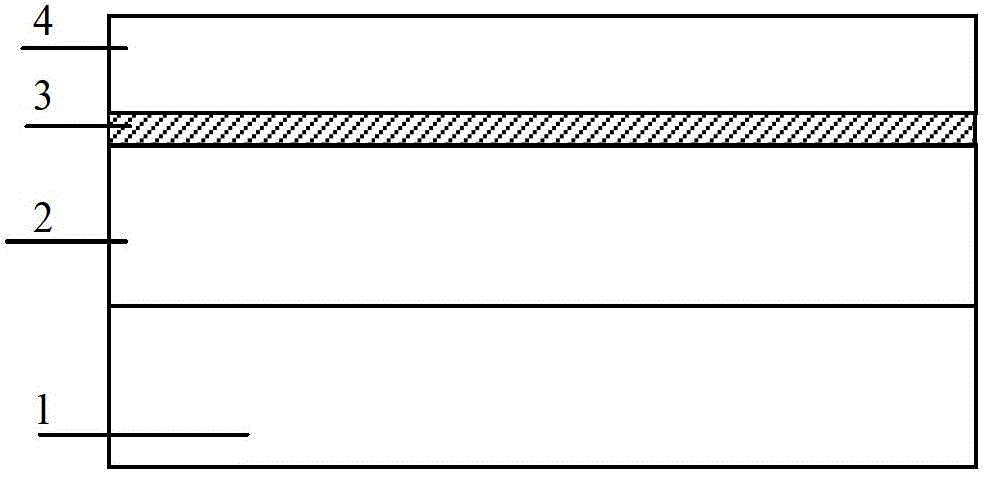
[0076] Step 1, epitaxial material preparation, as shown in Figure 2(a).
[0077] (1a) Select the doping concentration as 10 15 cm -3 Left and right P-type Si substrate sheets 1;
[0078] (1b) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 600°C, grow a layer of N-type Si epitaxial layer 2 with a thickness of 2.5 μm on the substrate as the drain region, with a doping concentration of 5×10 19 cm -3 ;
[0079] (1c) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), grow an N-type strained SiGe layer 3a with a thickness of 5nm on the substrate at 600°C, with a doping concentration of 5×10 17 cm -3 , the Ge composition is 10%, as the first lightly doped source and drain region (LDD) layer;
[0080] (1d) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 600°C, grow a P-type SiGe layer 3 with a thickness of 45 nm on the Si epi...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the strained SiGe back channel NMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 30nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0110] Step 1, epitaxial material preparation, as shown in Figure 2(a).
[0111] (1a) Select the doping concentration to be 5×10 15 cm -3 Left and right P-type Si substrate sheets 1;
[0112] (1b) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 700°C, grow a layer of N-type Si epitaxial layer 2 with a thickness of 2.5 μm on the substrate as the drain region, with a doping concentration of 1×10 20 cm -3 ;
[0113] (1c) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), grow an N-type strained SiGe layer 3a with a thickness of 4nm on the substrate at 700°C, with a doping concentration of 1×10 18 cm -3 , the Ge composition is 10%, as the first lightly doped source and drain region (LDD) layer;
[0114] (1d) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 700°C, grow a P-type SiGe layer 3 with a thickness of 30 nm on the S...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Embodiment 3: the preparation of the strained SiGe back channel NMOS integrated device and circuit with a conductive channel of 22nm, the specific steps are as follows:
[0144] Step 1, epitaxial material preparation, as shown in Figure 2(a).
[0145] (1a) Select the doping concentration as 10 16 cm -3 Left and right P-type Si substrate sheets 1;
[0146] (1b) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 750°C, grow a layer of N-type Si epitaxial layer 2 with a thickness of 2 μm on the substrate as the drain region, with a doping concentration of 5×10 20 cm -3 ;
[0147] (1c) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), grow an N-type strained SiGe layer 3a with a thickness of 3nm on the substrate at 750°C, with a doping concentration of 5×10 18 cm -3 , the Ge composition is 10%, as the first lightly doped source and drain region (LDD) layer;
[0148] (1d) Using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), at 750°C, grow a P-type SiGe layer 3 with a thickness of 22nm on the Si epitax...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com