Rear-contact heterojunction photovoltaic cell
A photovoltaic cell and back surface technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, circuits, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effects of simplified manufacturing process, good passivation, and small ohmic loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] In the following description, the invention will be described in more detail without limitation with reference to photovoltaic applications of the invention.
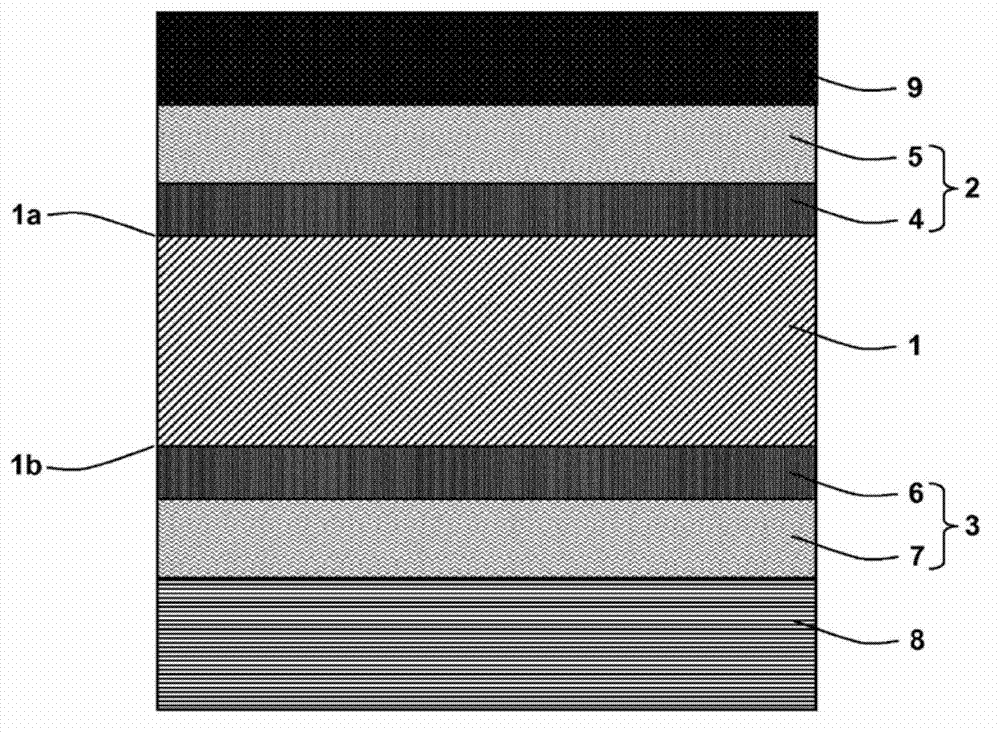
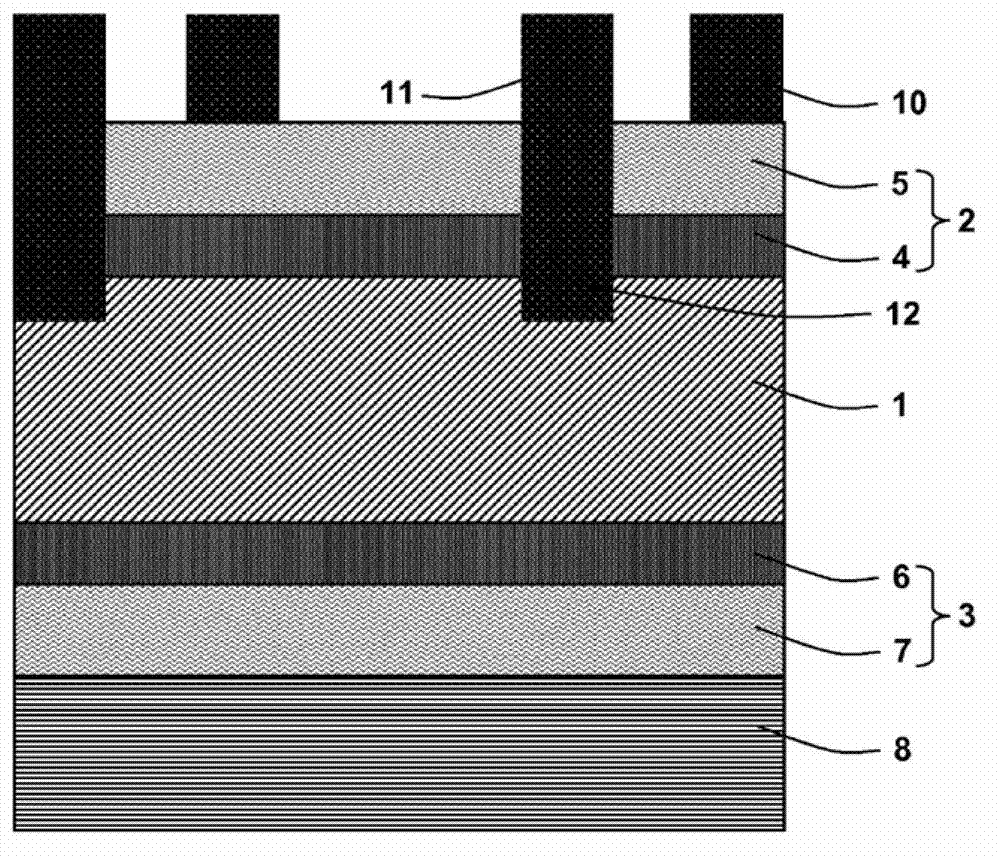
[0062] see figure 1 , the semiconductor device according to the present invention can be fabricated as follows.
[0063] First, a crystalline semiconductor substrate 1 having a front surface 1a and a back surface 1b is provided. Preferably, the crystalline semiconductor substrate 1 is a crystal, especially a monocrystalline or polycrystalline (preferably monocrystalline) silicon substrate (or wafer) in the form of a wafer.
[0064] The substrate can be doped n-type or p-type. The use of n-type doped substrates is particularly advantageous due to their longer lifetime. In the following, an n-type doped substrate is taken as an example. Advantageously, the substrate 1 does not have any oxide material.
[0065] Preferably, the substrate 1 has sufficient doping to have a resistivity between about 0.1 and 1 Ω·cm....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com