Method for extracting natural algicide from Acorus calamus L and algae inhibition method
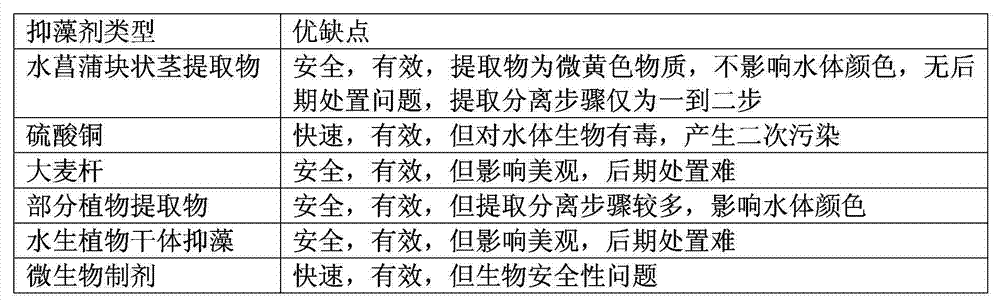
The technology of an algae inhibitor and water calamus, which is applied in the field of algae inhibitory active ingredients, can solve the problems of high cost, difficult separation and the like, and achieve the effects of low cost, strong environmental affinity, and simple and easy extraction method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
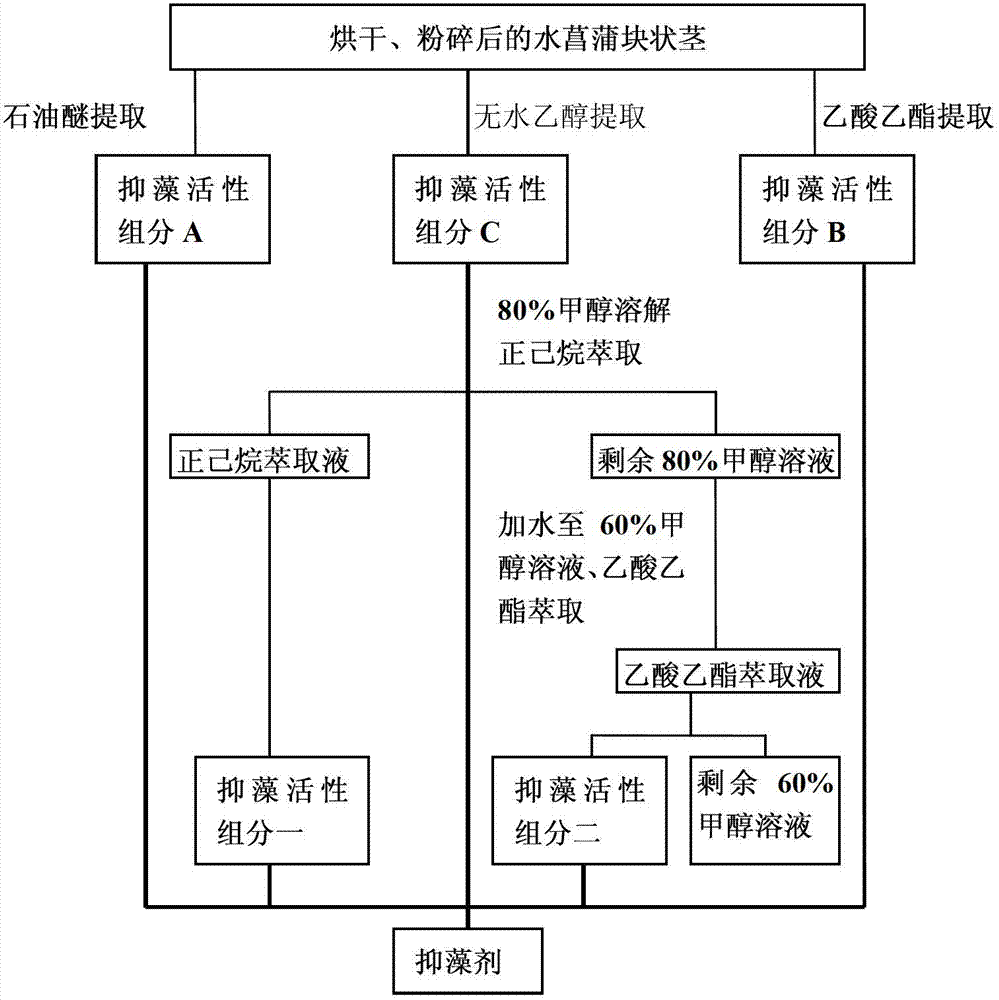
[0030] Embodiment 1: The massive rhizomes of Calamus calamus are collected, dried and pulverized. Take by weighing 50 g of calamus massive rhizome after crushing, extract 2-3 times at 50 C, each 12 hours. After filtration, the petroleum ether extracts were combined and concentrated by rotary evaporation at 35°C to obtain algae-inhibiting active component A. The active component A was subjected to acute toxicity experiments on aseptically cultured single-cell Microcystis aeruginosa, population Microcystis aeruginosa, A. aeruginosa and Anabaena blooms. Several concentration gradients were set, and blank and three The groups were parallel, observed once every 24 hours, and observed continuously for three days. The results were expressed as 96-hour inhibition rates, and the results were as follows:
[0031] Algae-inhibiting active ingredient A, when the mass volume concentration reaches 50mg / L (therefore 1 liter of water contains 50mgA), its inhibition rate on single-cell Microcy...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: The massive rhizomes of Calamus calamus are collected, dried and pulverized. Weigh 50 g of crushed calamus massive rhizomes, extract 2-3 times at 50 degrees, each time for 12 hours. After filtration, the ethyl acetate extracts were combined and concentrated by rotary evaporation at 35°C to obtain algae-inhibiting active component B.
[0033] The active component B was subjected to acute toxicity experiments on aseptically cultured single-cell Microcystis aeruginosa, population Microcystis aeruginosa, A. aeruginosa and Anabaena blooms. Several concentration gradients were set, and blank and three The groups were parallel, observed once every 24 hours, and observed continuously for three days. The results were expressed as 96-hour inhibition rates, and the results were as follows:
[0034] Algae-inhibiting active ingredient B, when the concentration reaches 50mg / L, its inhibition rate on single-cell Microcystis aeruginosa reaches 91%; when the concentration...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: The massive rhizomes of Calamus calamus are collected, dried and pulverized. Weigh 50 g of crushed calamus massive rhizomes, extract 2-3 times at 50 degrees, each time for 12 hours. After filtration, the anhydrous ethanol extracts were combined and concentrated by rotary evaporation at 35°C to obtain algae-inhibiting active component C.
[0036] The active component C was subjected to acute toxicity experiments on aseptically cultured single-cell Microcystis aeruginosa, colony Microcystis aeruginosa, A. aeruginosa and Anabaena blooms. Several concentration gradients were set, and blank and three The groups were parallel, observed once every 24 hours, and observed continuously for three days. The results were expressed as 96-hour inhibition rates, and the results were as follows:
[0037] Algae-inhibiting active ingredient C, when the concentration reaches 50mg / L, its inhibition rate on single-cell Microcystis aeruginosa reaches 95%; when the concentration...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com