Highly specific gene fragment of Enterobacter sakazakii and its application
A technology of Enterobacter sakazakii and genes, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of poor specificity, large sequence differences, and low specificity of 16SrDNA genes, and achieve the effects of low false positive rate, high specificity, and improved sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Acquisition of Specific Gene Fragments
[0053] 1. Use 16SrDNA universal primers to amplify the target sequence with Enterobacter sakazakii genomic DNA as a template;
[0054] 2. Obtain detailed sequence information through sequencing, and use NCBI's Blast tool to compare and analyze the obtained sequences to obtain highly conserved fragments. The matching rate of Enterobacter sakazakii is as high as 98%, but not that of Enterobacter sakazakii Less than 80% is the standard;
[0055] 3. Select the sequences at both ends, and design specific amplification primers based on the criterion that the last base at the end of the primer only matches the sequence of Enterobacter sakazakii and does not match the sequence of non-Enterobacter sakazakii, and use the designed primers to match the sequence of Enterobacter sakazakii Genomic DNA of Enterobacter sakazakii and non-Enterobacter sakazakii was amplified and tested;
[0056] 4、对选取的不同序列的结果进行比较和选择,最终获得了对不同阪崎肠杆菌菌株均具有高...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: Nucleic acid probe specific verification
[0058] 1. Design specific nucleic acid probes:
[0059] Using the specific sequence obtained by screening in Example 1 as a template, a specific capture probe for Enterobacter sakazakii was designed. The sequence of the probe is as follows:
[0060] PB: 5'-TCGTGCTGCGAGTTTGAGAGACTCTGACACACCGCG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2).
[0061] 2. Probe specificity detection verification:
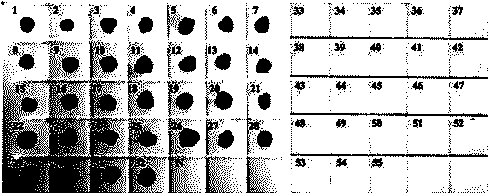
[0062] The specific recognition and capture of nucleic acid probes were verified by Southern Blotting hybridization experiment. The detailed steps are as follows: 32 strains of Enterobacter sakazakii and 23 strains of non-Sakazakii Enterobacter (including common intestinal pathogenic bacteria and probiotics) were taken respectively. ), and the genomic DNA of each strain was extracted, and after heat denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes, it was quickly placed in an ice-water bath (to treat it as a single strand); the heat-denatured genomic DNA was spott...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: PCR primer specificity verification
[0065] 1. Primer design:
[0066] Using the specific sequence obtained by screening in Example 1 as the target sequence as a template, Enterobacter sakazakii-specific amplification primers were designed, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0067] CsppF1: 5'-TCGTGCTGCGAGTTTGAGAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3)
[0068] CsppR1: 5'-CCTCGCGTGCTCACACAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0069] CsppF2: 5'-AGAGACTCTGACACACCGCG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5)
[0070] CsppR2: 5'-AATGAGTGAAAGGCGTTACCG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6)
[0071] 2. Verification of primer specificity
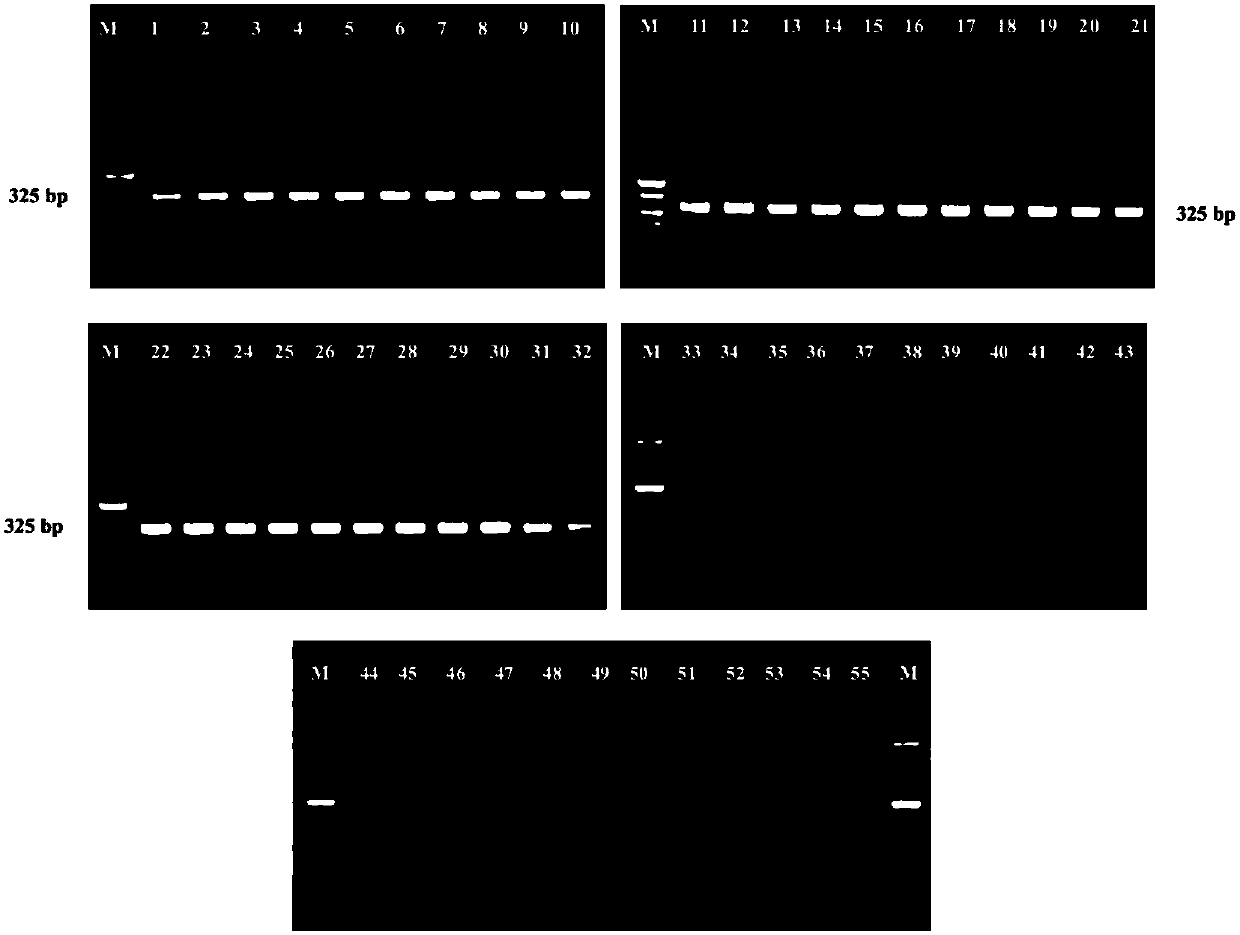
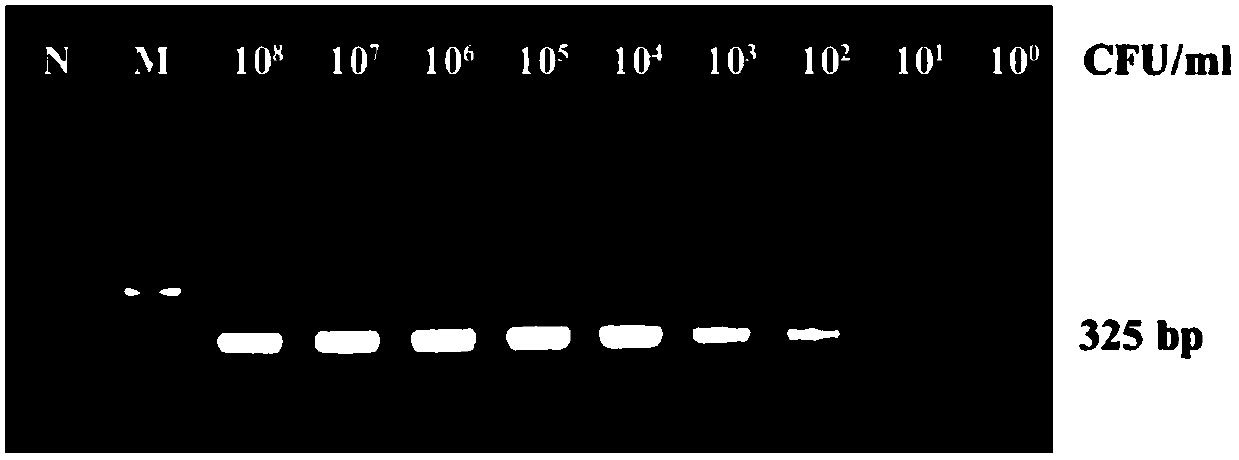
[0072] The specificity of primers CsppF1 / CsppR1 and CsppF2 / CsppR2 was verified by nested PCR amplification using the genomic DNA of the above 32 strains of Enterobacter sakazakii and 23 strains of non-Enterobacter sakazakii as templates. Proceed as follows:
[0073] The genomic DNA template of each strain was used for the first round of nested PCR amplification. PCR reaction system (20 μL): 2×...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com