Method for preparing galactose homopolymer/polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber membrane
A technology of composite nanofibers and polyacrylonitrile, which is applied in textiles, papermaking, non-woven fabrics and other directions, can solve the problems of affecting the service stability of membranes, poor hydrophilicity, membrane fouling, etc., and achieves low cost, simple preparation, and easy products. processing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
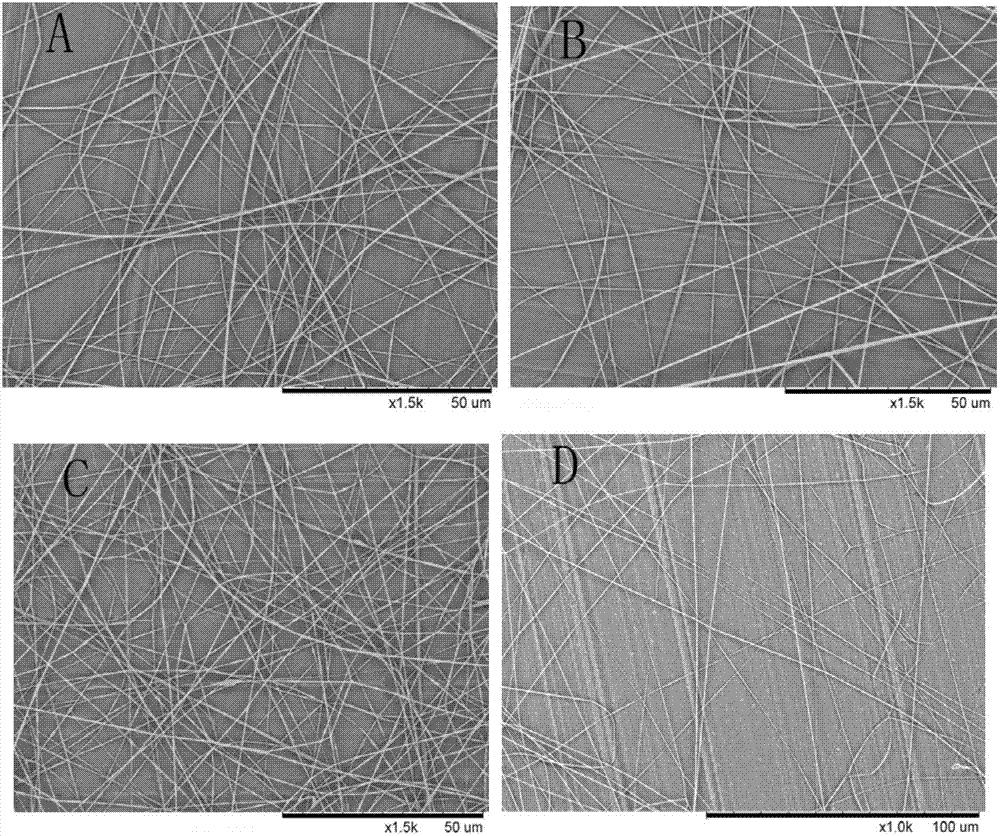
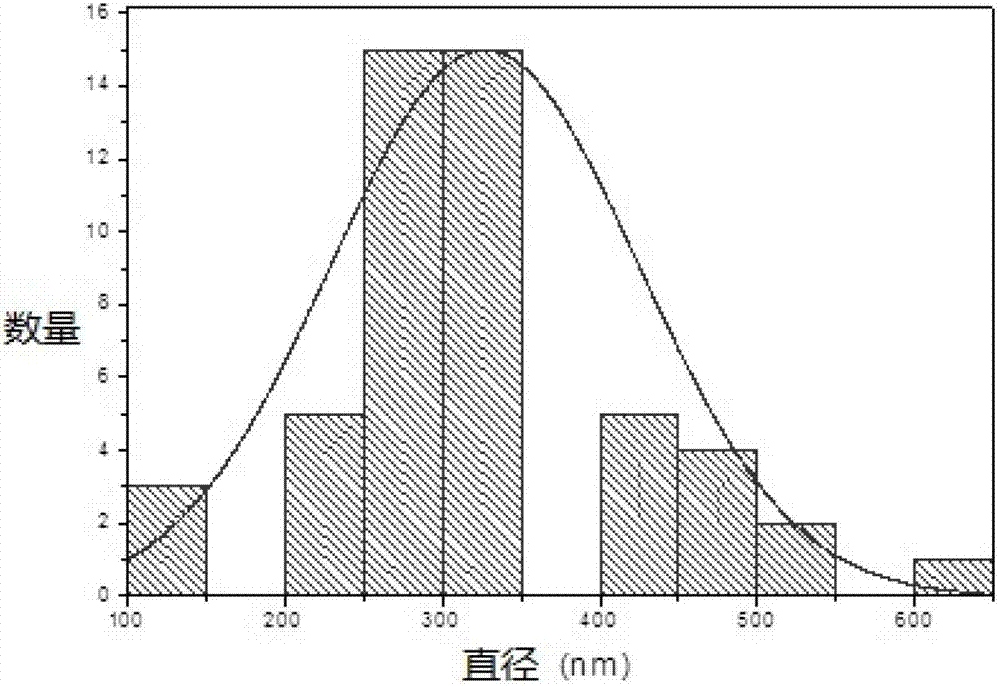
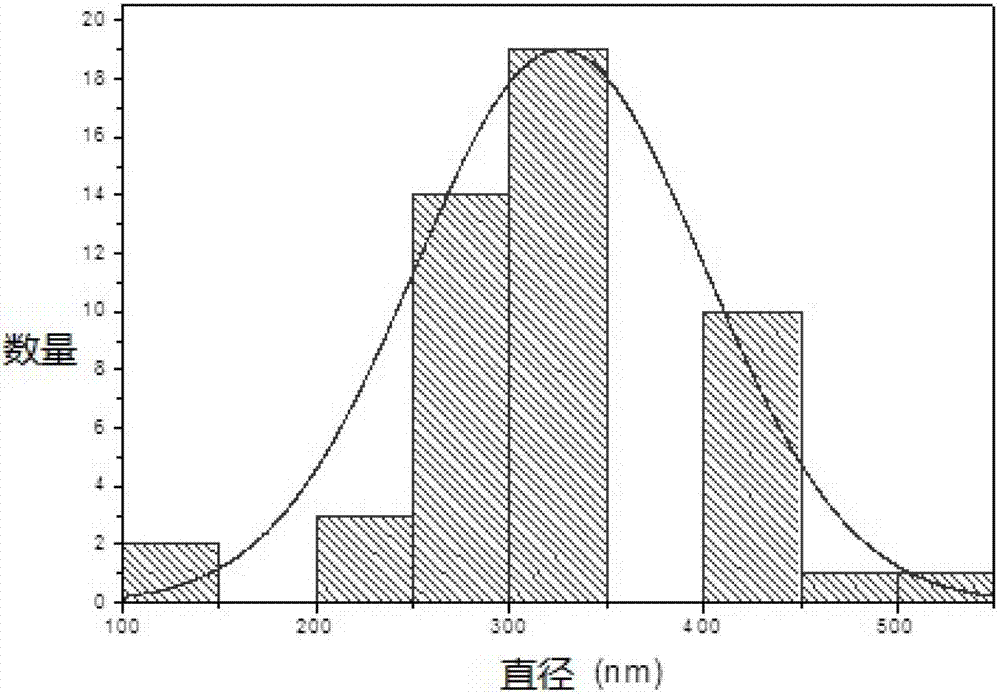
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (1) Dissolve divinyl diacid and galactose in 100 mL of anhydrous pyridine at a molar ratio of 3:1, add 0.5 g of alkaline protease, and react in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 40°C for 4 days at a speed of 210 rpm. Synthesis of galactosyl vinyl esters by enzymatic synthesis.
[0039] (2) Put the above-mentioned glycolipids in a micropolymerization tube, use ammonium persulfate (APS) (accounting for 1.0 mass fraction of galactose ethylene lipid) as an initiator, and add H 2 O as solvent (monomer concentration is 2.0mol / L H 2 O), sealed, vacuumed by an oil pump, and nitrogen gas, repeated several times. The system was placed at 55-60° C. under the protection of nitrogen and stirred for 5 h.
[0040] (3) Dissolve a certain mass of PAN in DMF to obtain a PAN solution with a concentration of 0.1g / mL; then add galactoresin to homopolymerize so that the mass fraction is 40% respectively, stir for several hours until completely dissolved, and let stand for several...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (1) Dissolve divinyl diacid and galactose in 100 mL of anhydrous pyridine at a molar ratio of 3:1, add 1.0 g of alkaline protease, and react in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 45°C for 4 days at a speed of 210 rpm. Synthesis of galactosyl vinyl esters by enzymatic synthesis.
[0044] (2) Put the above-mentioned glycolipids in a micropolymerization tube, use ammonium persulfate (APS) (accounting for 1.0 mass fraction of galactose ethylene lipid) as an initiator, and add H 2 O as solvent (monomer concentration is 2.0mol / L H 2 O), sealed, vacuumed by an oil pump, and nitrogen gas, repeated several times. The system was placed at 55-60° C. under the protection of nitrogen and stirred for 5 h.
[0045] (3) Dissolve a certain mass of PAN in DMF to obtain a PAN solution with a concentration of 0.1g / mL; then add galactose for homopolymerization so that the mass fraction is 50% respectively, stir for several hours until completely dissolved, and let stand for sever...
Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) Dissolve divinyl diacid and galactose in 100 mL of anhydrous pyridine at a molar ratio of 3:1, add 1.5 g of alkaline protease, and react in a constant temperature shaking incubator at 60°C for 4 days at a speed of 210 rpm. Synthesis of galactosyl vinyl esters by enzymatic synthesis.
[0049] (2) Put the above-mentioned glycolipids in a micropolymerization tube, use ammonium persulfate (APS) (accounting for 1.0 mass fraction of galactose ethylene lipid) as an initiator, and add H 2 O as solvent (monomer concentration is 2.0mol / L H 2 O), sealed, vacuumed by an oil pump, and nitrogen gas, repeated several times. The system was placed at 55-60° C. under the protection of nitrogen and stirred for 4 h.
[0050] (3) Dissolve a certain mass of PAN in DMF to obtain a PAN solution with a concentration of 0.1g / mL; then add galactose vinyl lipid homopolymerization so that the mass fraction is 60% respectively, stir for several hours until completely dissolved, and statically ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com