Photoelectrochemical method for separating p-type silicon micro-channel from substrate
A photoelectrochemical, p-type silicon technology, applied in the field of photoelectrochemistry, can solve the problems of lack of surface flatness, unfavorable processing, silicon wafer damage, etc., and achieve the effect of high aspect ratio, low cost, and avoidance of damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The method of separating the p-type microchannel from the silicon substrate by increasing the current is as follows:
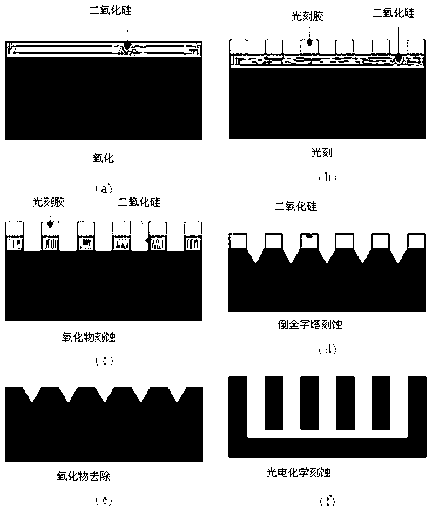
[0044] 1. Select a p-type silicon wafer with a (100) crystal orientation of 7 degrees, and a resistivity of 2-5Ω*cm;
[0045] 2. Using thermal oxidation to form silicon dioxide as a mask;
[0046] 3. Define the window (2um*2um) array by lithography, and define the window through the steps of development, primer, and silicon dioxide removal;
[0047] 4. Put the silicon wafer with the defined window into tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH 80°C) to corrode, and take it out from time to time and watch it under the microscope until a clear cross is seen, as in figure 2 As shown in , the silicon wafer is a silicon wafer engraved with an inverted pyramid structure at this time;
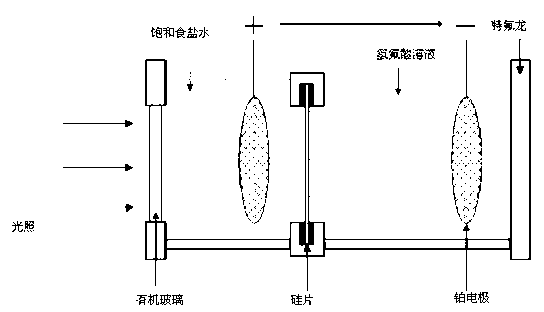
[0048] 5. Put the silicon wafer engraved with the inverted pyramid into the etching tank, install the device, pour 2M hydrofluoric acid etching solution, set the total etching cur...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The method of separating the p-type microchannel from the silicon substrate by reducing the voltage is as follows:
[0052] 1. Select a p-type silicon wafer with (100) crystal orientation, and the resistivity is 2-5Ω*cm;
[0053] 2. Using thermal oxidation to form silicon dioxide as a mask;
[0054] 3. Define the window (2um*2um) array by lithography, and define the window through the steps of development, primer, and silicon dioxide removal;
[0055] 4. Put the silicon wafer with the defined window into tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH 80°C) to corrode, and take it out from time to time and watch it under the microscope until a clear cross is seen, as in figure 2 As shown in , the silicon wafer is a silicon wafer engraved with an inverted pyramid structure at this time;
[0056] 5. Put the silicon wafer engraved with the inverted pyramid into the etching tank, install the device, pour 2M hydrofluoric acid etching solution, set the etching current to 510mA, and se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com