Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of solar cells and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of low photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cells, and achieve the effects of reducing recombination, reducing electrical contact area, and reducing ohmic contact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
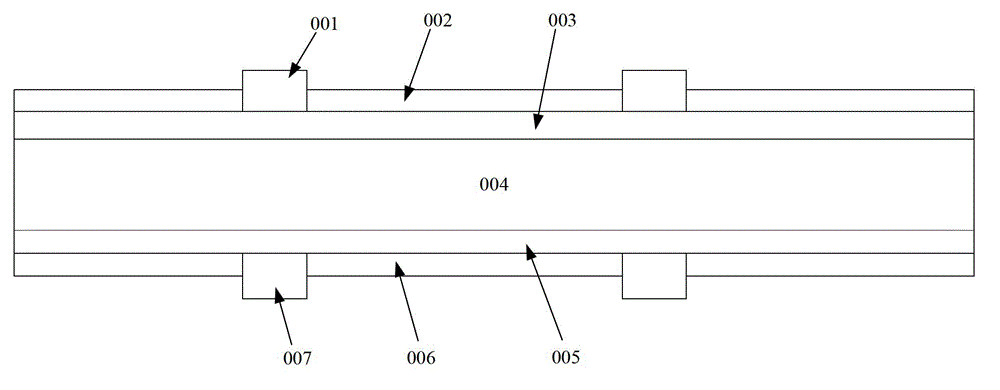
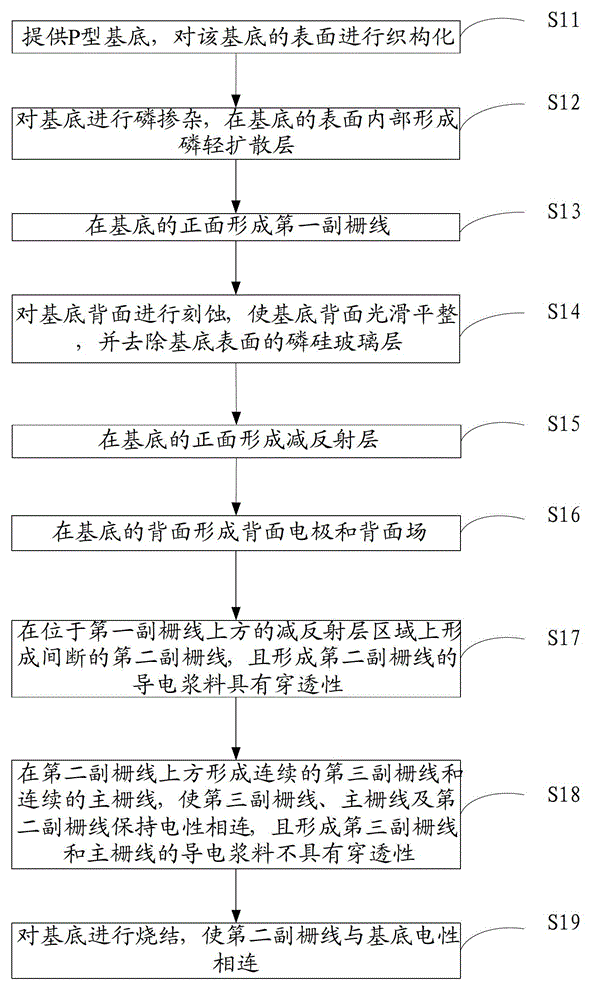
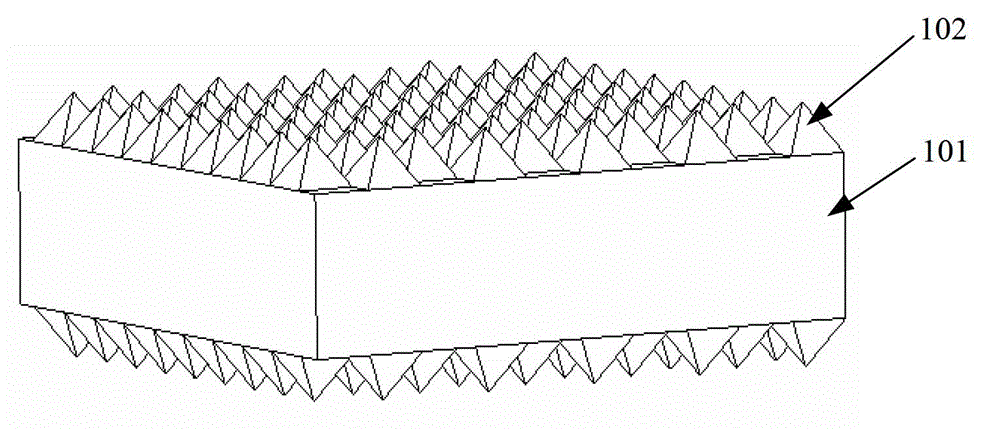
[0065] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a solar cell, such as figure 2 As shown, it is a flow chart of the manufacturing method of the solar cell provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention, such as Figure 3-Figure 11 As shown, it is a perspective view of each step of the method, including:
[0066] Step S11: providing a P-type substrate, and texturing the surface of the substrate.
[0067] Such as image 3 As shown, a P-type monocrystalline silicon wafer is provided as a substrate, most of the substrate is the body layer 101, and the substrate has a specification of 125mm×125mm, a resistivity of 1.5Ω·cm, and a thickness of 180μm; chemical etching is then used The substrate surface is textured by the method, and the pyramid structure 102 is finally formed. The chemical reagent used in the process is a sodium hydroxide solution with a temperature of 80°C and a mass percentage of 2.5%, and the corrosion time lasts for 25 minutes.
[0068] It should ...
Embodiment 2
[0137] This embodiment provides a method for manufacturing a solar cell, such as Figure 12 As shown, it is a flow chart of the manufacturing method of the solar cell provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0138] Step S21: providing an N-type substrate, and texturing the surface of the substrate.
[0139] An N-type monocrystalline silicon wafer is provided as the substrate, most of the substrate is the body layer 201, and the specification of the substrate is 156mm×156mm, the resistivity is 1.5Ω·cm, and the thickness is 180μm; The surface of the substrate is textured to finally form a pyramid structure 202. The chemical reagent used in the process is a sodium hydroxide solution with a temperature of 80°C and a mass percentage of 2.5%, and the corrosion time lasts for 25 minutes.
[0140] Step S22: Boron doping is performed on the substrate to form a boron light diffusion layer inside the surface of the substrate. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com