Preparation method of monolithic BEA molecular sieve catalyst for direct N2O catalysis decomposition
A catalytic decomposition and molecular sieve technology, which is applied in the fields of chemical engineering and environmental protection, to achieve high-efficiency removal, low conversion temperature, and stable catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Preparation of 5% aluminum sol Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0039] Accurately weigh the H-BEA molecular sieve catalyst (SiO 2 / Al 2 o 3 =30) (commercial molecular sieve) 10.0g, Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O (analytical pure) 0.729g, deionized water 300mL, put it in a three-necked flask, and stir in a constant temperature water bath at 90°C for 6 hours. Then it was filtered and washed 3 times, dried in a drying oven at 100°C for 12 hours, then placed in a muffle furnace to program the temperature to 550°C, and roasted at a constant temperature for 5 hours to obtain a Fe ion-modified BEA molecular sieve powder sample, in which Fe The mass percentage of ions in the modified molecular sieve is 1%.
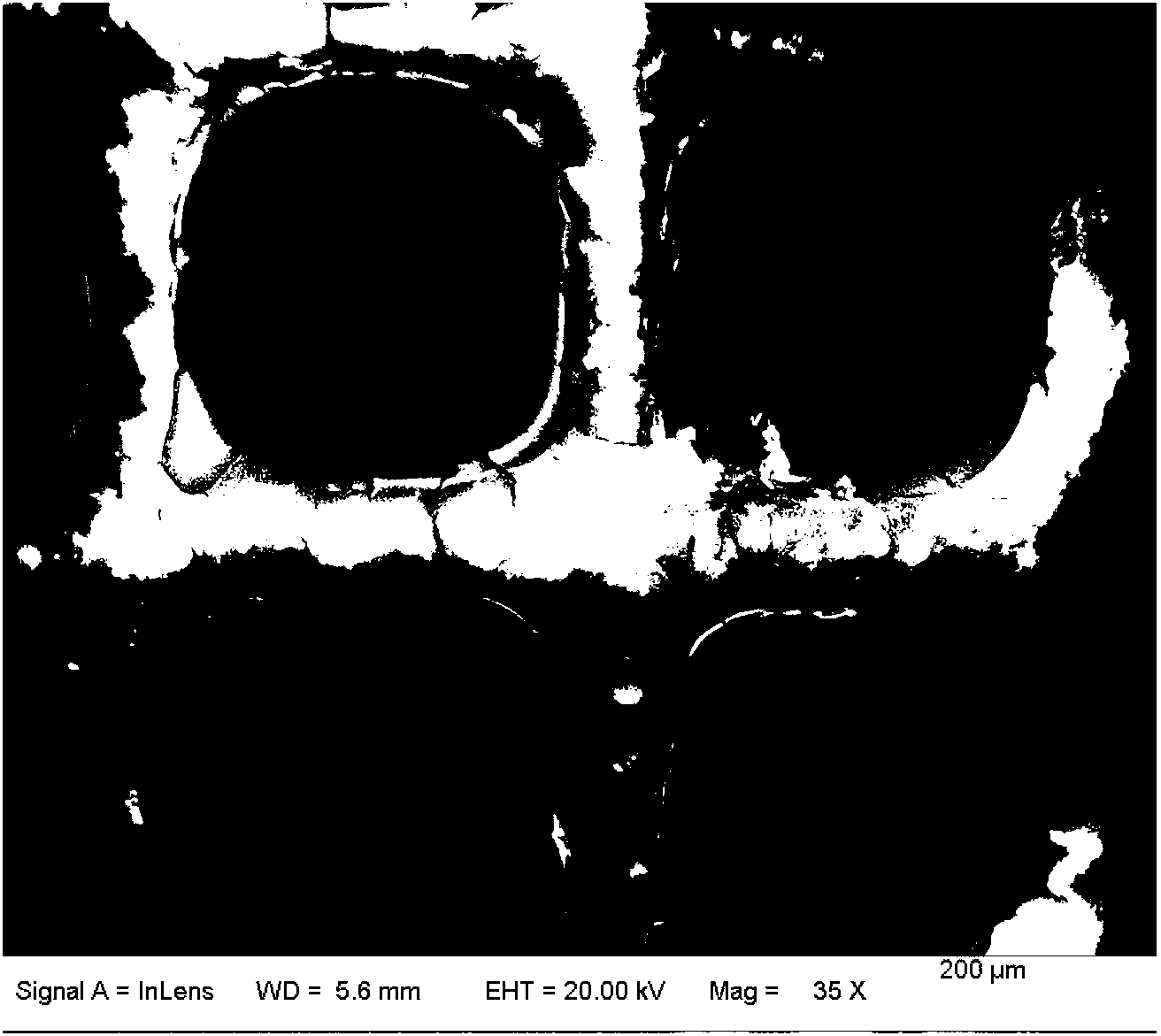
[0040] A large piece of cordierite (diameter 16.5mm, height 11mm, hole density 400cell / inch 2 ) into a small piece of cordierite with a hole number of 10×10, then grind it to a height of 5mm, and finally pick it into the required cylindrical shape with a p...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Preparation of 10% aluminum sol Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0044] The preparation of Fe-BEA powder molecular sieve is as described in Example 1. Select aluminum sol with a mass percentage of 20% as a binder, accurately weigh 4.000 g of Fe-BEA molecular sieve, 6.858 g of aluminum sol, and 2.824 g of deionized water. The rest of the preparation steps are as described in Example 1, and a Fe-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst with 10% aluminum sol and a Fe-BEA loading capacity of 41.5% can be obtained. The activity evaluation means are the same as in Example 1, and the activity evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Preparation of 5% silica sol Co-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst
[0046] Accurately weigh 10.0 g of H-BEA molecular sieve catalyst (commercial molecular sieve), Co(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O (analytical pure) 0.490g and deionized water 300mL, the rest of the preparation steps are the same as the preparation process of Fe-BEA modified molecular sieve in Example 1 to obtain Co-BEA powder molecular sieve, wherein Co accounts for the mass of modified molecular sieve (Co-BEA) The percentage is 1%.
[0047] The pretreatment of the original carrier of cordierite is the same as in Example 1.
[0048] Select silica sol with a mass percentage of 30% as a binder, accurately weigh 4.000 g of Co-BEA molecular sieve, 2.131 g of silica sol, and 6.528 g of deionized water. The remaining preparation steps are as described in Example 1, and 5% silica sol, 48.0% (mass percentage, based on the Co-BEA monolithic molecular sieve catalyst, the same below) Co-BEA monolithic molecu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com