Method for removing heavy metals Zn and Cu in dredged river sediment
A heavy metal and sediment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long cycle, slow effect, high investment cost and power consumption, and achieve The effect of short treatment period, lower moisture content and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
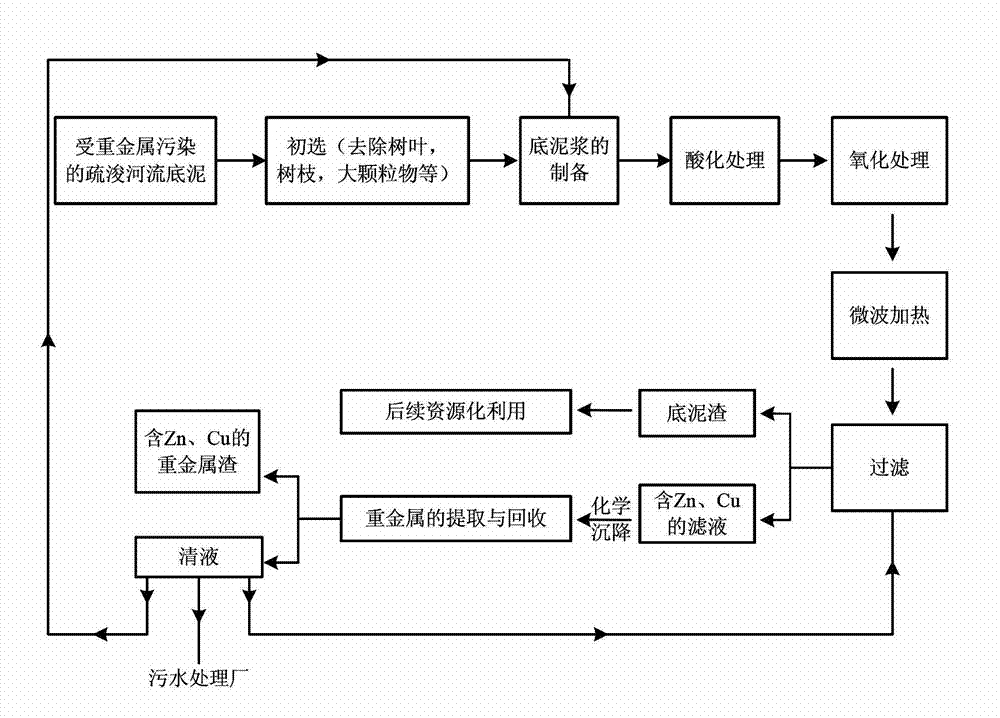
[0019] A method for removing heavy metals Zn and Cu from the sediment at the estuary of Xiawan Port, Xiangjiang River, Zhuzhou (for the technical route, see figure 1 ), including the following steps:
[0020] (1) Preparation of bottom mud: Take 50g of dried bottom mud at the estuary of Xiawan Port in Xiangjiang, Zhuzhou, remove leaves, branches, large particles, etc. in the bottom mud, add 200mL deionized water, stir until uniform, and get bottom mud .
[0021] (2) Acidification treatment: select industrial-grade concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98%, and slowly add concentrated sulfuric acid to the bottom mud while stirring until the pH is 2.
[0022] (3) Oxidation treatment: Add 30% hydrogen peroxide (the mass of hydrogen peroxide is 11% of the dry sediment mass) to the mixture obtained from the acidification treatment, and stir until uniform.
[0023] (4) Microwave heating: place the oxidized reaction product in a microwave reactor for microwave heat...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for removing heavy metals Zn and Cu from the bottom mud of Zhuzhou Xiangjiang Xiawan Port sewage outlet (technical route see figure 1 ), including the following steps:
[0029] (1) Preparation of bottom mud: Take 50g of dried bottom mud from the sewage outlet of Xiawan Port, Xiangjiang, Zhuzhou, remove leaves, branches, large particles, etc. in the bottom mud, add 200mL deionized water, stir until uniform, and get bottom mud .
[0030] (2) Acidification treatment: select industrial-grade concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98%, and slowly add concentrated sulfuric acid to the bottom mud while stirring until the pH is 2.
[0031] (3) Oxidation treatment: Add 30% hydrogen peroxide (the mass of hydrogen peroxide is 11% of the dry sediment mass) to the acidified mixture, and stir until uniform.
[0032] (4) Microwave heating: place the oxidized reaction product in a microwave reactor for microwave heating to 60°C, keep it warm for 10 minutes, ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A method for removing heavy metals Zn and Cu from the sediment at the estuary of Xiawan Port, Xiangjiang River, Zhuzhou (for the technical route, see figure 1 ), including the following steps:
[0038] (1) Preparation of bottom mud: Take 50g of dried bottom mud at the estuary of Xiawan Port in Xiangjiang, Zhuzhou, remove leaves, branches, large particles, etc. in the bottom mud, add 200mL deionized water, stir until uniform, and get bottom mud .
[0039] (2) Acidification treatment: select industrial-grade concentrated sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 98%, and slowly add concentrated sulfuric acid to the bottom mud while stirring until the pH is 2.
[0040] (3) Oxidation treatment: Add 30% hydrogen peroxide (the mass of hydrogen peroxide is 11% of the dry sediment mass) and 0.08g FeSO to the acidified mixture. 4 ·7H 2 O, stir until uniform.
[0041] (4) Microwave heating: place the oxidized reaction product in a microwave reactor for microwave heating to 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com