Method for synthesizing oxalate by CO gas-phase coupling
An oxalate ester and gas phase technology, applied in the field of regeneration technology, can solve the problems of difficult gas separation and purification, discharge pollution of nitric acid-containing wastewater, and low yield of nitrite, achieving high utilization rate, reduced investment, and short process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
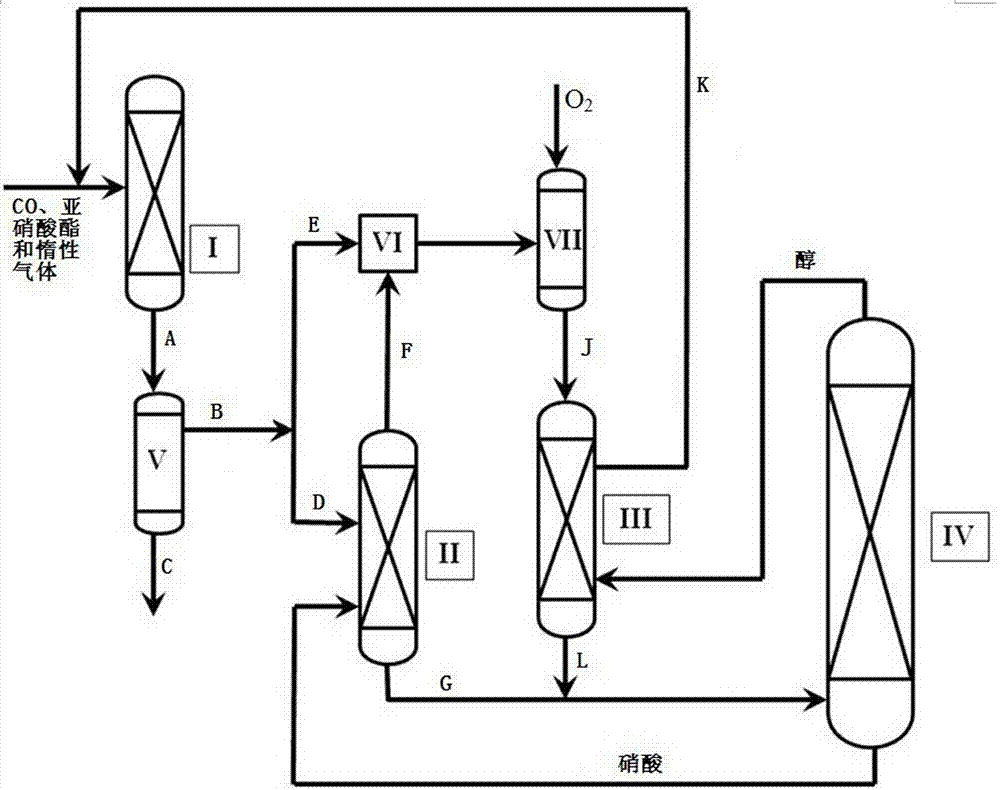
[0056] With CO and ethyl nitrite as raw materials, N 2 As a dilution gas, the raw material first enters the coupling reactor I, reacts under the action of the Pd catalyst, and generates effluent A containing diethyl oxalate, NO, unreacted ethyl nitrite and unreacted CO, and effluent A After gas-liquid separation in the condenser, the gas phase effluent B containing NO, ethyl nitrite and CO and the liquid phase effluent C containing diethyl oxalate are obtained respectively. The gas phase effluent B is divided into two streams, namely gas phase effluent D and gas phase effluent E, gas phase effluent D reacts with 68% nitric acid solution in reactor II, and the reaction temperature is 30 o C, the reaction pressure is normal pressure, and the residence time of the gas phase effluent D during the reaction is 1 second. NO 2 The tail gas F and the still liquid G containing nitric acid are mixed, and the tail gas F is mixed with the gas phase effluent E to obtain the gas phase effl...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Using CO and methyl nitrite as raw materials, N 2 As a dilution gas, the raw material first enters the coupling reactor I, reacts under the action of the Pd catalyst, and generates effluent A containing dimethyl oxalate, NO, unreacted methyl nitrite, and unreacted CO, and effluent A After gas-liquid separation in the condenser, the gas phase effluent B containing NO, methyl nitrite and CO and the liquid phase effluent C containing dimethyl oxalate are obtained respectively. The gas phase effluent B is divided into two streams, namely gas phase effluent D and gas phase effluent E, gas phase effluent D is reacted with 30% nitric acid solution in reactor II, and the reaction temperature is 90 o C, the reaction pressure is normal pressure, and the residence time of the gas phase effluent D during the reaction is 50 seconds. NO 2 The tail gas F and the still liquid G containing nitric acid are mixed, and the tail gas F is mixed with the gas phase effluent E to obtain the g...
Embodiment 3
[0062] With CO and isopropyl nitrite as raw materials, N 2 As a dilution gas, the raw material first enters the coupling reactor I, and reacts under the action of the Pd catalyst to generate effluent A containing diisopropyl oxalate, NO, unreacted isopropyl nitrite, and unreacted CO, and flows out After the product A is separated from the gas and liquid by the condenser, the gas phase effluent B containing NO, isopropyl nitrite and CO and the liquid phase effluent C containing diisopropyl oxalate are respectively obtained. Divide gaseous phase effluent B into two streams, namely gaseous phase effluent D and gaseous phase effluent E, gaseous phase effluent D reacts with 55% nitric acid solution in reactor II, the reaction temperature is 65 o C, the reaction pressure is normal pressure, and the residence time of the gas phase effluent D during the reaction is 30 seconds. NO 2 The tail gas F and the still liquid G containing nitric acid are mixed, and the tail gas F is mixed wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com