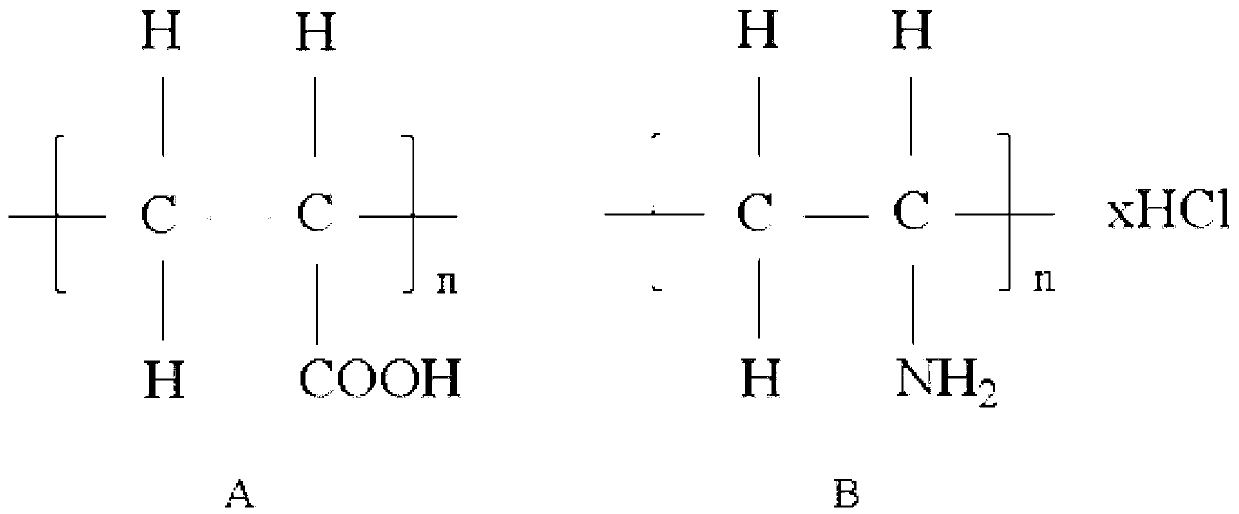
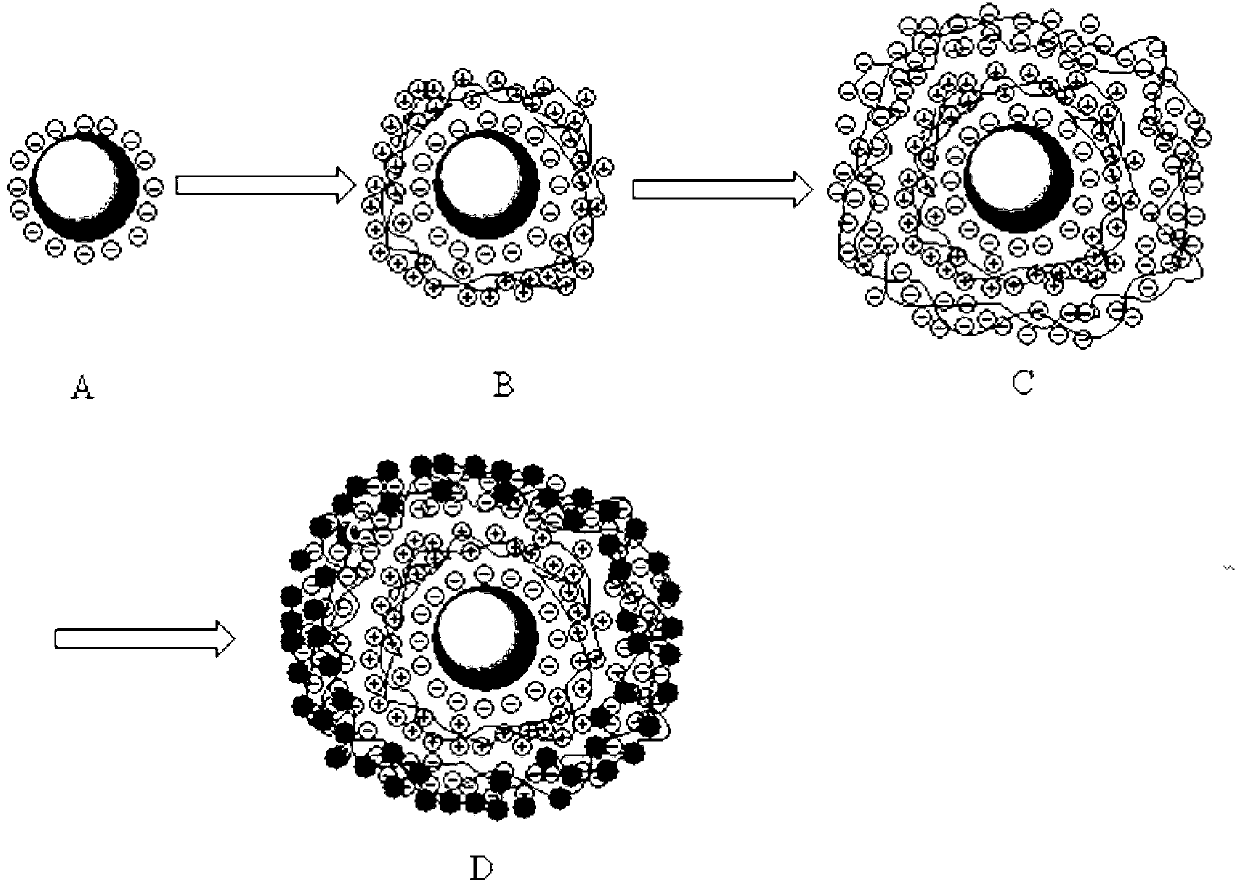
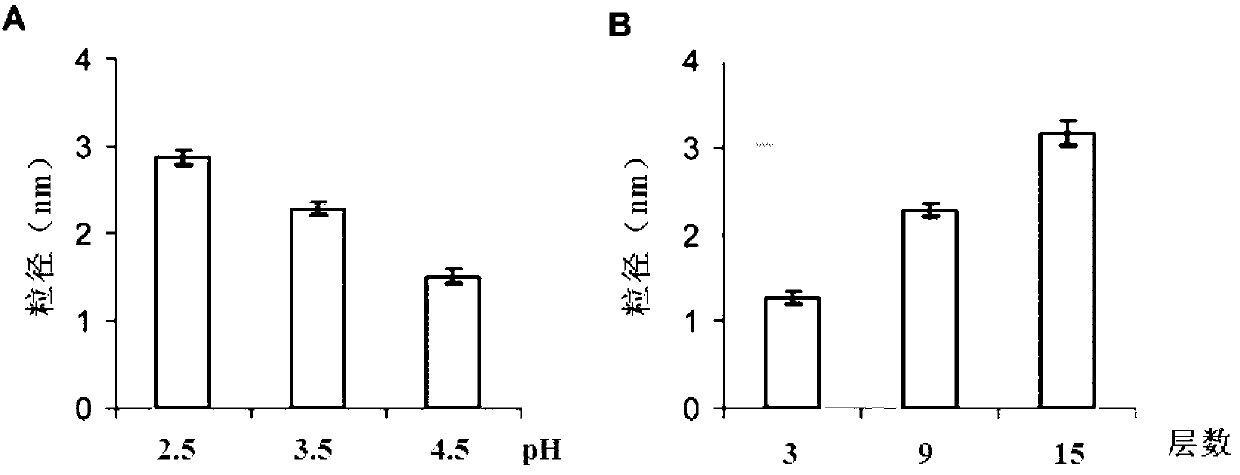
Method for preparing nanoscale zero-valent iron loaded on surfaces of glass beads by virtue of layer-by-layer assembly
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and glass microbeads, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, can solve the problems that inorganic synthesis has not been developed, and achieve the effect of controllable activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. Prepare 0.1mol / L HCl and NaOH solution and 10mmol / L NaBH in advance 4 Solution, 5:1:1 (volume ratio) H 2 O / H 2 o 2 (30wt%) / HCl (36wt%) mixed solution and 5:1:1 (volume ratio) H 2 O / H 2 o 2 (30wt%) / NH 4 · OH (25wt% ~ 28wt%) mixed solution.
[0040] 1. Prepare PAA and PAH solutions with a concentration of 1g / L and 0.1mol / L FeSO 4 solution, and adjust the pH to 3.5 with 0.1mol / L HCl and NaOH solution.
[0041] 2. Preheat the ultrasonic machine to 70C, weigh 200 mesh glass beads and immerse them in 5:1:1 (volume ratio) H 2 O / H 2 o 2 / HCl mixed solution, sonicate at 70°C for 10 minutes, pour out the waste liquid after taking it out, wash with water 3 times, 2 minutes each time.
[0042] 3. Immerse in 5:1:1 (volume ratio) H 2 O / H 2 o 2 / NH 4 ·OH mixed solution, sonicate at 70°C for 10 minutes, pour out the waste liquid after taking it out, wash with water 3 times, 2 minutes each time.
[0043] 4. Immerse in 1g / L PAH for 5 minutes, wash with water 3 times, 2 m...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Test of reducing ability of trichlorethylene (TCE).
[0053] Comparing nano-sized zero-valent iron synthesized by layer-by-layer assembly and ordinary zero-valent iron (nano-iron powder, 99.9%, 50nm, Aladdin’s reagent, http. / / www.aladdin-reagent.com / thir.asp? Rea_SubID=10750 ) to the reduction efficiency of TCE. React in a 40mL headspace bottle, isolate oxygen, trichlorethylene concentration 10mg / L, self-assemble nano zero-valent iron layer by layer under the condition of pH 3.5, 15 layers of polyelectrolyte, and 9 layers of assembled iron. During the reaction, it was placed in a shaker with a rotation speed of 80 rpm. At each time point, 250 μl samples were taken, and the concentration of trichlorethylene was detected by gas chromatography (HP-5890). This reaction obeys the first-order kinetics reaction, and the results of changing various reaction conditions are as follows: Image 6 . In the same reaction system, the reaction rate constant obtained by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com