Application of heparinase II to preparation of LMWH (low-molecular-weight heparin) by depolymerization of heparosan
A technology for low molecular weight heparin and heparin precursors, which is applied in the field of preparing low molecular weight heparin by depolymerizing heparin precursors with recombinant heparinase II, and achieves the effects of cost saving, mild reaction conditions and easy separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of recombinant heparanase II
[0038] 1. E. coli BL21(DE3) / pET15b-hepB expresses heparanase II
[0039] According to the reported Flavobacterium heparinum heparanase II gene sequence (Genbank access number U27585.1) and amino acid sequence (Genbank access number AAB18277.1)
[0040] Design primers (HepII-F: 5'-CATGCCATGGATGAAAAGACAATTAT-3'
[0041] HepII-R: 5'-GGAATTCCATATGTTATCTCAAAAAACGGT-3' is a restriction site, the upstream primer is added with NcoI restriction site, and the downstream primer is with NdeI restriction site), amplified from Flavobacterium heparinum genomic DNA to heparin Enzyme II (Heparinase II) gene fragment (SEQ ID No.1), cloned into pET-15b expression vector (Novagen, WI) to obtain recombinant vector pET15b-hepB, which contains an N-terminal His6-tag tag for easy recombination protein follow-up Ni 2+ Column affinity chromatography. Transform E. coli BL21(DE3) with pET15b-hepB to obtain recombinant strain E. coli ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Effect of reaction conditions on the depolymerization effect of heparanase II on heparosan:
[0051] (1) Heparanase Ⅱ depolymerization method of heparosan
[0052] A certain amount of heparosan was weighed and dissolved in different enzymatic hydrolysis buffers to dissolve completely, preheated in a water bath at 25°C for 10 minutes, added different amounts of heparanase II, and carried out the degradation reaction at 25°C, at different reaction times sampling. Boiling water bath for 5 min to inactivate the enzyme and cool to room temperature.
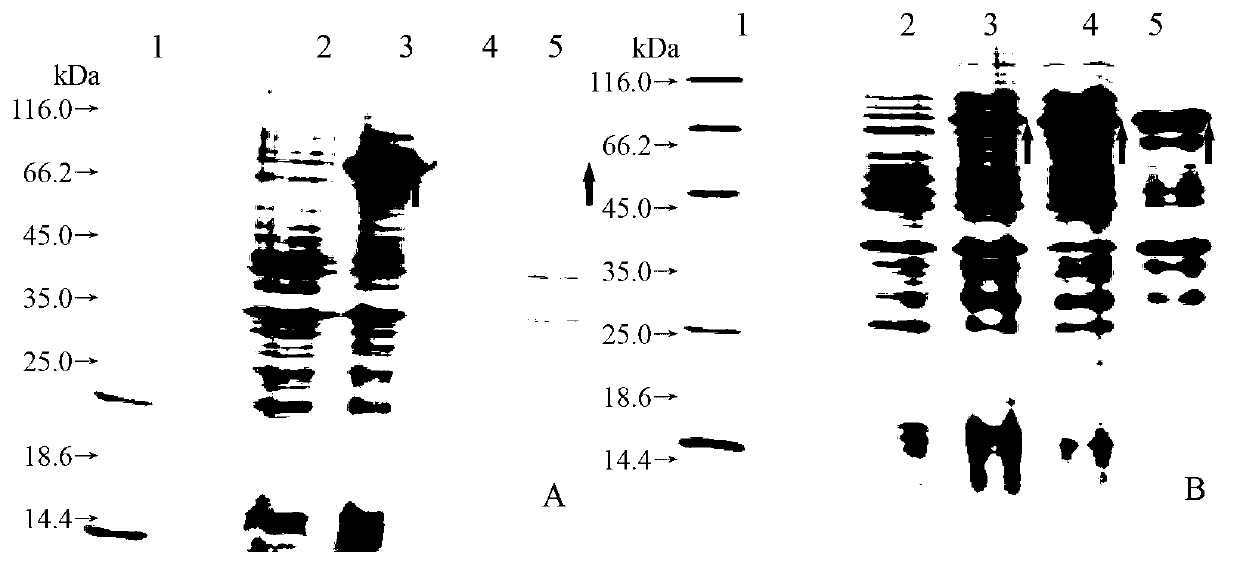
[0053] After being treated with Heparinase II, it was found that the crude product of heparosan depolymerized, from Figure 5 It can be seen from the figure that as the action time of Heparinase II increases, the large molecular weight bands of heparosan become less and less, and the small molecular weight bands gradually increase. By 4 h, almost all of them are small molecules. It shows that heparinase II has a go...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3: Preparation of low molecular weight heparin
[0068] (1) Depolymerization of heparosan:
[0069] Dissolve 0.05 g heparosan in 1 mL of enzymatic digestion buffer B (100 mM sodium acetate, 0.01% BSA and 10 mM calcium acetate, the solvent is water, pH7.0) to make it completely dissolved, and preheat it in a water bath at 25 °C 10 min, add 100 μL of heparinase II with a total activity of 199 U / mL (Hep II, obtained according to the method in Example 1), carry out the degradation reaction at 25°C for 1.5 h, and place in a boiling water bath for 5 min after the degradation reaction to deactivate the enzyme live, cooled to room temperature. See embodiment 2 for specific results.
[0070] (2) Deacetylation and sulfation
[0071] Dissolve 5 mg of depolymerized Heparosan in 1 mL of 2M sodium hydroxide solution, react at 60°C for 3 h, dilute the reaction solution to 5 mL after the reaction, cool and adjust the pH to 7 with 1M hydrochloric acid, and then add carboxy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com