Method for replacement dissolution of bastnaesite (bastnasite)
The technology of lanthanum fluoride and bastnasite is applied in the field of non-ferrous metal rare earth separation, which can solve the problems of long process flow, large consumption of electric energy and steam, low equipment utilization efficiency, etc., and achieves the effect of reducing cost and energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
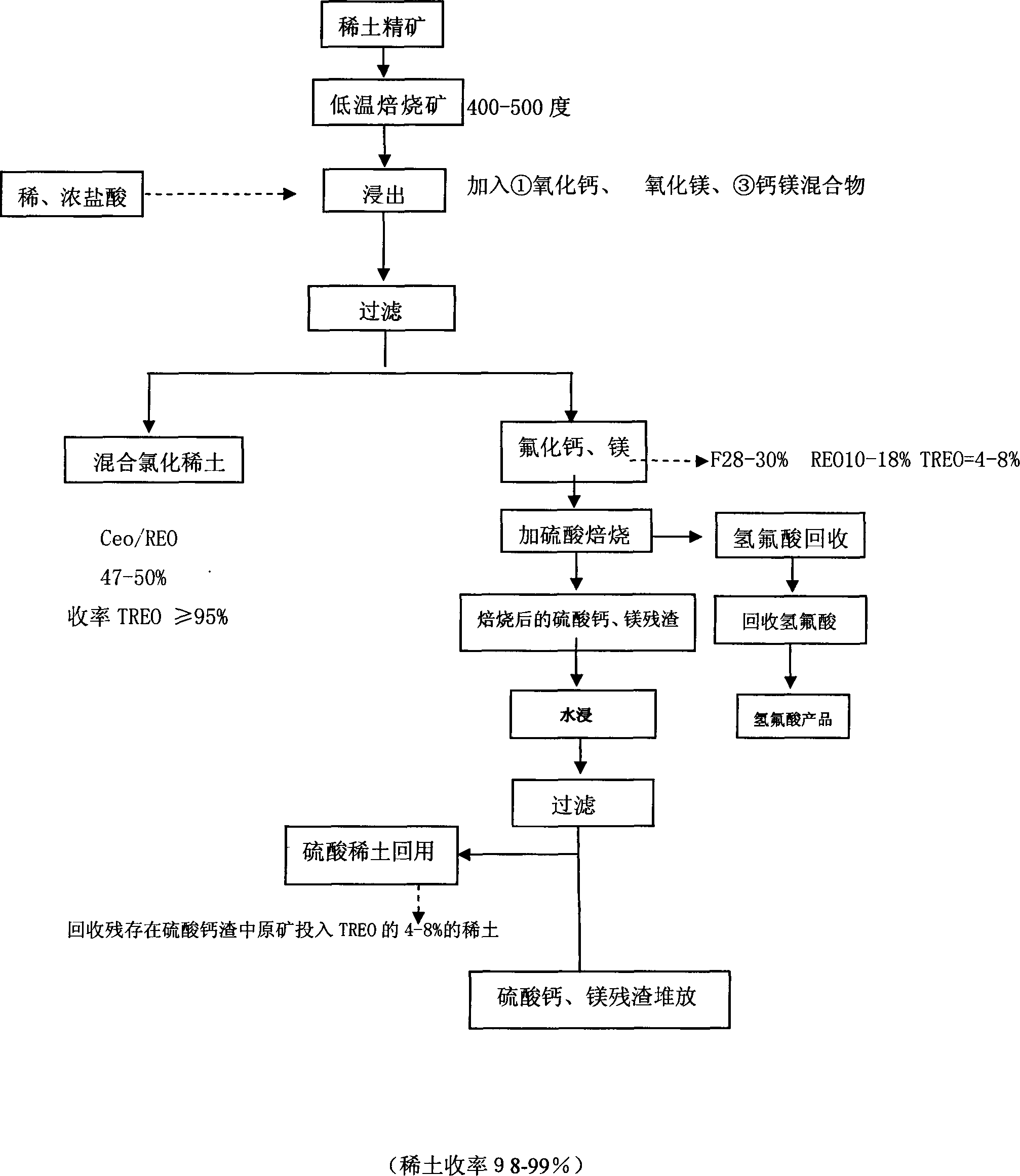
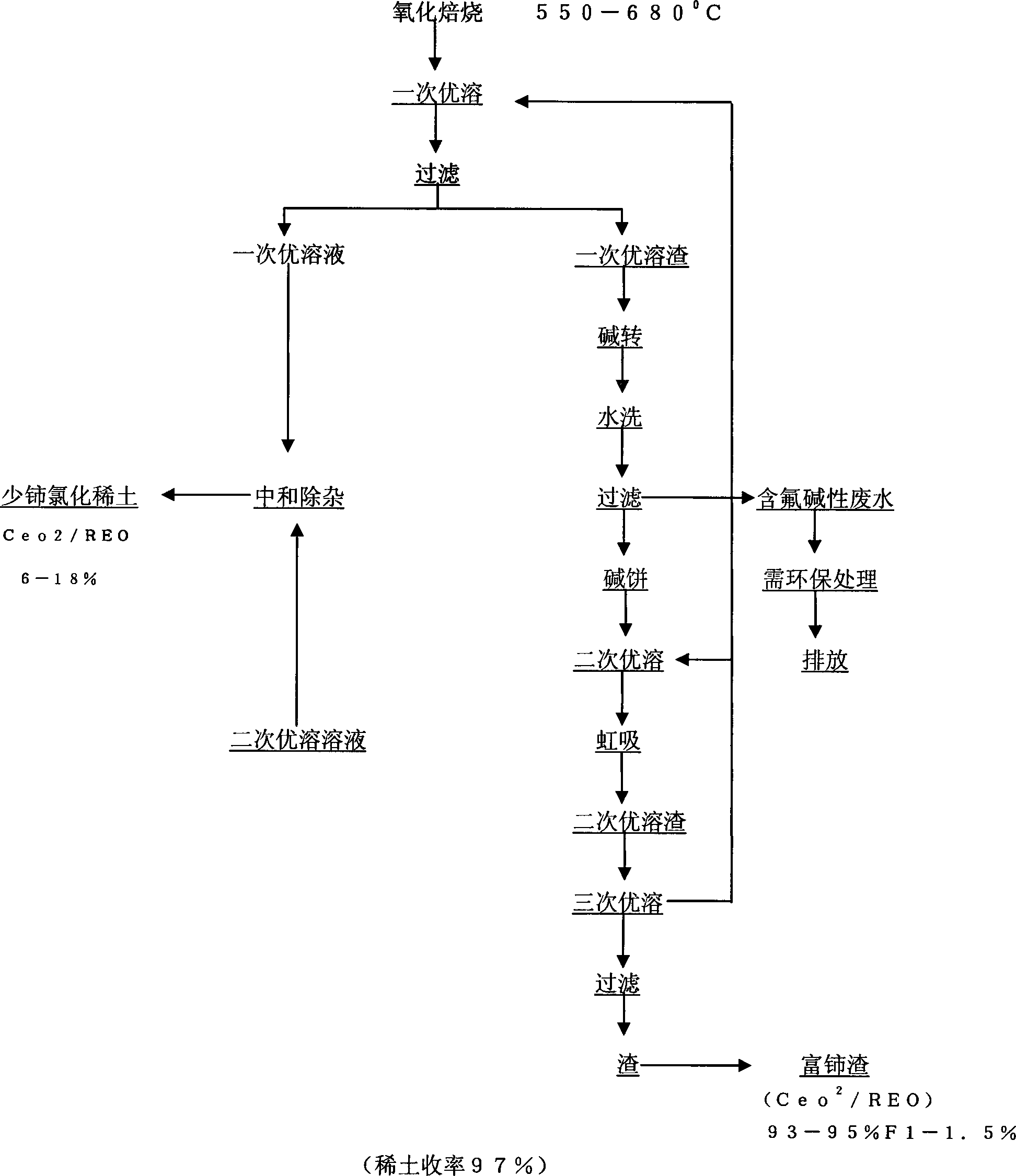
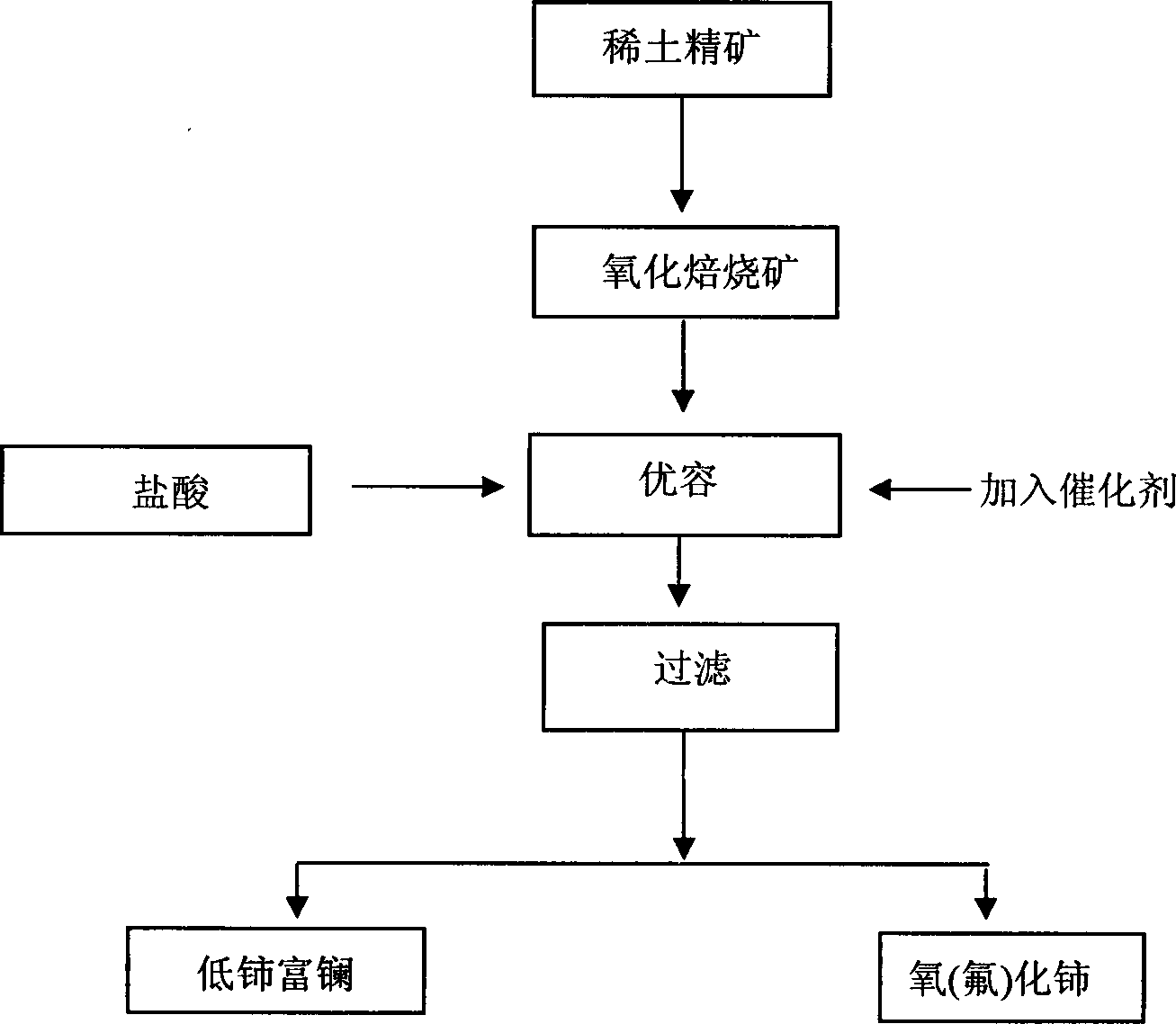
[0037] The bastnaesite (bastnaesite) displacement dissolution method comprises the following steps:
[0038] A. Oxidation roasting bastnaesite, bastnaesite
[0039] B. Add calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, and magnesium mixture hydrochloric acid to the roasted concentrate to dissolve;
[0040] C, solid-liquid separation is carried out to the dissolved rare earth solution and the combined fluoride generated;
[0041] D. After separation, fluoride is added to sulfuric acid and burned at low temperature to recover hydrofluoric acid gas to prepare hydrofluoric acid;
[0042] E. After recovering the hydrofluoric acid gas, the residue is further recovered by water immersion to obtain rare earth sulfate solution;
[0043] The experimental results show that:
[0044] Calcium introduction and dissolution method: add calcium oxide (calcium carbonate and calcium hydroxide have the same effect) of the actual weight according to the weight ratio of the rare earth after roas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com