Bacterial strain of high-yielding acidic glycoside hydrolases
A glycoside hydrolase and acidic technology, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of poor understanding of acidophilus and limited acidophilus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 strain isolation
[0019] YF liquid medium (300mL): 8ml HBS (50×) (basic salt solution); 0.08g yeast extract; 0.12g Fructose; 292ml distilled water; 0.4ml trace elements solution; pH 3.0 (H 2 SO 4 ).
[0020] Enrichment medium (g / L): (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 3.0, KCl 0.1, K 2 HPO 4 0.5, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 0.01, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 3.0, glucose 2, pH 2.0-2.5.
[0021] Separation medium (g / L): (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2.0, KCl 0.1, MgSO4 7H 2 O 0.25, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 0.01, glucose 1.0, yeast extract 0.1, pH 2.5-3.0.
[0022] LB medium: peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, prepared with distilled water, with natural pH.
[0023] Take 20mL of the tail liquid of uranium leaching microorganisms in Jiangxi uranium mine, add it to 80mL enrichment medium for 72 hours at 30°C and 160rpm, shake and culture, pick a single colony and transfer them to YF medium and culture for two generations under the same conditions, repeat in parallel 3 times. The enri...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2 bacterial strain liquid fermentation produces enzyme analysis
[0026] Fermentation medium (g / L): (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2.0,K 2 HPO 4 1.0,; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5; wheat bran: okara = 1:1 (total 1%), pH 3.0.
[0027] DNS method: The specific method is as follows: at pH 4.0, 50°C, 1 mL of reaction system includes 100 μL of appropriate diluted enzyme solution, 900 μL of glue beans, react for 10 minutes, add 1.5 mL of DNS to terminate the reaction, and boil for 5 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, the OD value was measured at 540 nm. One enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme that releases 1 μmol of reducing sugar per minute under given conditions.
[0028] pNPG method: substrate p-nitrophenyl β-D glucoside (pNPG) or p-nitrophenyl-β-galactopyranoside, p-nitrophenol α-D galactopyranoside was dissolved in 250uL at a concentration of 2mM Add 250uL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution to pH 4.0 buffer, react at 50°C for 10min, the...
Embodiment 3
[0030] The optimum pH of different enzymes of embodiment 3
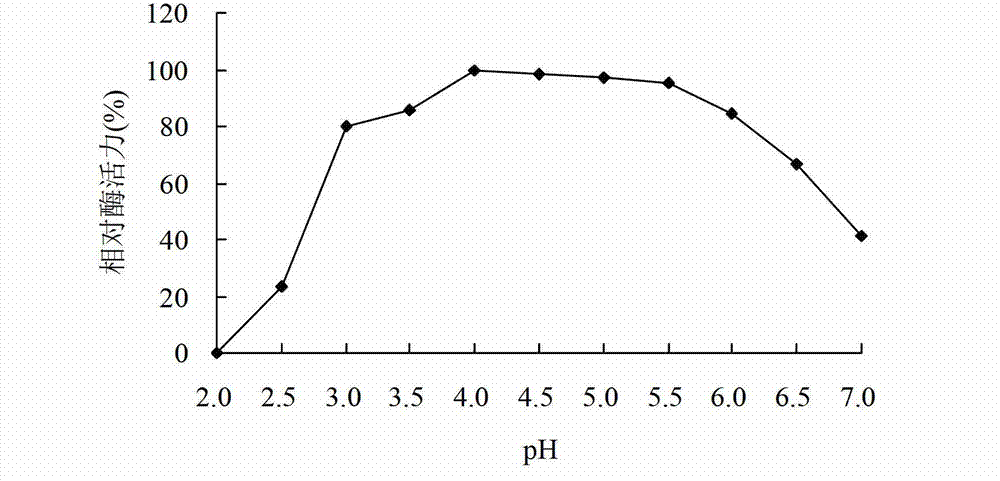
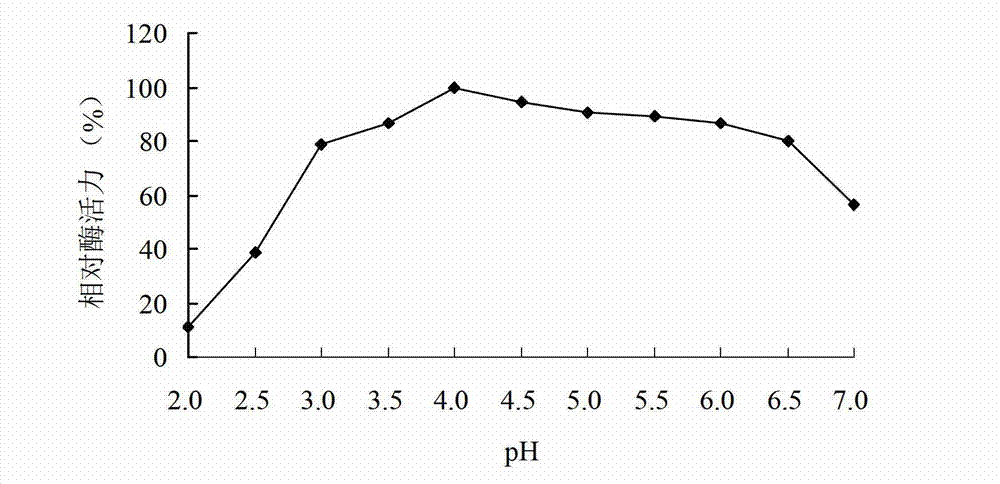
[0031] Separation and purification of α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, β-glucosidase, and mannanase, and performing enzymatic reactions at different pHs to determine their optimum pH. The substrates were tested for enzyme activity in 0.1mol / L citric acid-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer solution with different pH at 50°C. result( figure 2) shows that the optimal pH of α-galactosidase is 4.0, and there is more than 80% relative enzyme activity at pH 3.5~6.5. The pH of β-galactosidase is 4.0, and it has more than 50% relative enzyme activity at pH 3.0~7.0. The optimal pH of β-glucosidase is 3.0, and there is more than 60% relative enzyme activity at pH 2.5~6.0. The optimal pH of mannanase is 3.5, and there is more than 40% relative enzyme activity at pH 3.0~7.0. The above results indicated that the optimal pH of the glycoside hydrolase produced by strain RBS-4 was in the acidic range, and it had higher activity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com