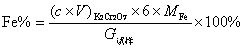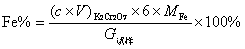Volumetric analysis method adopting ascorbic acid to carry out reductometry on iron
A technology of ascorbic acid and capacity analysis, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, which can solve the problems of unsatisfactory measurement results, expensive reducing agents, and reducing agent purity. Low cost, short measurement time, and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Dissolve the iron-containing sample according to the literature method, take the iron sample solution in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add the newly prepared ascorbic acid solution drop by drop, and heat to about 30°C, shake slowly to make it fully react until the yellow color disappears, and then Add an extra drop of ascorbic acid solution. Add 2,6-dichloroindophenol solution dropwise until the solution changes from colorless to light pink, and oxidize the remaining ascorbic acid. Then slowly add sulfur-phosphorus mixed acid dropwise, add dropwise sodium diphenylamine sulfonate indicator, and immediately use K 2 Cr 2 o 7 The standard solution was titrated to a stable purplish red as the end point.
[0028] The iron content (mass fraction) in the iron-containing sample is calculated by the following formula:
[0029]
[0030] In the formula:
[0031] c : concentration of potassium dichromate standard solution, mol / mL;
[0032] V : volume of potassium dichromate s...
Embodiment 2
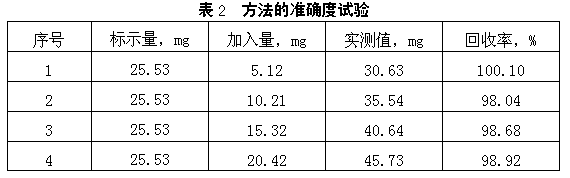
[0040] Using the classic stannous chloride-mercuric chloride-potassium dichromate method and the method of the present invention, that is, the ascorbic acid-2,6-dichloroindophenol-potassium dichromate method, the same iron-containing sample is subjected to comparative determination. The measurement results are shown in Table 3. It shows that the accuracy of the method of the present invention is high.
[0041]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com