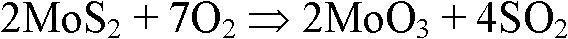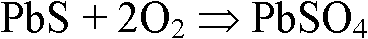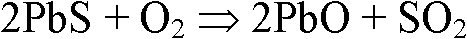Method for extracting lead and molybdenum from lead and molybdenum associated mineral
An associated ore and roasting technology, applied in the field of extracting lead and molybdenum, can solve the problems that are not suitable for processing low-grade ore or complex lead-molybdenum associated ore
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025]
[0026] The extraction steps are as follows:
[0027] 1. Put the above-mentioned lead-molybdenum associated ore into a muffle furnace with a constant temperature of 600°C for oxidative roasting for 1 hour to obtain calcined sand containing 2.25% molybdenum, 25.41% lead, and 5.12% sulfur;
[0028] 2. Mix the calcined sand obtained in step 1 with a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 30% by weight, and the weight ratio is calcined sand: NaOH=1: 1.2, place it in a reaction kettle, heat up to 130°C, and react Hours later, the slurry was filtered to obtain leachate and slag containing sodium plumbate and sodium molybdate. The concentrations of lead and molybdenum in the leaching solution are 85.82g / L and 6.63g / L respectively; the leaching residue contains 0.11% molybdenum and 0.87% lead. The leaching rates of lead and molybdenum are 98.3% and 97.5% respectively.
[0029] 3. Evaporate and concentrate the leaching solution obtained in step 2 to an alkali so...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The extraction steps are as follows:
[0032] 1. Put the above-mentioned lead-molybdenum associated ore into a muffle furnace at a constant temperature of 700°C for oxidative roasting for 0.5 hours to obtain calcined sand containing 2.04% molybdenum, 25.67% lead, and 12.69% sulfur;
[0033] 2. Mix the calcined sand obtained in step 1 with a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 20% by weight. The weight ratio is calcined sand: NaOH=1:0.6, place it in a reaction kettle, heat up to 110°C, and react 2 Hours later, the slurry was filtered to obtain leachate and slag containing sodium plumbate and sodium molybdate. The concentrations of lead and molybdenum in the leaching solution are 100.10g / L and 8.39g / L respectively; the leaching residue contains 0.14% molybdenum and 6.42% lead. The leaching rates of lead and molybdenum are 85.29% and 95.99% respectively.
[0034] 3. Evaporate and concentrate the leaching solution obtained in step 2 to an alkali solution con...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The extraction steps are as follows:
[0037] 1. Put the above-mentioned lead-molybdenum associated ore into a muffle furnace at a constant temperature of 550°C for oxidative roasting for 2 hours to obtain calcined sand containing 2.16% molybdenum, 23.43% lead, and 5.92% sulfur;
[0038] 2. Mix the calcined sand obtained in step 1 with a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 15% by weight, and the weight ratio is calcined sand: NaOH=1:1, place it in a reaction kettle, heat up to 150° C., and react 3 Hours later, the slurry was filtered to obtain leachate and slag containing sodium plumbate and sodium molybdate. The concentrations of lead and molybdenum in the leaching solution were 42.17g / L and 3.62g / L respectively; the leaching residue contained 0.11% molybdenum and 2.04% lead. The leaching rates of lead and molybdenum are 95.68% and 97.11% respectively.
[0039] 3. Evaporate and concentrate the leaching solution obtained in step 2 to an alkali solution c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com