Cholesterol-modified biodegradable polycation carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of polycation and cholesterol, applied in the directions of non-active ingredient medical preparations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulas, etc., can solve the problems of low transfection efficiency and toxicity, achieve high gene delivery efficiency, cell Low toxicity and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Synthesis of the polyamide-amine of embodiment 1 cholesterol modification (brominated quaternary ammonium salt connection)
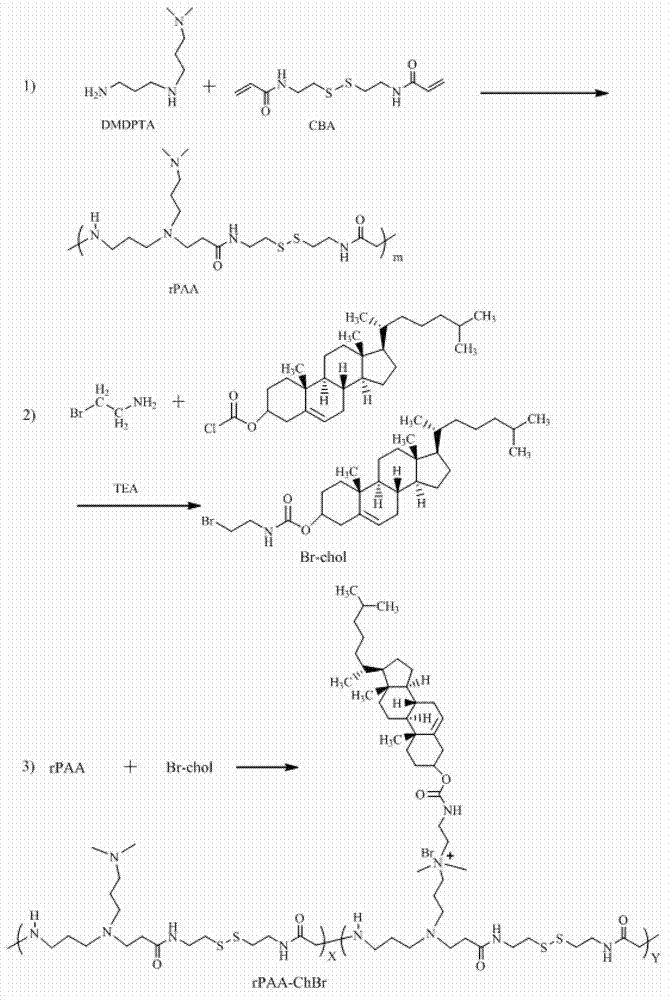
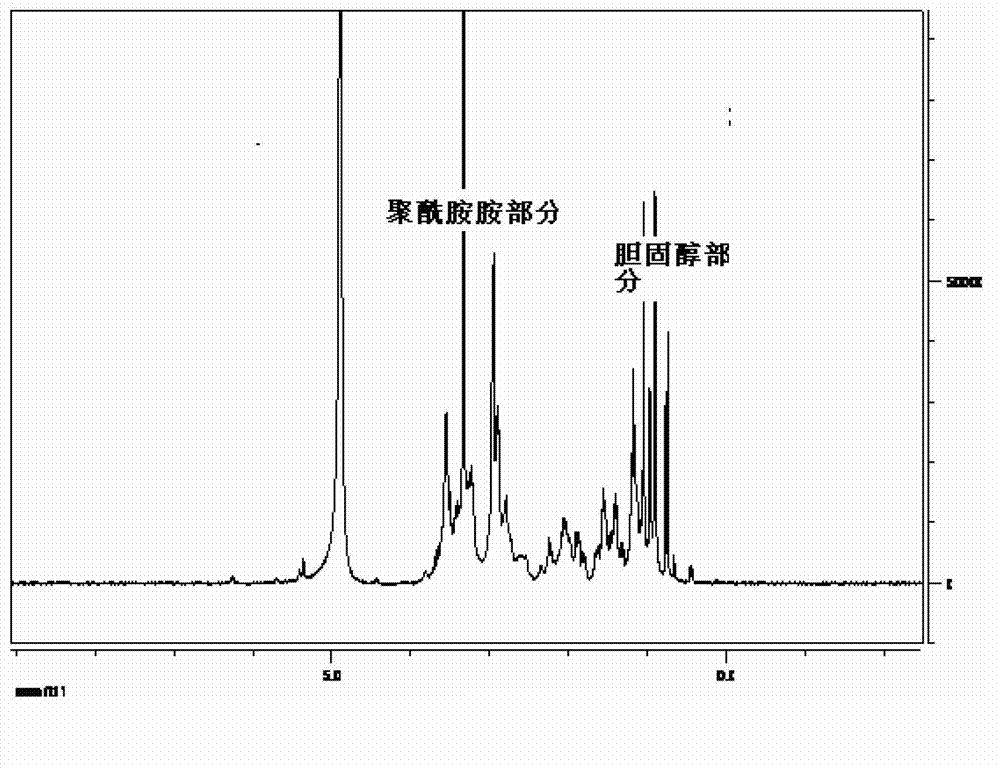
[0047] Synthesis of rPAA Accurately measure two commercially available monomers N,N'-dimethyldipropylenetriamine (DMDPTA) and N,N'-bis(acryloyl)cystamine (CBA) in equimolar ratio, Dissolve in an appropriate amount of mixed solvent of methanol and water, the concentration of each monomer is 2mmol / 3.5mL, under the condition of argon protection at 37°C, react in the dark for 3 days, after the reaction solution becomes viscous, add excess ( 10mol%) DMDPTA continued to react for 2 days, and the product was dialyzed with absolute ethanol (molecular weight cut-off 3.5KDa), and the ethanol solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and the product was vacuum-dried for 24 hours to finally obtain polyamide-amine cationic polymer (rPAA) ( figure 1 ).
[0048] Synthesis of Brominated Cholesterol (CH-Br) The synthesis of this material used the method reporte...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Synthesis of polyamide-amine (rPAA-Ch) modified by cholesterol (directly linked by amide bond)
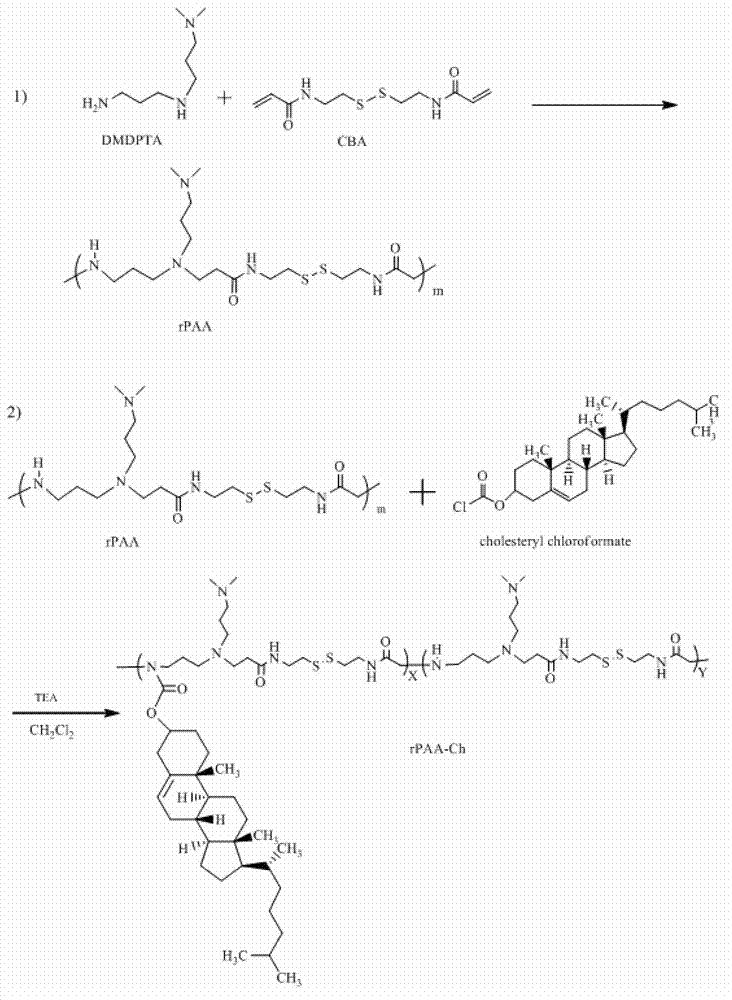
[0051]Synthesis of P(CBA-DMDPTA) polymer Precisely measure two commercially available monomers N, N'-dimethyldipropylenetriamine (DMDPTA) and N, N'-bis(acryloyl) in equimolar ratio ) Cystamine (CBA), dissolved in an appropriate amount of mixed solvent of methanol and water, the concentration of each monomer is 2mmol / 3.5mL, under the condition of argon protection at 37°C, react in the dark for 3 days until the reaction solution becomes viscous After thickening, add excessive (10mol%) DMDPTA and continue to react for 2 days, the product is dialyzed with dehydrated alcohol (molecular weight cut-off 3.5KDa), and the ethanol solvent is removed by rotary evaporation, and the product is vacuum-dried for 24 hours to finally obtain the polyamide-amine polymer ( rPAA).
[0052] Synthesis of Cholesterol Modified (Direct Amide Linkage) Polyamide-Amine (rPAA-Ch) Dissolve 100mg...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Evaluation of physical and chemical properties of rPAA-Ch polymer in vitro
[0054] Determination of Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) This example illustrates the determination of the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of the cholesterol-modified rPAA of the present invention. According to the reference (Biomaterials 2007; 28: 4132-42.), the CMC of the polymer was determined by the fluorescent probe method. In short, an equal volume of pyrene in acetone solution was added to 10 mL glass tubes one by one. After the acetone evaporated, 6 mL of polymer solutions with different concentrations (0.01-1000 μg / mL) were added to each tube. The final concentration of pyrene was 6.0× 10 -7 M. Under the condition of avoiding light, the aqueous polymer solution was sonicated in a bath at 37°C for 2 hours, and then shaken on a shaker at 37°C for 20 hours. The fluorescence spectrum of the solution was measured with a fluorescence spectrophotometer, the scattering wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com