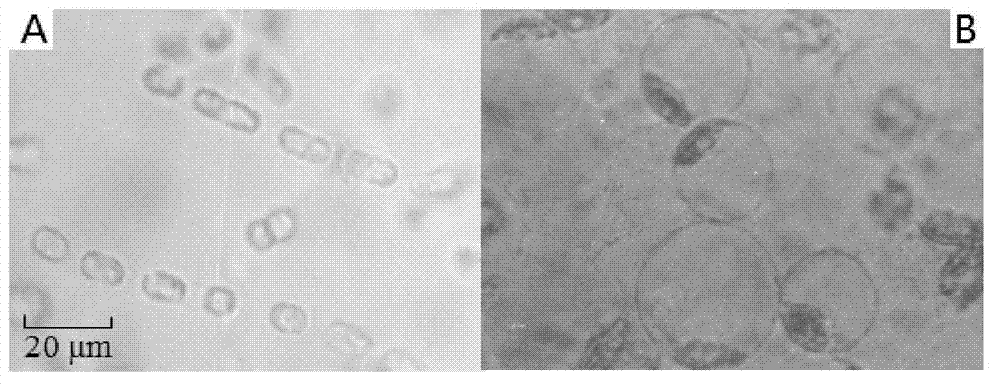
Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1 with capacity of dissolving skeletonema costatum and application thereof
A technology of spore rod and rib, applied in the field of microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The screening method of Skeletalum costa marine algae-lytic bacteria in embodiment 1
[0021] 1. Isolation and purification of marine bacteria
[0022] The surface seawater samples were collected from the sea area where the red tide broke out in Nanao, Dapeng Bay, Shenzhen. After filtering with a 0.7 μm glass cellulose membrane, they were serially diluted and then coated with a bacterial isolation medium plate. They were cultured at a constant temperature of 28°C for 48 hours, and the colonies with obvious differences in characteristics were picked and marked. Incubate at a constant temperature of 28°C for 48h. Repeat the above operation twice to obtain purely cultured bacteria. The bacterial isolation medium used was 2216E agar medium, and its ingredients were: 5g of peptone, 1g of yeast extract, 0.1g of ferric phosphate, 20g of agar powder, 1000ml of aged seawater, pH 7.6-8.2.
[0023] 2. Screening of marine algae-lytic bacteria from Scleraceae costarum
[0024] Pi...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The phylogenetic tree of embodiment 2 Halobacillus kuroii HSQAY1
[0027] 1.16S rDNA gene sequence determination
[0028]Using UNIQ-10 Column Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd.) to extract the DNA of Bacillus kuroii HSQAY1, after electrophoresis analysis of the genomic DNA, it was used as a template for PCR amplification. The added upstream primer was 27F: 5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′, and the downstream primer was 1492R: 5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′. The reaction process included: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 5 minutes, denaturation at 95°C for 35S, annealing at 55°C for 35s, and 72 There were 35 cycles of extension at ℃ for 90 s, and the last cycle was maintained at 72 °C for 8 min to complete the extension of the product. After electrophoresis purification of the PCR product, its full sequence was determined. ATGCAAGTCGAGCGCGGGAAGCGAGTGGATCCCTTCGGGGTGAAGCTCGTGGAACGAGCG 60GCGGACGGGTGAGTAACACGTGGGCAACCTGCCTGTAAGATCGGAATAACCCCG...
Embodiment 3
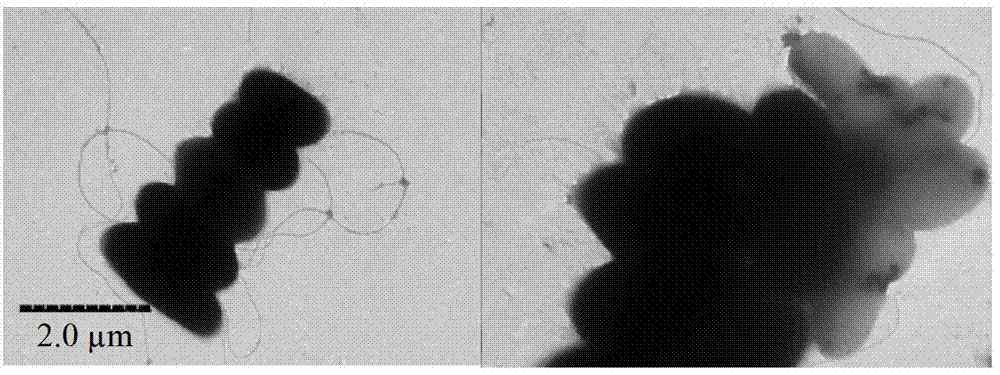
[0031] Example 3 Colony Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1 (Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1)
[0032] The colony of Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1 (Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1) was dark yellow, round, opaque, with neat edges, smooth and moist; the morphology of the bacteria was slightly short and thick bacilli, and the size was (0.6-1.2) μm×( 1.6~2.4) μm, with flagella, see cell morphology image 3 , the physiological and biochemical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Combined with the results of 16S rDNA sequence analysis of the bacteria, it was finally determined that HSQAY1 was a bacterium of the genus Halobacillus krusei.
[0033] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Halobacillus kuroshimensis HSQAY1
[0034]
[0035] Note: "+" means positive; "-" means negative
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com