Thin film transistor array substrate, preparing method and display device
A technology of thin film transistors and array substrates, applied in the field of display, can solve the problems of low production efficiency, high production cost, waste of materials for forming pixel electrodes, etc., and achieve the effects of improving utilization rate, reducing usage, and reducing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] A method for preparing a thin film transistor array substrate, comprising the following steps: forming a gate electrode layer, a gate insulating layer, an active layer, a source-drain electrode layer, and a passivation layer on the substrate, wherein the passivation layer is formed by a patterning process The structural pattern includes a via hole, the pixel electrode layer is formed in the structural pattern area by dripping, and the source and drain electrode layers are connected to the pixel electrode layer through the via hole.
[0028] A thin film transistor array substrate is formed by the above method for preparing a thin film transistor array substrate.
[0029] A display device includes the above thin film transistor array substrate.
Embodiment 1
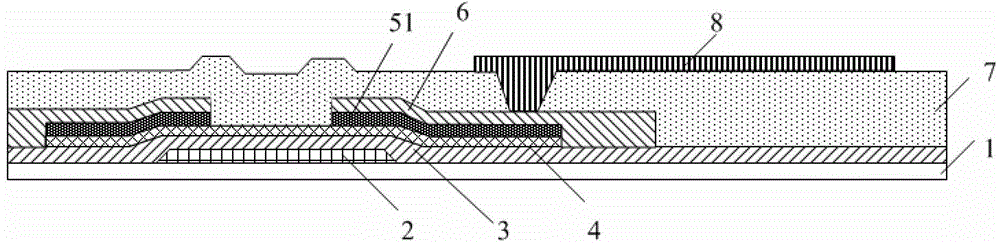
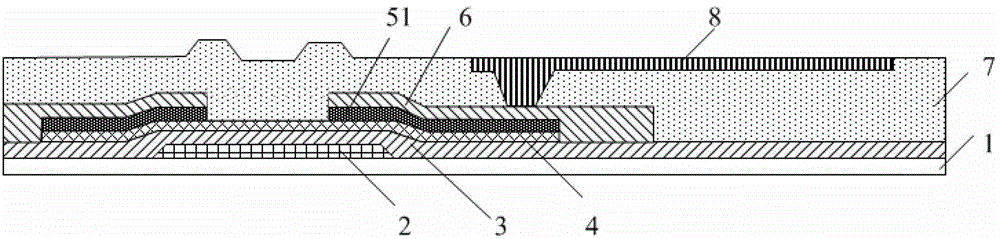
[0031] like image 3 As shown, the thin film transistor array substrate in this embodiment includes forming a gate electrode layer 2, a gate insulating layer 3, an active layer 4, a source-drain electrode layer 6, and a passivation layer 7 on a substrate 1 (also called a substrate). and the pixel electrode layer 8 . Wherein, the passivation layer 7 forms a structural pattern including via holes through a patterning process, the pixel electrode layer 8 is formed in the structural pattern area by dripping, and the source and drain electrode layers 6 and the pixel electrode layer 8 Connect via vias.
[0032] In this embodiment, the active layer 4 is formed of amorphous silicon material, correspondingly, an ohmic contact layer 51 is formed on the active layer 4, and the ohmic contact layer 51 is made of doped phosphorus element Formed from amorphous silicon material, the typical cross-sectional view of the thin film transistor array substrate is as follows image 3 shown.
[0...
Embodiment 2
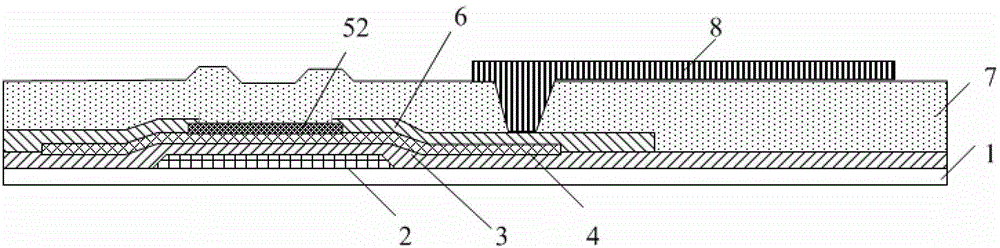
[0053] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the active layer 4 in the thin film transistor array substrate of this embodiment is formed of a metal oxide semiconductor. A typical cross-sectional view of the thin film transistor array substrate is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0054] In this embodiment, the preparation process of the thin film transistor array substrate is as follows: Figures 6a-6g shown.
[0055] Among them, such as Figure 6c As shown, an active layer 4 is formed on the gate insulating layer 3 . In this embodiment, the active layer 4 is formed of a metal oxide semiconductor made of oxygen (O) and indium (In), gallium (Ga), zinc (Zn), tin At least two elements in (Sn) are formed (that is, it must contain oxygen), and the active layer uses indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO), indium zinc oxide (IZO), indium tin oxide (InSnO), indium gallium oxide Tin (InGaSnO) forms, preferably IGZO and IZO. The active layer is formed by sputtering,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com