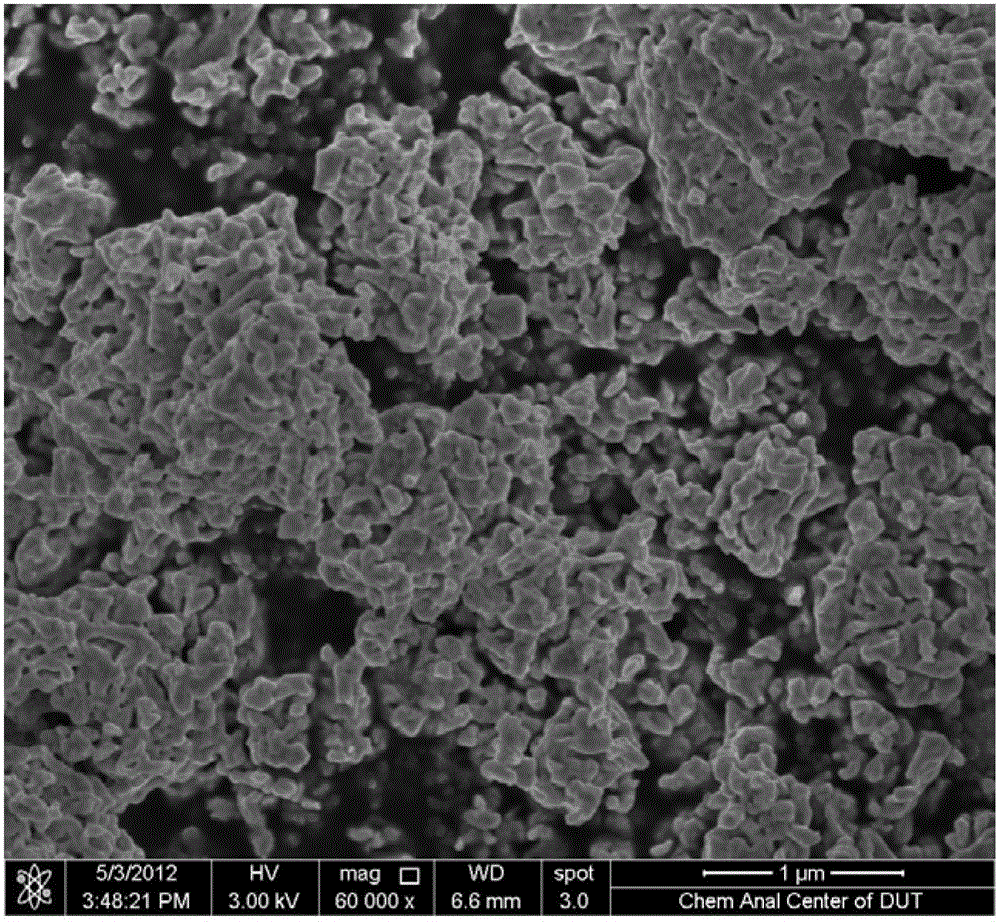
A kind of preparation method of molybdenum carbide material not containing non-stoichiometric ratio carbon
A non-stoichiometric ratio, molybdenum carbide technology, applied in the direction of tungsten/molybdenum carbide, carbide, etc., can solve the problem of difficult control of carbon content, and achieve the effect of fast process, uniform particle size and cheap raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) Add 10g of melamine to 1000mL of water, o Stir at a temperature of C until the melamine powder is completely dissolved to prepare a melamine aqueous solution;
[0018] (2) Add 20g of ammonium molybdate to 500mL of water. o Stir at a temperature of C until the ammonium molybdate powder is completely dissolved to prepare an ammonium molybdate aqueous solution;
[0019] (3) Stir and mix the melamine aqueous solution and the ammonium molybdate aqueous solution to obtain a white precipitate. The white precipitate was collected by filtration and filtered at 120 o Dry at a temperature of C;
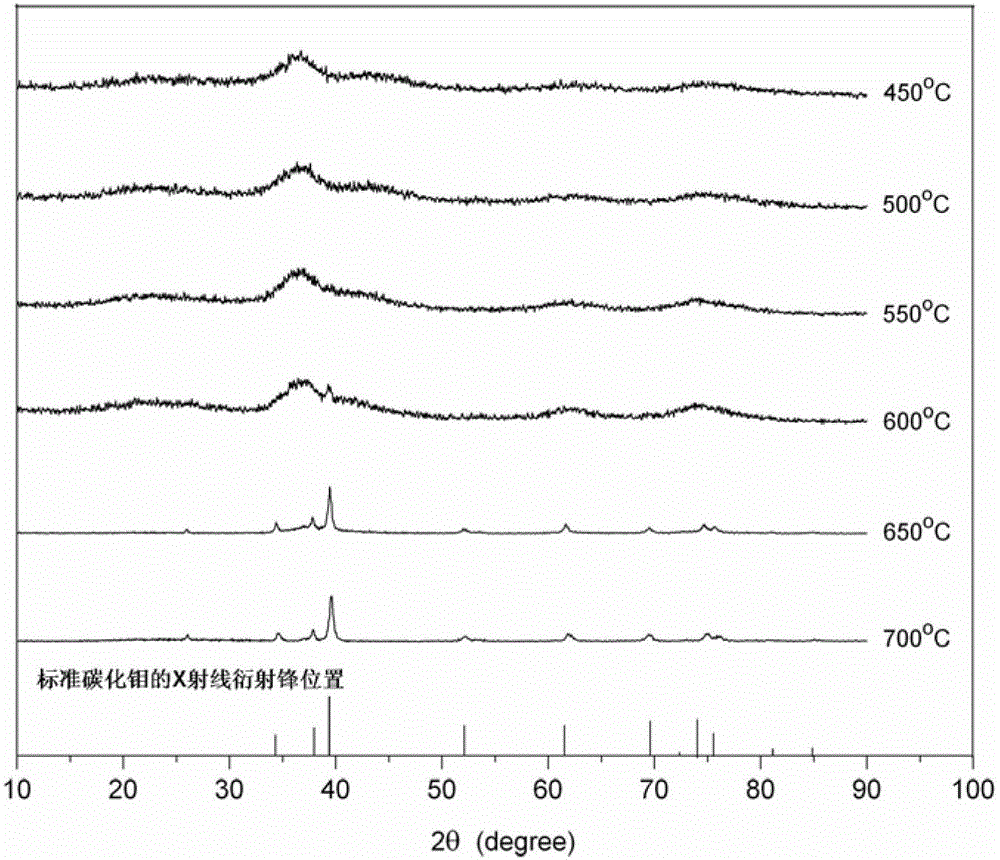
[0020] (4) Put the dried white solid into a tube furnace, and mix it in an argon-hydrogen mixture with an argon flow rate of 50 mL / min and a hydrogen flow rate of 20 mL / min. o The heating rate of C / min rises to 650 o C. Maintain the temperature for 1 hour, turn off the gas, and obtain molybdenum carbide after natural cooling.
Embodiment 2
[0022] (1) Add 10g of melamine to 1000mL of water, o Stir at a temperature of C until the melamine powder is completely dissolved to prepare a melamine aqueous solution;
[0023] (2) Add 20g of ammonium molybdate to 500mL of water. o Stir at a temperature of C until the ammonium molybdate powder is completely dissolved to prepare an ammonium molybdate aqueous solution;
[0024] (3) Stir and mix the melamine aqueous solution and the ammonium molybdate aqueous solution to obtain a white precipitate. The white precipitate was collected by filtration and filtered at 120 o Dry at a temperature of C;
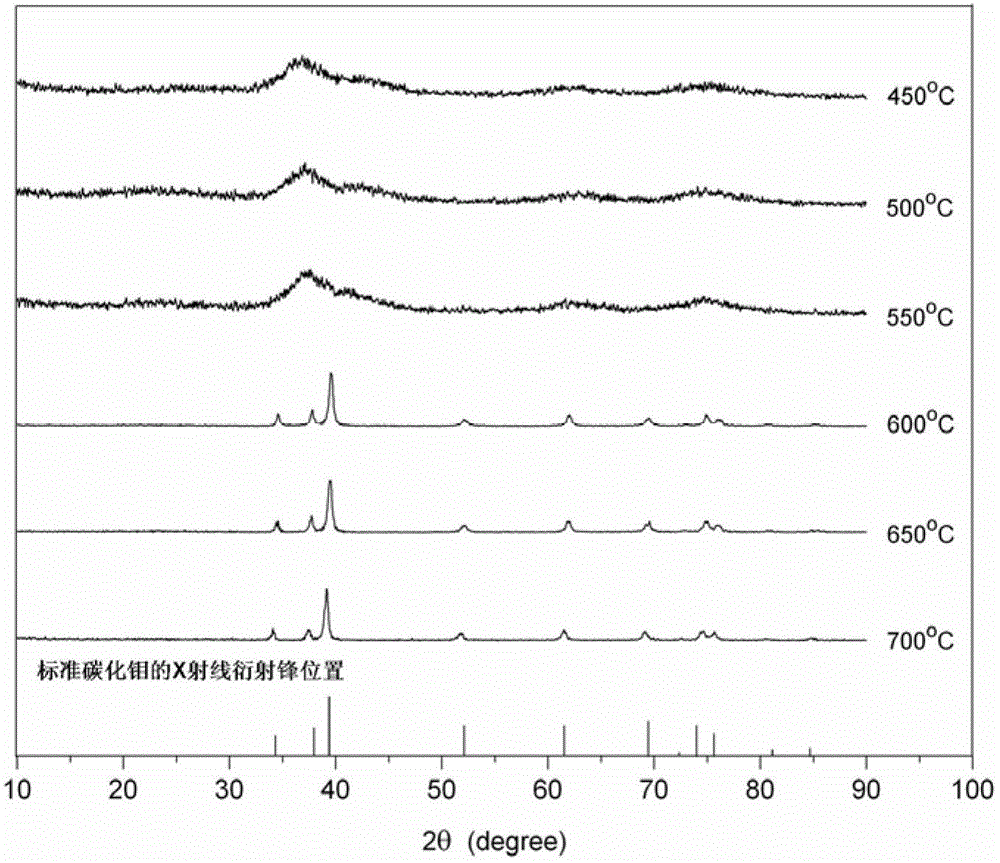
[0025] (4) Put the dried white solid into a tube furnace, and add 5 o The heating rate of C / min rises to 650 o C. Maintain the temperature for 1 hour, turn off the gas, and obtain molybdenum carbide after natural cooling.
Embodiment 3
[0027] (1) Add 10g of melamine to 500mL of ethylene glycol, o Stir at a temperature of C until the melamine powder is completely dissolved to prepare a melamine glycol solution;
[0028] (2) Add 20g of ammonium molybdate to 500mL of water. o Stir at a temperature of C until the ammonium molybdate powder is completely dissolved to prepare an ammonium molybdate aqueous solution;
[0029] (3) Stir and mix the melamine glycol solution and the ammonium molybdate aqueous solution to obtain a white precipitate. The white precipitate was collected by filtration and filtered at 120 o Dry at a temperature of C;
[0030] (4) Put the dried white solid into a tube furnace, and mix it in an argon-hydrogen mixture with an argon flow rate of 50 mL / min and a hydrogen flow rate of 20 mL / min. o The heating rate of C / min rises to 650 o C. Maintain the temperature for 1 hour, turn off the gas, and obtain molybdenum carbide after natural cooling.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com