Low-temperature nitriding method for forming corrosion-resistant hardened layer on surface of stainless steel
A low-temperature nitriding and stainless steel technology, which is applied in coating, solid-state diffusion coating, metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problems of decreased corrosion resistance and reduced chromium content of the substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
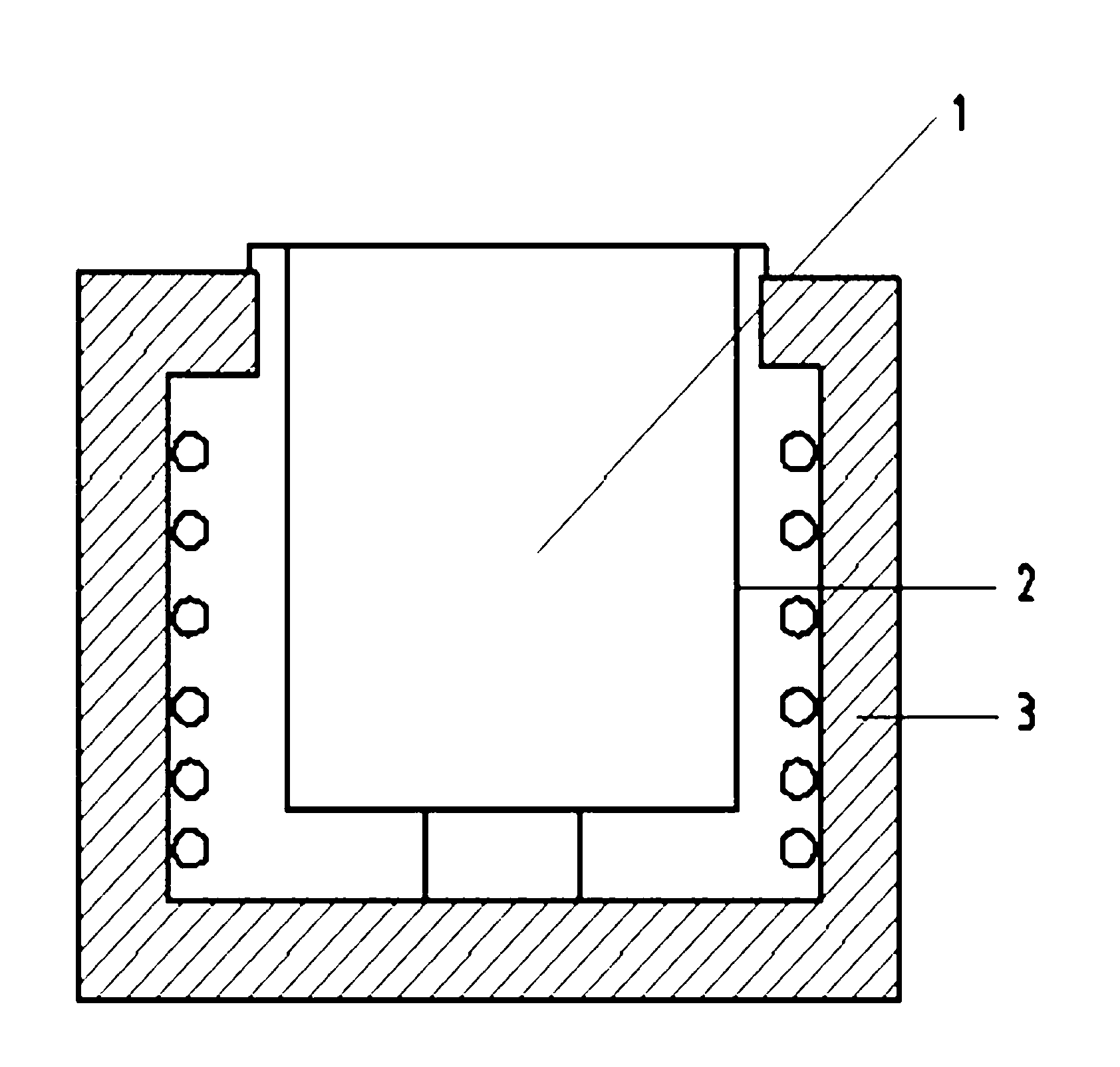
[0027] Firstly, put the flux containing 5-12% borax, 10-18% boric acid, 50-75% potassium fluoroborate, 5-15% potassium fluoride, and 5-15% lithium chloride into the figure 1 In the shown crucible furnace (marked in the drawings are: 1. flux melt 2. crucible 3. heating furnace), heated to 600 ° C until the flux is completely melted into a liquid melt, and then the austenitic stainless steel (such as AISI304 or 316) products are immersed in flux melt for 10 to 15 minutes, then cooled in 10% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution until the flux adhered to the surface of stainless steel products is completely cleaned, and the removal is completed at this time The process of passivation film on the surface of stainless steel. The above-mentioned product that has removed the passivation film is immersed in carbon tetrachloride solution to keep its surface in an activated state, and within 1 hour, it is transferred to a nitriding furnace for nitriding treatment. Because the nitriding fur...
Embodiment 2
[0034] First, put the brazing flux consisting of 5% borax, 10% boric acid, 55% potassium fluoroborate, 15% potassium fluoride, and 15% lithium chloride into the crucible furnace, and heat it to 600°C until the flux is completely melted into a liquid melt. body, immerse stainless steel parts made of 316Ti in flux melt at 500-600 ° C for 12 minutes to remove the passivation film on the surface of the parts, and then soak in 10% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution and carbon tetrachloride solvent for 20 minutes. In the vacuum furnace, after evacuating to -0.1MPa, pass hydrogen (H2) into the furnace and heat up to 420°C. At this temperature, evacuate again to remove the gas in the furnace, and then pass ammonia (NH3) for nitriding After 30 hours, cool to below 100°C and take out the parts.
[0035] After the above-mentioned activation and nitriding treatment steps, the thickness of the hardened layer in different parts of the same part fluctuates in the range of 20-26 μm, and the t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com