In-situ assembling method of lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, in-situ assembly technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte storage batteries, etc., can solve problems such as lithium intercalation transmission behavior, to fill market gaps, meet experimental needs, and simple preparation principle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Example 1: In situ assembly of liquid electrolyte lithium ion battery
[0015] In this embodiment, a high-resolution transmission electron microscope produced by the Swedish Nanofactory Company was selected, and a lithium-ion battery was constructed on its in-situ sample stage. The specific process steps are:
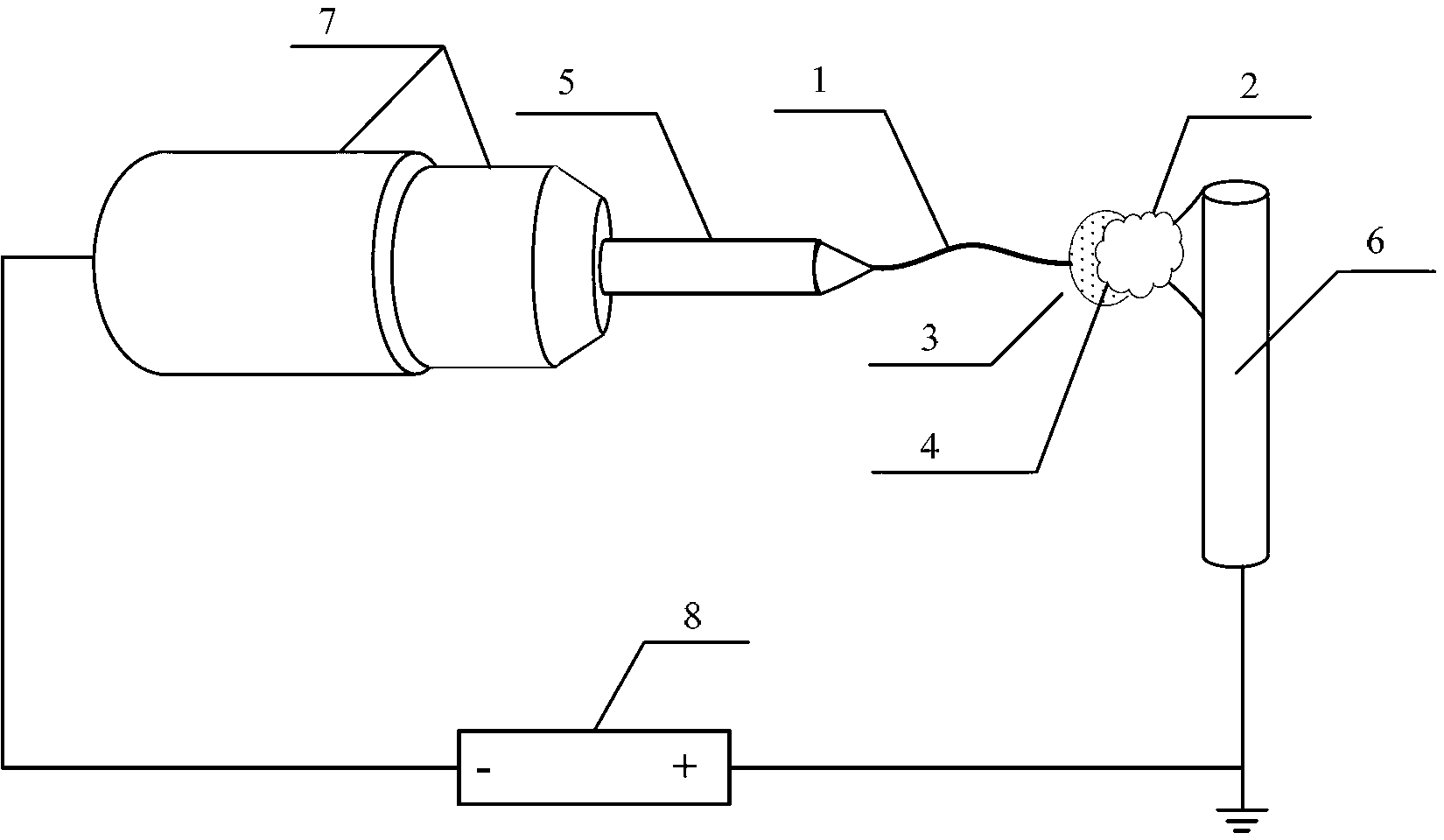
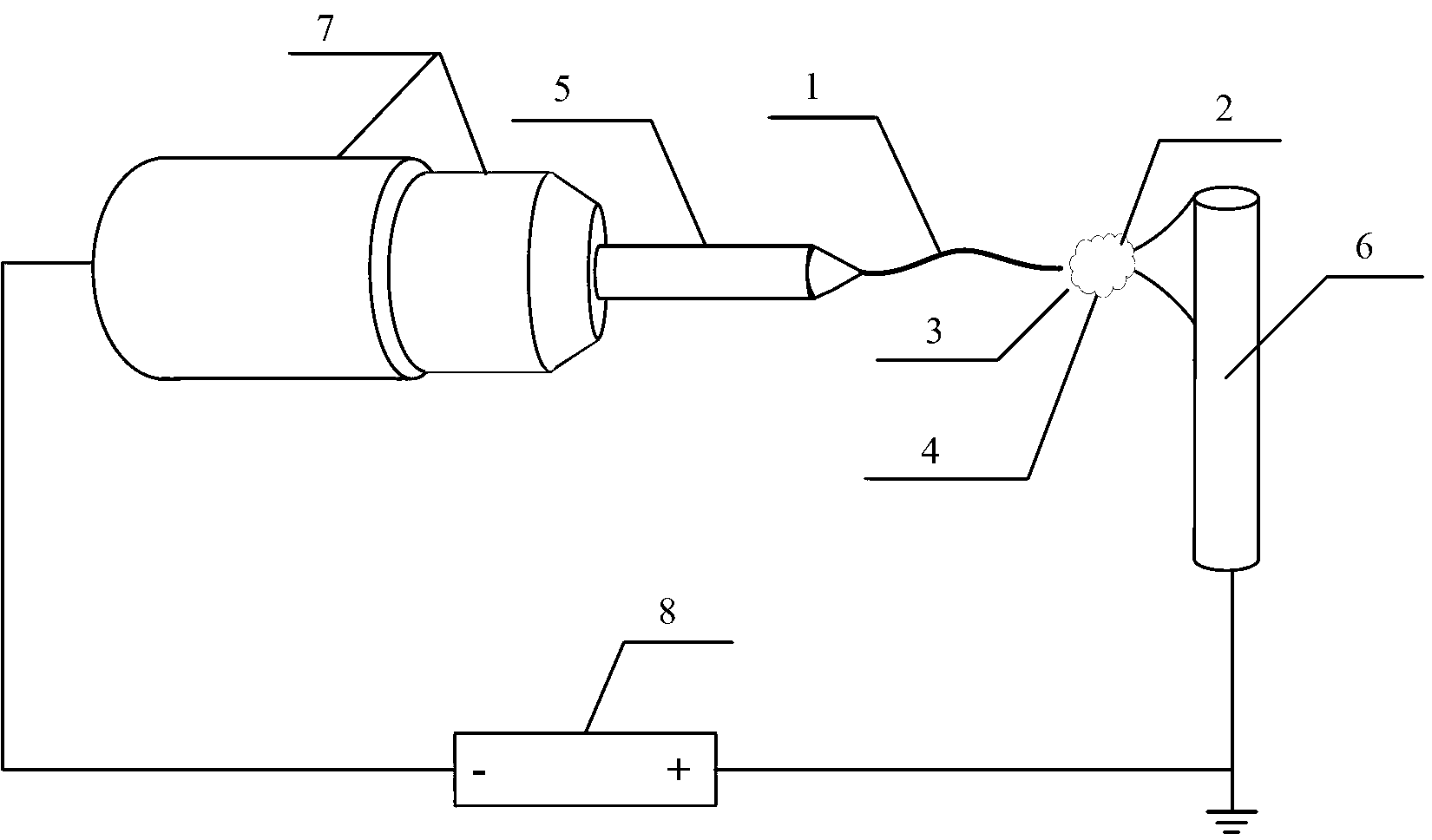
[0016] (1) LiCoO 2 Particles 2 adhere to the AFM probe head 4 of the in-situ sample stage as a cathode;
[0017] (2) Then in LiCoO 2 The surface of the particle 2 is dripped with an imine-based ionic liquid 3 as a liquid electrolyte, and then the in-situ sample stage is inserted into the transmission electron microscope;
[0018] (3) Drop the liquid dispersed with metal oxide nanowires 1 on the gold probe 5 of the in-situ sample stage, so that the metal oxide nanowires adhere to the tip of the gold probe 5 as the anode, which is selected Metal oxides include iron oxide, copper oxide and zinc oxide;
[0019] (4) Inside the high-resolution transmission electron...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: in-situ assembly of solid electrolyte lithium ion battery
[0021] In this embodiment, a high-resolution transmission electron microscope produced by the Swedish Nanofactory Company was selected, and a lithium-ion battery was constructed on its in-situ sample stage. The specific process steps include:
[0022] (1) first metal Li2 is adhered to the AFM probe head 4 of the conventional in-situ sample stage as the cathode;
[0023] (2) Insert the in-situ sample stage into the transmission electron microscope again. Since metal Li2 is easily oxidized, during the insertion into the transmission electron microscope, oxides (Li 2 O) Layer 3 acts as a solid electrolyte;
[0024] (3) Drop the liquid dispersed with metal oxide nanowires 1 on the gold probe 5 of the in-situ sample stage, so that the metal oxide nanowires adhere to the tip of the gold probe 5 as the anode, which is selected Metal oxides include iron oxide, copper oxide and zinc oxide;
[0025] (4) ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] In this embodiment, the steps of Examples 1 and 2 are repeated, and the metal oxide nanowires are replaced with metal oxide nanotubes, respectively, to prepare lithium-ion battery structures with a single metal oxide nanotube as the negative electrode.
[0028] In this embodiment, the purpose of the present invention is achieved by using a single metal oxide nanowire or nanotube to assemble a lithium-ion battery structure in situ, and at the same time complete the performance measurement of a single metal oxide nanowire or nanotube. For the dimensional characteristics of wires or nanotubes, only this embodiment can realize their performance measurement at present.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com