Mineral separation process for recycling iron and rare earth in baotite oxidized ore flotation tailings
A technology for flotation of tailings and oxidized ore, applied in flotation, mechanical material recovery, recycling technology, etc., can solve the problems of rare earth loss, deterioration of flotation fine-grained rare earth minerals, and inability to achieve monomer dissociation, etc. Achieve the effect of saving grinding costs and reducing grinding energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
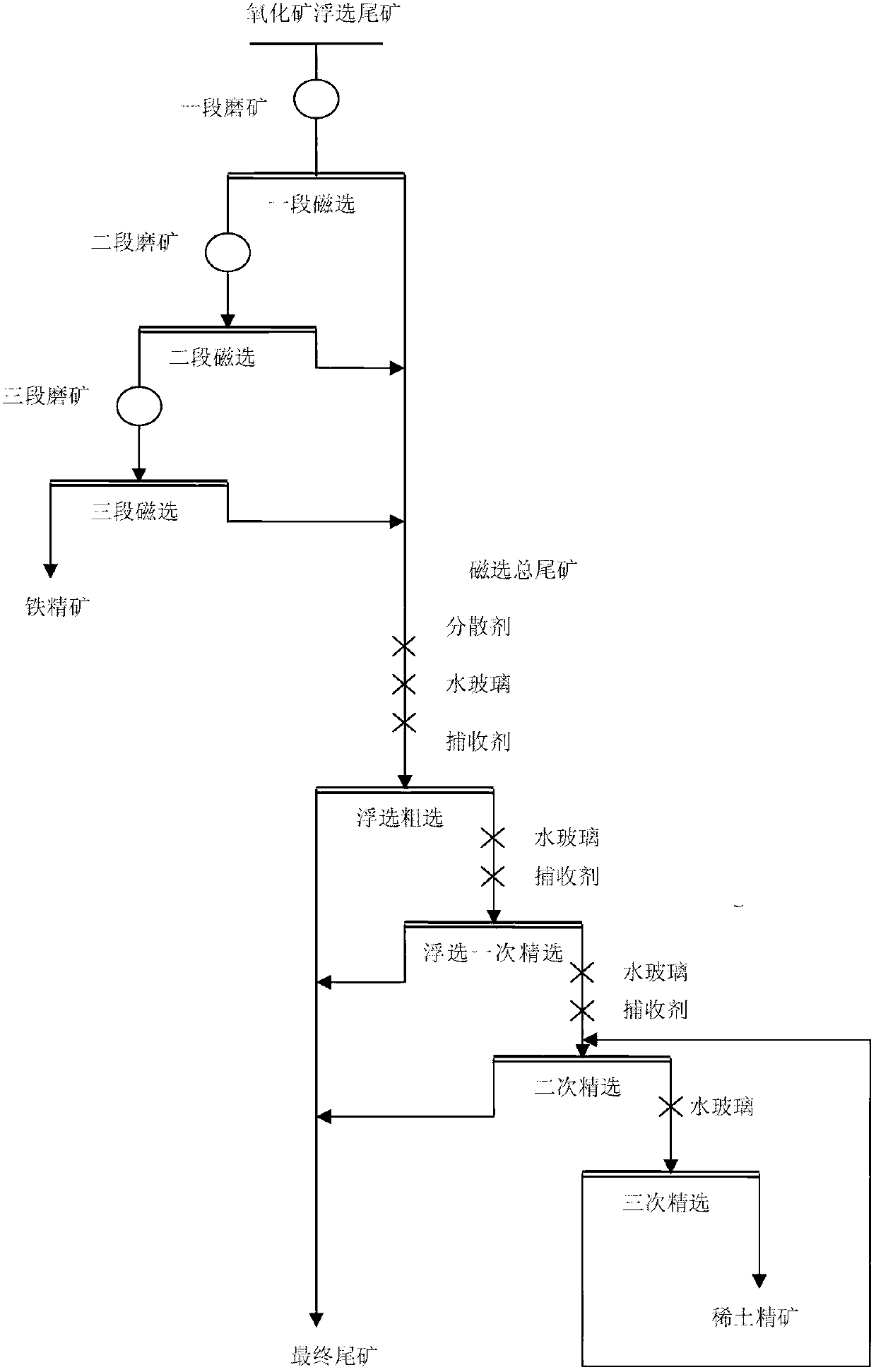
[0013] The beneficiation process for recovering iron and rare earth from oxidized ore flotation tailings in Baotou Mine mainly includes the following parts:
[0014] 1. The flotation tailings of oxidized ore are naturally dried, crushed, mixed and ground to -500 mesh, accounting for 86.6%, and magnetically separated under the condition of 119.4kA / m to obtain a first-stage magnetically separated coarse concentrate, and part of it is thrown away tailings.
[0015] 2. Finely grind the magnetically separated coarse concentrate obtained in the above step 1 to -500 mesh, accounting for 93.2%, and then conduct magnetic separation under the condition of 99.5 kA / m to obtain the second-stage magnetically separated concentrate, and discard part of the tailings.
[0016] 3. The magnetic separation concentrate obtained in the above step 2 is subjected to three-stage grinding, and the grinding fineness is -500 mesh, accounting for 96.8%, and finally magnetic separation is carried out under ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The beneficiation process for recovering iron and rare earth from oxidized ore flotation tailings in Baotou Mine mainly includes the following parts:
[0023] 1. The flotation tailings of oxidized ore are naturally dried, crushed, mixed and ground to -500 mesh, accounting for 86.6%, and magnetically separated under the condition of 119.4kA / m to obtain a first-stage magnetically separated coarse concentrate, and part of it is thrown away tailings.
[0024] 2. Finely grind the magnetically separated coarse concentrate obtained in the above step 1 to -500 mesh, accounting for 93.2%, and then conduct magnetic separation under the condition of 99.5 kA / m to obtain the second-stage magnetically separated concentrate, and discard part of the tailings.
[0025] 3. The magnetic separation concentrate obtained in the above step 2 is subjected to three-stage grinding, and the grinding fineness is -500 mesh, accounting for 96.8%, and finally magnetic separation is carried out under ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com