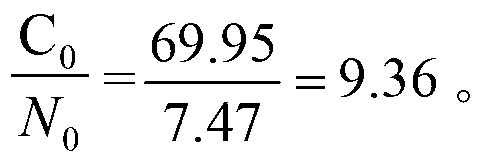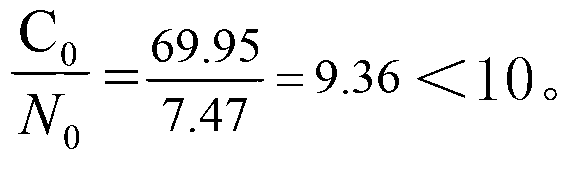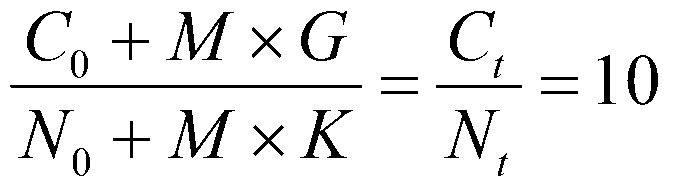Method for controlling farmland soil nitrogen non-point source pollution with carbon
A non-point source pollution and soil nitrogen technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effects of nitrogen non-point source pollution, crop yield reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: The effect of increasing soil carbon on controlling the risk of farmland soil nitrogen non-point source pollution
[0043] (1) Test soil, test crops and carbon source materials
[0044] Soil for testing: red soil where rice has been planted for many years, which belongs to red soil paddy soil.
[0045] Test crops: rice.
[0046] Carbon source material: Cow dung. The tested cow dung was obtained from local farmers (it can also be purchased through commercial channels). The carbon content in the cow dung was determined by the potassium dichromate volumetric method, and the nitrogen content in the cow dung was determined by the Kjeldahl method. The measurement results: in mass fraction Calculated, the carbon content of cow dung is 8.4%, and the nitrogen content is 0.3%.
[0047] (2) Calculation of soil initial carbon storage, nitrogen storage and carbon-nitrogen ratio:
[0048] Before the test, measure the soil bulk density, soil pH, soil initial nitrogen co...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2 Effect of soil nitrogen reduction on controlling farmland soil nitrogen non-point source pollution risk
[0105] (1) Test soil, test crops and nitrogen source materials
[0106] Soil for testing: red soil paddy soil.
[0107] Test crops: garlic (garlic variety: Wenjiang Hongqixing, Sichuan.)
[0108] Nitrogen source material: urea (N, 46%).
[0109] (2) Calculation of soil initial carbon storage, nitrogen storage and carbon-nitrogen ratio:
[0110] Before the test, the soil bulk density, soil pH, soil initial nitrogen content and soil initial carbon content in the 0-30cm plow layer of farmland were measured according to conventional methods (the measurement method was the same as in Example 1), and the initial soil carbon storage, soil initial Calculation of nitrogen storage and initial soil carbon-nitrogen ratio.
[0111] Soil bulk density B=1.37t / m 3 , farmland area R=10000m 2 , C N =0.247%, C C =2.34%. Soil cultivation layer thickness L=0.3m.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3 Effect of soil carbon increase and nitrogen reduction on controlling the risk of farmland soil nitrogen non-point source pollution
[0138] (1) Test soil, test crops, carbon source materials, nitrogen source materials
[0139] Test crops: rice.
[0140] Soil for testing: red soil paddy soil.
[0141] Carbon source material: cow dung, the cow dung for testing is taken from local farmers, the carbon content in cow dung is determined by the potassium dichromate volumetric method, the nitrogen content in cow dung is determined by the Kjeldahl method, and the measurement results: in terms of mass fraction , the carbon content of cow dung is 8.4%, and the nitrogen content is 0.3%. Cow manure is also commercially available.
[0142] Nitrogen source material: Urea (N, 46%) (chemical fertilizer).
[0143] (2) Calculation of soil initial carbon storage, nitrogen storage and carbon-nitrogen ratio:
[0144] Before the test, the soil bulk density, soil pH, soil initia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com