High performance liquid chromatography detection method for penicillin G in penicillin fungi residues
A high performance liquid chromatography, penicillin bacteria residue technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problem of inability to detect penicillin G quickly and accurately, and achieve high accuracy, improve detection efficiency, and good linear relationship. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
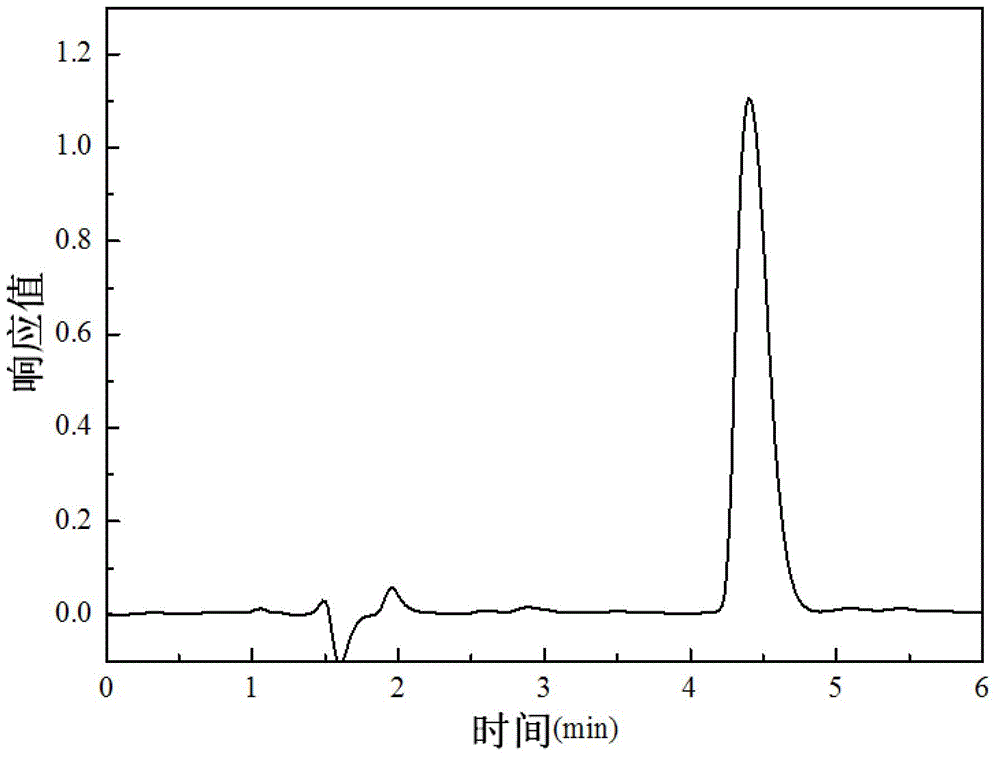
[0016] Specific embodiment one: present embodiment is a kind of high performance liquid chromatography detection method of penicillin G in penicillin scum, specifically completes according to the following steps:
[0017] 1. Draw the standard curve and fit the standard curve equation: the penicillin G standard is dissolved in a solvent, and diluted with a solvent to prepare a concentration of 0.1 μg·mL -1 ~2000μg·mL -1 Penicillin G standard solutions with different gradient concentrations between them were filtered through a 0.45 μm needle filter and detected by high performance liquid chromatography. Chromatography detection is drawn into standard curve, then fits, and obtains standard curve equation: Y=kX+b, Y represents the chromatographic peak area in the equation, and X represents the concentration of penicillin G, and k and b are constants; Described solvent is by Acetonitrile and water are mixed according to the volume ratio of acetonitrile and water is 1:1;
[0018] ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the specific operation of the high-performance liquid chromatography method described in step 1 is as follows: an HPLC composed of a binary pump, a thermostat, an ultraviolet detector and a chemical workstation In the present invention, the volume ratio of aqueous phase A and organic phase B is 60:40, and the flow rate is 1.0 mL min. -1 Constant elution. Constant elution, chromatographic conditions are as follows:
[0028] a. Chromatographic column: Eelipse XDB-C 18 ;
[0029] B, mobile phase: water phase A: the formic acid aqueous solution whose mass fraction is 0.3%; organic phase B: acetonitrile; and the volume ratio of the water phase A and the organic phase B is 60:40;
[0030] c. Elution method: isocratic elution 0.8mL·min -1 ~1.2mL·min -1 ;
[0031] d. Detection wavelength: UV215nm;
[0032] e. Column temperature: 30℃;
[0033] f. Injection volume: 10 μL.
[0034] Others are the sa...
specific Embodiment approach 3
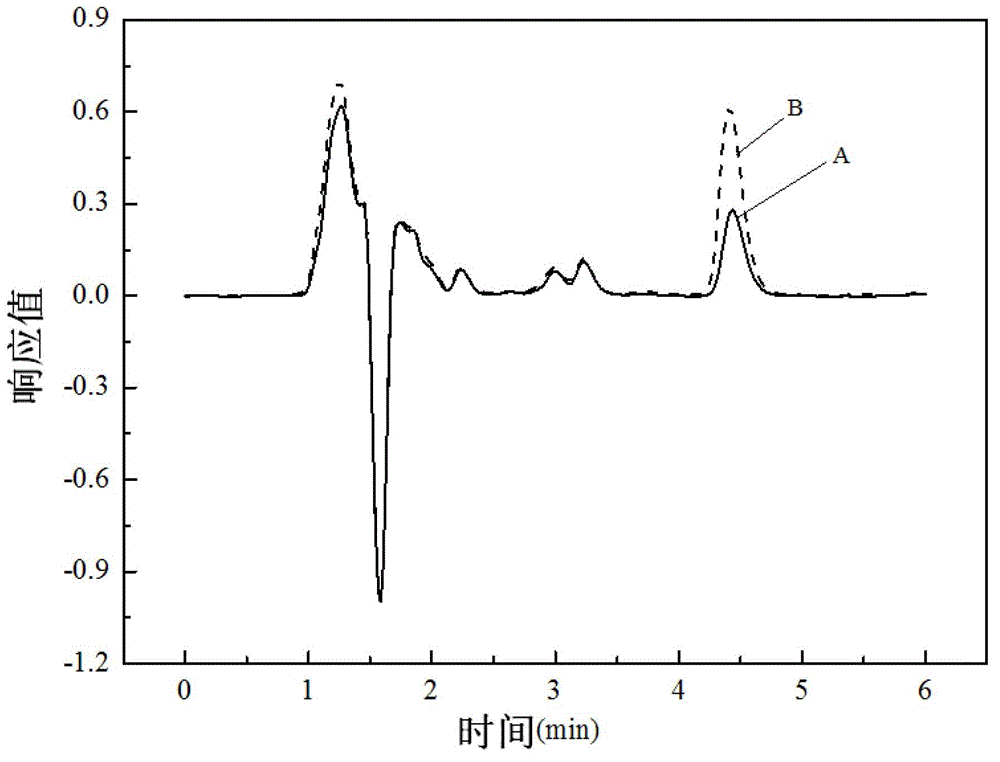
[0038] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that: in step 2, the penicillin bacterial residue is firstly added to the extraction solution, and after mixing evenly, ultrasonic extraction is performed for 30 minutes, and then centrifugation is performed. The supernatant is the crude extract of penicillin G. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com