Method used for screening polypeptide in vitro
An in vitro screening and ribosome technology, applied in the field of chemical biology, can solve the problems that RNA-polypeptide fusions are difficult to withstand screening requirements, are susceptible to RNase, and affect the screening process. High stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, in vitro screening polypeptide
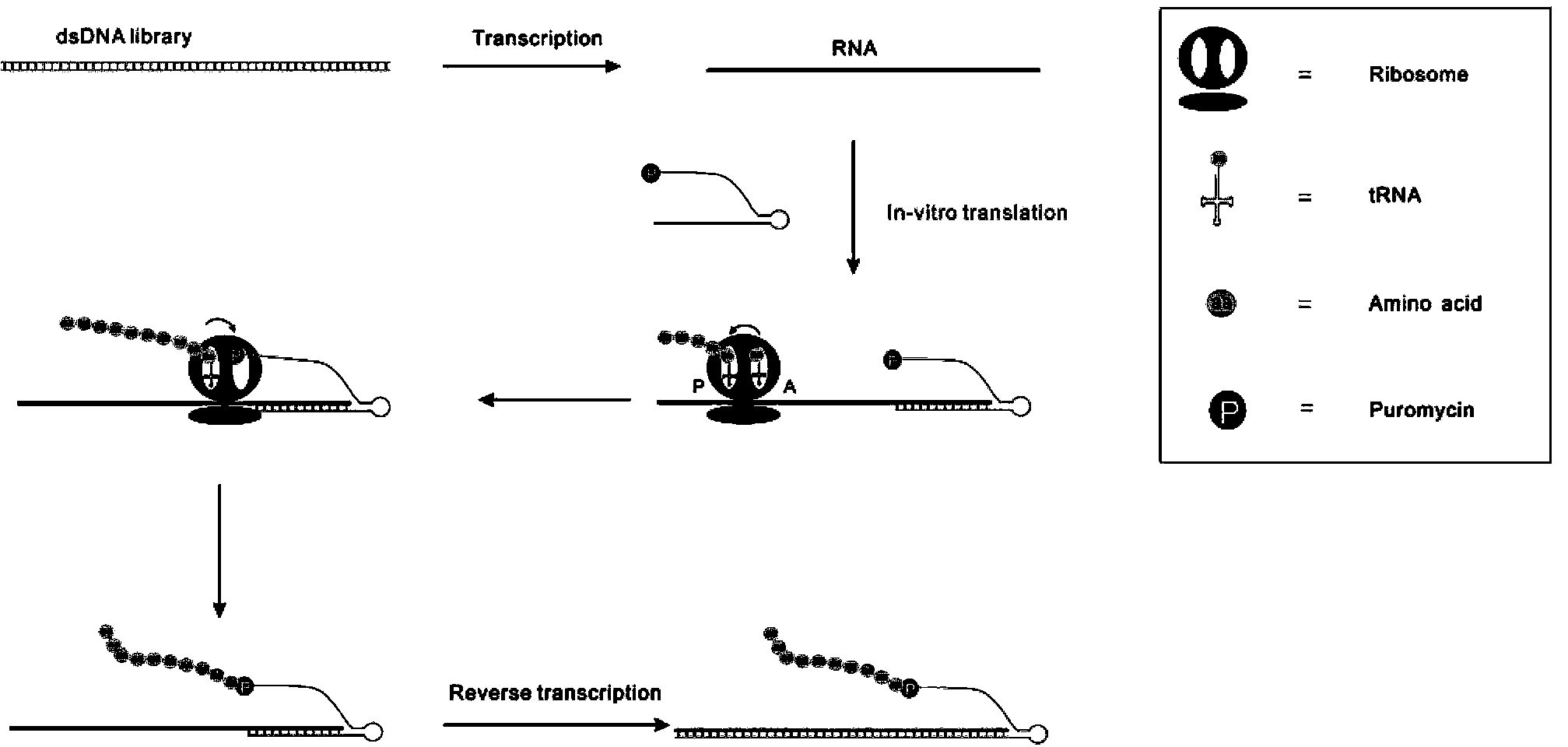
[0039] For the procedure of screening peptides in vitro, see figure 1 .
[0040] (1) Construction of a double-stranded DNA library containing random sequences. Synthesize a single-stranded DNA library with random sequences by chemical methods, add equal concentrations of downstream primers for two cycles of PCR amplification, and finally obtain T7 promoters, enhancers, start codons, random sequences, and affinity purification Double-stranded DNA random library of tag-encoding sequences.
[0041] Single-stranded DNA random sequence:
[0042] TAATACGACTCACTATAGGAGGACGAAATG(NNN)9CACCACCACCATCATCATCAGC TGCGTAACTC
[0043] Downstream primer: GAG TTA CGC AGC TGA TGA
[0044] Reaction system and PCR conditions:
[0045]
[0046] The PCR conditions are: preheating at 95°C for 1min; denaturation at 95°C for 30s, renaturation at 45°C for 45s, extension at 72°C for 45s, 2 cycles.
[0047] (2) In vitro transcription. Using d...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2, the chemical modification of puromycin
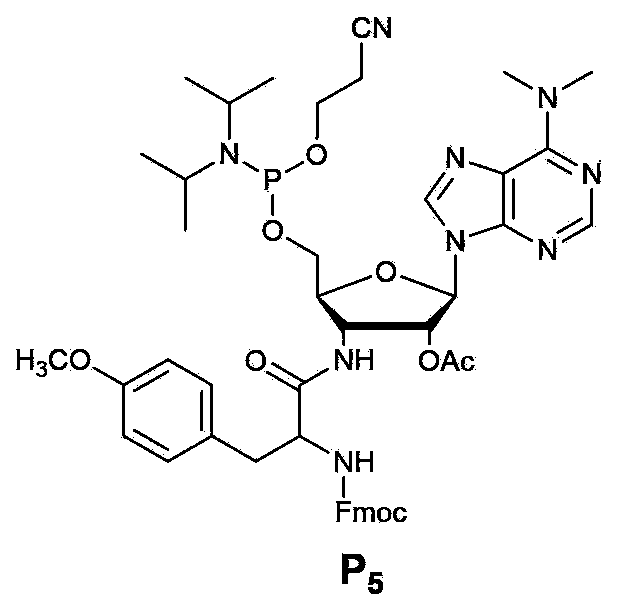
[0061] The final product obtained by chemical modification of puromycin see figure 2 . The specific operation steps are as follows: a. Dissolve 100mg of puromycin in CH 3 CN (2ml), stirred at 0°C, added Et 3 N (60ul), the solution was clear, Fmoc-oSu (72mg) was dissolved in CH 3 CN (1ml) was added dropwise to the reaction solution at 0°C, and continued to stir. It turned into a white turbid liquid after 30 minutes. The reaction time was about 2h at 0°C and 1h at RT. After the reaction, the white solid product P1 was recovered by filtration through a funnel. b. Dissolve 150mg of P1 in 2ml of pyridine, stir well, add 200ul triethylamine, and stir at 0°C; dissolve 400mg of DMTrCl in 2ml of pyridine, inject it into the reaction solution with a needle, stir at 0°C to room temperature, and The column recovers product P2. c. Dissolve 420mg of P2 in 6ml of pyridine, add 10mg of DMAP, cool in an ice-water bath to 0°C, ...
Embodiment 3
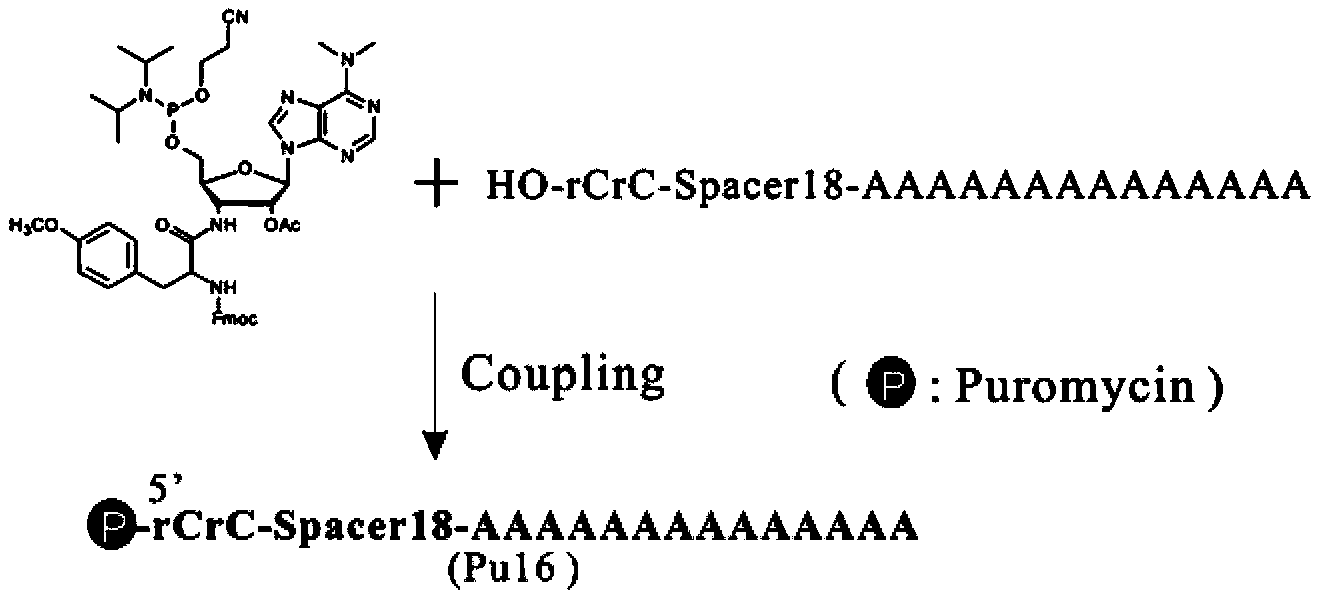
[0062] Example 3. The modified puromycin is connected to a DNA with a fixed sequence. The reaction steps are basically the same as the widely used solid-phase phosphoramidite triester method, and the coupling product is obtained by high-performance liquid phase separation and purification. Such as image 3 As shown, Spacer18 near the 5' end of DNA represents polyethylene glycol with 12 carbons, and rC represents the base reversed in the 5'-3' direction on the oligonucleotide chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com