Extraction method of suspected lymph nodes in gastric CT images based on sparse dynamic integration selection
A CT image and lymph node technology, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of high computational complexity and time-consuming, and achieve the effect of good classification performance and reduced computational complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] The present invention is a method for extracting suspected lymph nodes from a stomach CT image based on sparse dynamic integration selection. Current CT images are commonly used imaging methods. To extract suspected lymph node regions from adipose tissue regions of CT images, the adipose tissue regions must be extracted first . Lymph nodes are mainly distributed in the adipose tissue around the stomach wall, so accurate segmentation of the adipose tissue is the first priority.
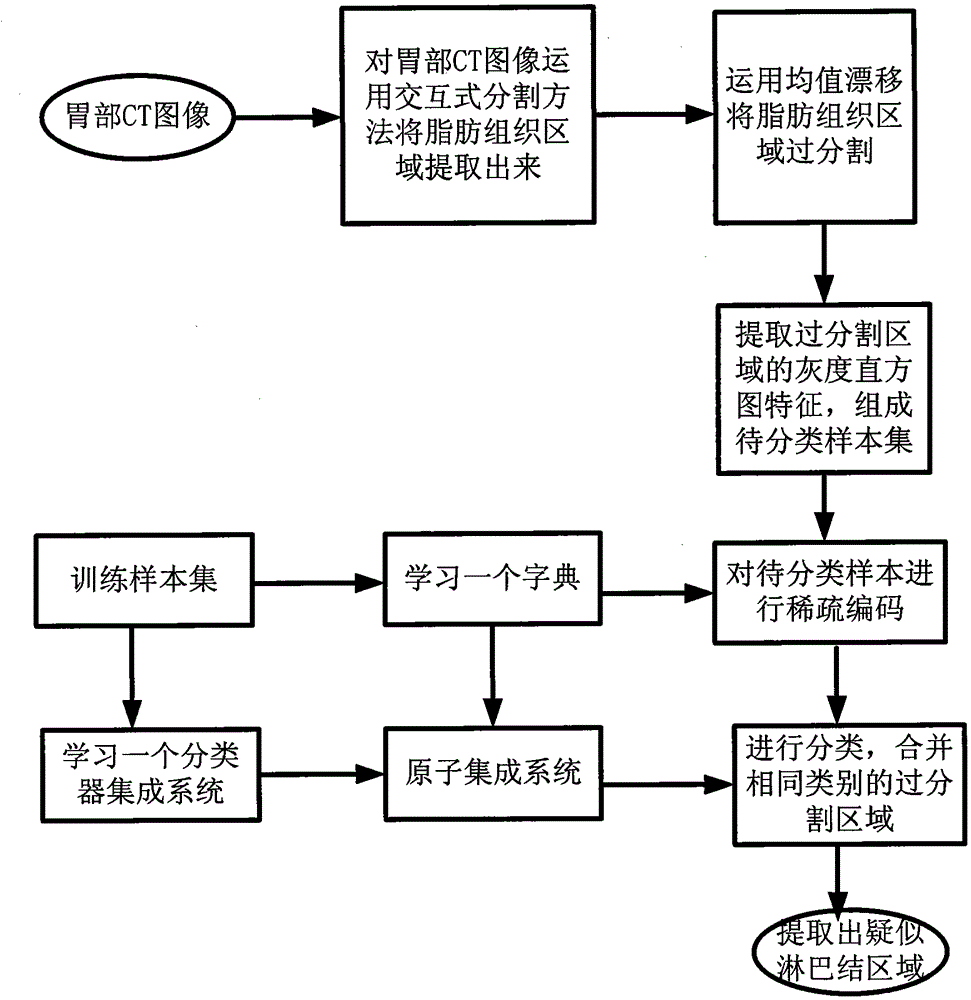
[0047] The process of the present invention for extracting the suspected lymph node region from the image of the gastric adipose tissue is as follows figure 1 Shown. The specific description is as follows:
[0048] Step 1. Extract a CT image of the stomach, see Figure 4 (a). The stomach CT images used in this example are from Beijing Cancer Hospital. Each CT image has 512x512 pixels. All image processing experiments are implemented on the MATLAB2009a experimental platform.
[0049] Step 2: Mark par...
Embodiment 2
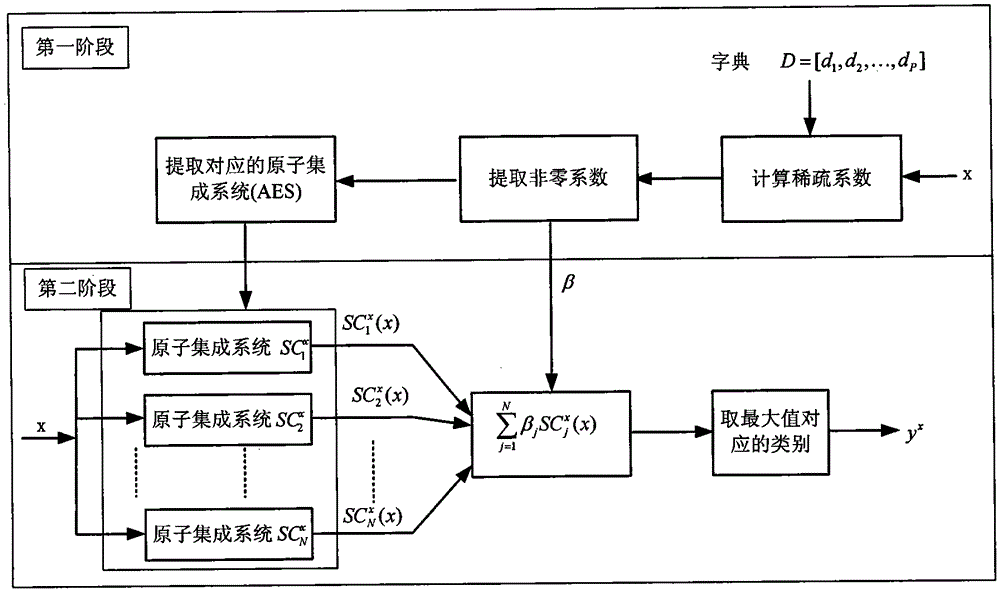
[0066] The method for extracting suspected lymph nodes from a stomach CT image based on sparse dynamic ensemble selection is the same as that in Example 1. The process of using the sparse dynamic ensemble selection method to classify the extracted adipose tissue region sample set to be classified in step 5 includes training and testing. stage:
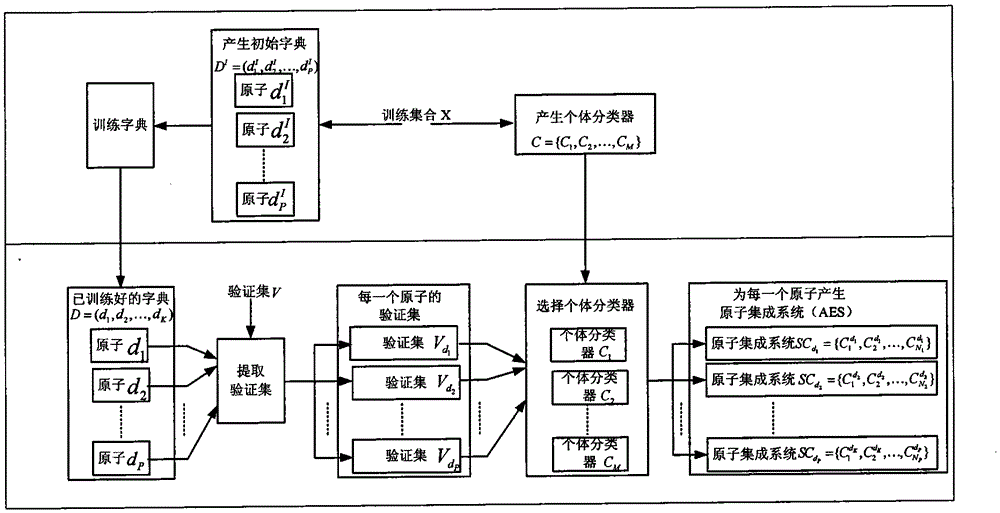
[0067] The flow chart of the training phase is as figure 2 As shown, the specific process is:
[0068] 5.1 Select training samples from some labeled images of adipose tissue that have been successfully classified. The training samples are denoted as X = {(x i , Y i )|x i ∈R F , Y i ∈{1, 2,..., L}, i=1, 2,..., r}, where x i Is the gray histogram feature of the sample extracted from the labeled image of adipose tissue, y i Is the mark of the sample, F is the dimension of the feature of the gray histogram, L is the number of segmentation categories, r is the number of samples extracted; the number of selected training samples should be greater...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The method for extracting suspected lymph nodes from the stomach CT image selected by the sparse dynamic integration is the same as in Example 1-2. In this example, the effectiveness of the present invention is verified through simulation experiments using stomach CT images from Beijing Cancer Hospital. Each image consists of 512x512 pixels, and 3 images are selected for experimentation. All experiments are implemented on the MATLAB2009a experimental platform. Figure 4-Figure 6 The results of adipose tissue extraction from three images. in Figure 4-Figure 6 In each picture, (a) is the original image, (b) is the result after inputting interactive information, (c) is the accurate adipose tissue region extraction result, (e) is the fat of the method used in the present invention The results of tissue region extraction, (d) is the partial enlarged view corresponding to (c), and (f) is the partial enlarged view corresponding to (e). Figure 4-Figure 6 The similarity between ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com