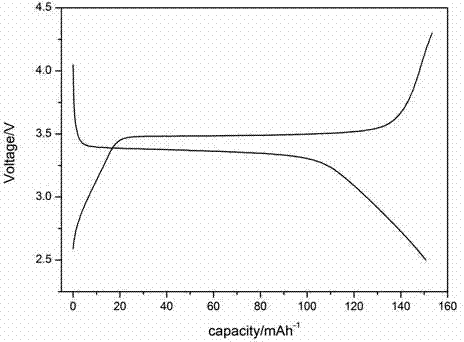
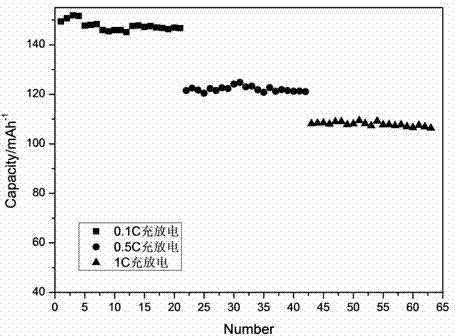
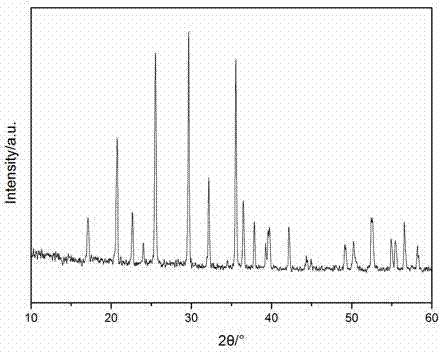
A kind of preparation method of positive electrode material of lithium ion battery
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and cathode materials, applied in battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., to achieve good rate performance and excellent cycle performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Dissolve lithium dihydrogen phosphate and ferrous nitrate in an appropriate amount of deionized water at a molar ratio of Li:Fe=1:1 to prepare solution A with a concentration of 3mol / L; use 1% copper sulfate and 1% Prepare Fehling's reagent with sodium hydroxide; slowly drop A solution into Fehling's reagent according to the ratio of Fe:Cu=10:1, and then adjust the pH value of the solution to 9 with ammonia water; slow down the concentration of 20% formaldehyde solution Add the above solution with a pH value of 9, and perform magnetic stirring at 70°C to form a precursor; after simply grinding the precursor, put it into a tube furnace protected by argon for sintering, and the sintering temperature is 300°C , the sintering time is 3 hours, and the pretreated powder is obtained; the pretreated powder is then sintered in a tube furnace with a mixed protective gas of argon and hydrogen, and the sintering temperature is 900°C (heating rate 10°C / min), and the sintering The ti...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Dissolve lithium phosphate and ferrous oxalate in an appropriate amount of deionized water at a molar ratio of Li:Fe=1:1 to prepare solution A with a concentration of 0.1mol / L; use 7% copper sulfate and 10% hydrogen Prepare Fehling's reagent with sodium oxide; slowly drop A solution into Fehling's reagent according to the ratio of Fe:Cu=100:1, and then adjust the pH value of the solution to 10 with ammonia water; slowly drop 40% formaldehyde solution Add the above solution with a pH value of 10, and carry out magnetic stirring at 90°C to form a precursor; after simply grinding the precursor, put it into a tube furnace with nitrogen protection for sintering, the sintering temperature is 450°C, and the sintering The time is 10 hours, and the pretreated powder is obtained; the pretreated powder is then sintered in a tube furnace with a mixed protective gas of nitrogen and hydrogen. Hours, the temperature is lowered by liquid nitrogen quenching and cooling, and 0.16wt% copp...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Dissolve lithium dihydrogen phosphate and ferrous acetate in a molar ratio Li:Fe=1:1 in an appropriate amount of deionized water to prepare solution A with a concentration of 1mol / L; use 5% copper sulfate and 10% Prepare Fehling's reagent with sodium hydroxide; slowly drop A solution into Fehling's reagent according to the ratio of Fe:Cu=50:1, and then adjust the pH value of the solution to 9 with ammonia water; slow down the concentration of 35% formaldehyde solution The above solution with a pH value of 9 was added dropwise, and magnetically stirred at 80°C to form a precursor; after the precursor was simply ground, it was put into a tube furnace with nitrogen protection for sintering, and the sintering temperature was 400°C. The sintering time was 5 hours to obtain the pretreated powder; the pretreated powder was then sintered in a tube furnace with a mixed protective gas of nitrogen and hydrogen, the sintering temperature was 850°C (heating rate 15°C / min), and the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com