Zinc oxide hollow micro ball and preparation method thereof
A zinc oxide and hollow technology is applied in the field of zinc oxide hollow microspheres and their preparation, and achieves the effects of simple process, no post-treatment and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] 1) Dissolve 1 g of zinc acetate dihydrate in 30 ml of ethanol, then add 0.5 ml of formic acid, stir until uniform to obtain a suspension.
[0017] 2) Transfer the suspension to a solvothermal device, perform a solvothermal reaction at 150 °C for 6 h, then centrifuge the obtained material, and then dry it at 80 °C to obtain zinc oxide hollow microspheres.
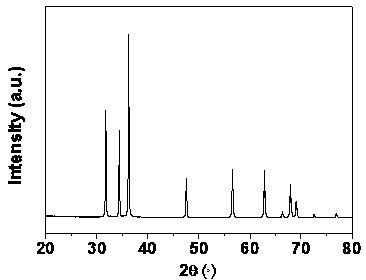
[0018] The X-ray diffraction pattern of the prepared zinc oxide hollow microspheres is shown in Figure 1, and its diffraction peaks are consistent with the standard pattern of hexagonal wurtzite phase zinc oxide, indicating that the obtained product is wurtzite zinc oxide. Scanning electron micrographs of ZnO hollow microspheres (see figure 2 ), it can be seen that the crystals of the outer layer of zinc oxide microspheres have hexagonal structure characteristics.
Embodiment 2
[0020] 1) Dissolve 1 g of zinc acetate dihydrate in 30 ml of methanol, then add 0.5 ml of formic acid, stir until uniform to obtain a suspension.
[0021] 2) Transfer the suspension to a solvothermal device, perform a solvothermal reaction at 150 °C for 6 h, then centrifuge the obtained material, and then dry it at 80 °C to obtain zinc oxide hollow microspheres.
Embodiment 3
[0023] 1) Dissolve 1 g of zinc acetate dihydrate in 30 ml of ethanol, then add 0.5 ml of formic acid, stir until uniform to obtain a suspension.
[0024] 2) Transfer the suspension to a solvothermal device, perform a solvothermal reaction at 170 °C for 36 h, then centrifuge the obtained material, and then dry it at 80 °C to obtain zinc oxide hollow microspheres.
[0025] The transmission electron micrographs of the prepared ZnO hollow microspheres are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen from the figure that the zinc oxide hollow microspheres are composed of two different sizes of zinc oxide crystals. The particle size of the inner layer of zinc oxide crystals is 100 nm, and the particle size of the outer layer of zinc oxide crystals with hexagonal structure characteristics is 600 nm. nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com