Method for preparing chlorophyll cuprate and sodium copper chlorophyll
A technology of chlorophyll cupric acid and copper sodium salt, applied in chemical instruments and methods, azo dyes, organic dyes, etc., which can solve the problems of recovery and storage equipment, time, and large amount of organic reagents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
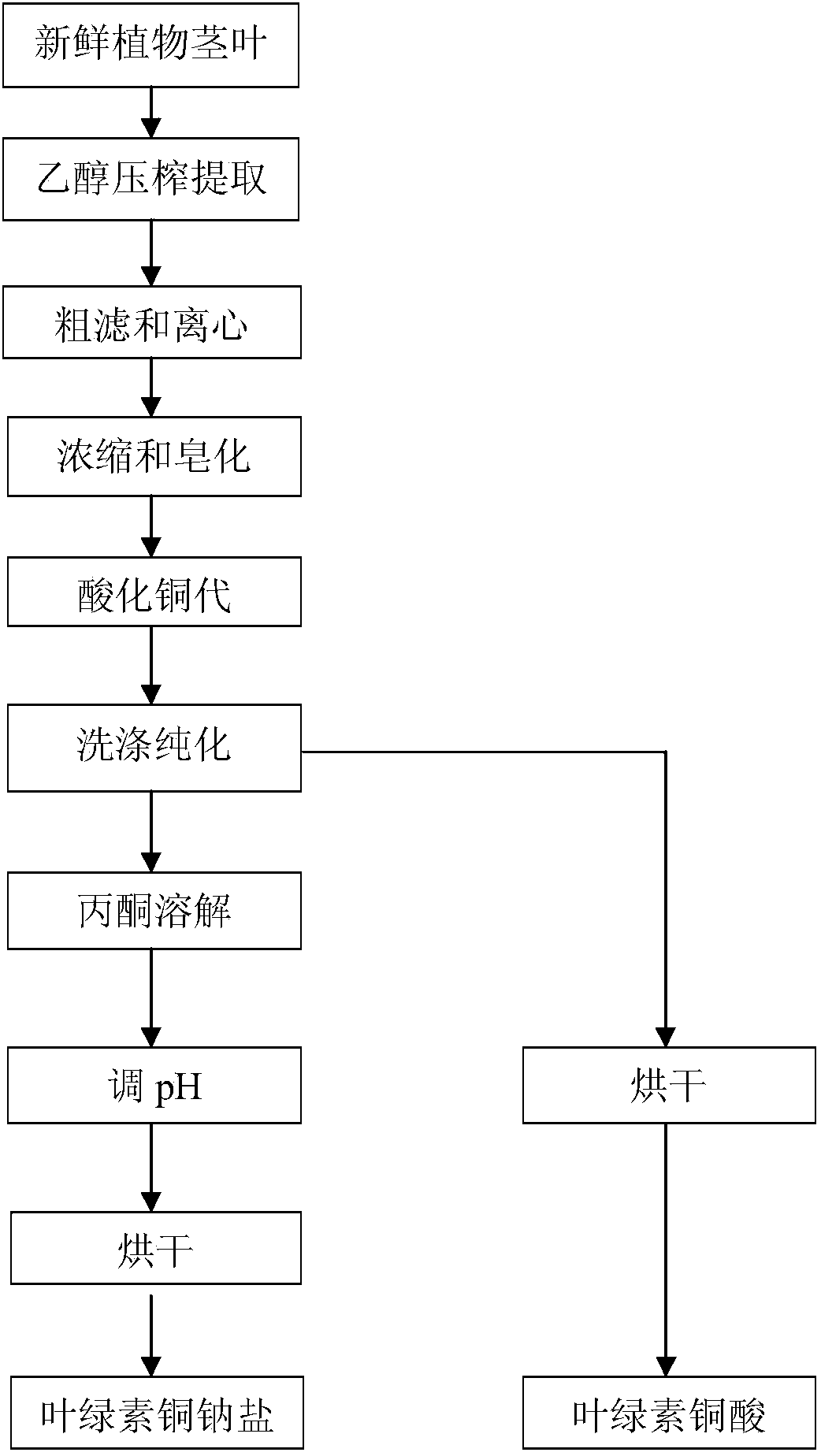
[0028] Example 1 Preparation of chlorophyll cupric acid and copper sodium salt from fresh Rumex.
[0029] Weigh 10kg of fresh Rumex stems and leaves, add 20g of CaCO3, add 40L of 90% ethanol solution, beat, and control the extraction temperature at 50°C. Squeeze the slurry with a belt press, collect 47.5L of juice, and remove waste residue. After the juice is roughly filtered with a 180-mesh filter cloth, it is centrifuged at a high speed at a speed of 4000 rpm to remove waste residue. Adjust the pH to 11 with 5% NaOH solution, control the temperature at 45°C and concentrate under reduced pressure while performing saponification to obtain 11.5 L of concentrated saponification solution. The pH of the saponification solution was adjusted to 2 with hydrochloric acid, 230ml of 10% CuSO4 solution was added, and the temperature was controlled at 75°C for 1.0h. After filtration under reduced pressure, the precipitate was washed three times with deionized water at a temperature of 4...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 Preparation of chlorophyll cupric acid and copper sodium salt from fresh spinach.
[0031] Weigh 10kg of fresh spinach stems and leaves, add 40g of CaCO3, add 60L of 95% ethanol solution, beat, and control the extraction temperature at 55°C. The slurry is squeezed by a belt press, and 67L of juice is collected to remove waste residue. After the juice is coarsely filtered with a 250-mesh filter cloth, it is centrifuged at a high speed at a speed of 6000 rpm to remove waste residue. Use 5% NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 12, control the temperature at 50°C and concentrate under reduced pressure while performing saponification to obtain 13.3 L of concentrated saponification solution. The pH of the saponification solution was adjusted to 2.7 with hydrochloric acid, 300ml of 10% CuSO4 solution was added, and the temperature was controlled at 70°C for 1.5h. After filtration under reduced pressure, the precipitate was washed three times with deionized water at a ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 Preparation of chlorophyll cupric acid and copper sodium salt from fresh spinach.
[0033] Weigh 10kg of fresh spinach stems and leaves, add 50g of CaCO3, add 50L of 95% ethanol solution, beat, and control the extraction temperature at 60°C. Squeeze the slurry with a belt press, collect 55L of juice, and remove waste residue. After the juice is coarsely filtered with a 300-mesh filter cloth, it is centrifuged at a high speed at a speed of 5000 rpm to remove waste residue. Use 5% NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 12, control the temperature at 60°C and concentrate under reduced pressure while performing saponification to obtain 12L of concentrated saponified solution. The pH of the saponified solution was adjusted to 3 with hydrochloric acid, 400ml of 10% CuSO4 solution was added, and the temperature was controlled at 60°C for 1.5h. After filtration under reduced pressure, the precipitate was washed three times with deionized water at a temperature of 50°C, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com