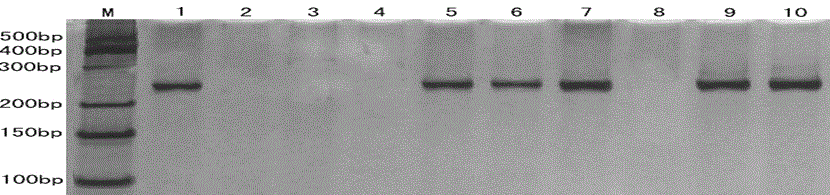
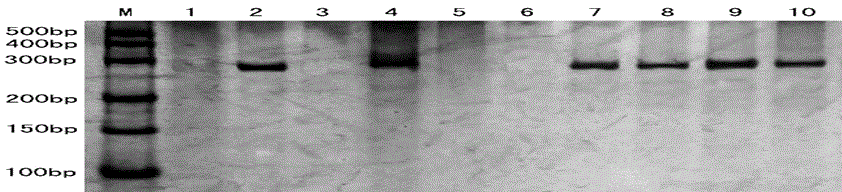
Functional molecular markers of related genes of sweetness and sourness characters of muskmelon and application of markers
A molecular marker and functional technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of research and reporting of functional molecular markers of genes related to sweet and sour traits of melon, so as to improve selection accuracy, high efficiency, and shorten breeding cycle Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1: Acquisition of functional molecular markers for genes related to sweet and sour taste traits of melon
[0063] Obtaining functional molecular markers of genes related to sweet and sour taste traits of melons includes the following steps:
[0064] (1) The high-sugar melon inbred line "Shouxing" was used as the female parent and the melon inbred line "Sour Melon" was used as the male parent to obtain the hybrid F 1 Namely "Flavor No. 4"; by Hybrid F 1 Self-pollination to obtain F 2 generation group, the parents, F 1 and each F 2 The sweet and sour taste of a single plant fruit was identified by instrumental measurement combined with tasting, and four types were obtained: only sour but not sweet, only sweet but not sour, both sour and sweet, and neither sour nor sweet.
[0065](2) Extract the genomic DNA of each material in (1) by CTAB method, 50 individual plants for 5 male parents, 5 female parents, only sour but not sweet, only sweet but not sour, neith...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Super-BSA based on simplified genome sequencing (SLAF-Seq)
[0069] (1) Extract 5 male parents, 5 female parents, F 2 Genomic DNA from each individual plant of 50 individual plants with only sweet but not sour, only sour but not sweet, and neither sour nor sweet, were mixed in equal amounts to form 5 mixed pools.
[0070] (2) SLAF -seq library construction and sequencing.
[0071] The first is to simplify the design and genomic DNA digestion: use the enzyme digestion prediction software to analyze the GC content, repeat sequence and gene characteristics of the five genomic DNA pools in step (1), and use XhoI+ MseI endonuclease to digest the mixed genomic DNA. Cut the DNA into 450-500bp fragments; the enzyme digestion system is 500ng of genomic DNA, 41L of buffer from New England Biolabs, 0.12L each of XhoI and MseI, supplemented with ddH 2 From 0 to 50 L, mix the reagents evenly after preparation, and incubate at 37°C for 15 hours, and purify with a kit...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: Mining of genes related to sweetness and sourness traits of melon
[0081] (1) Through instrumental measurement of fruit flavor combined with tasting identification, the female parent is only sweet but not sour, the male parent is only sour but not sweet, F 1 For both sour and sweet, F 2 In the population, there were 130 plants that were sweet but not sour, 77 plants that were only sour but not sweet, 60 plants that were neither sour nor sweet, and 233 plants that were both sour and sweet. Among them, sweet:not sweet=2.65:1, sour:not sour=1.63: 1. Combining parental traits and F 1 Traits and F 2 The segregation ratio of traits, sweetness and sourness are both dominant traits, sweetness is biased towards quality traits, sourness is biased towards quantitative traits, and a cross model with AAbbxaaBB as the parent is designed.
[0082] (2) Use the ratio correlation method to locate the sweetness and sourness traits. Select the pure sum mark with a / b>3 or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com