Light-emitting diode chip and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for light-emitting diodes and a manufacturing method, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as limited current expansion, reduced total reflection of light, and inability to emit outward, so as to improve luminous efficiency and brightness, and improve expansion. , the effect of improving brightness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A method for manufacturing a light-emitting diode chip, the manufacturing steps comprising:
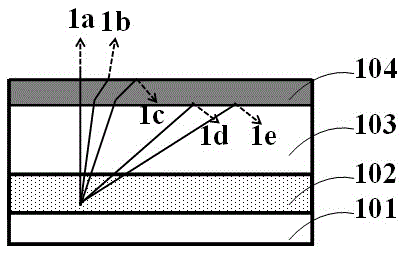
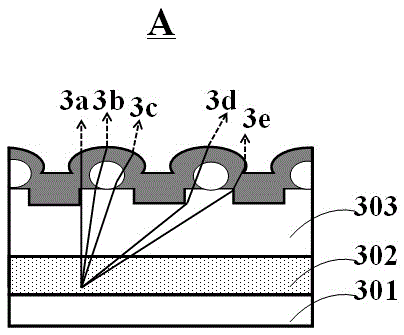
[0042] The first step: if image 3 As shown, a substrate 300 is provided, and the substrate can be an epitaxial substrate, a thermally conductive substrate, a conductive substrate or an insulating substrate. In this embodiment, sapphire (Al 2 o 3 ) as an epitaxial substrate. In other embodiments, the substrate can be a silicon carbide (SiC) substrate, a silicon (Si) substrate, a gallium nitride (GaN) substrate, a gallium arsenide (GaAs) substrate, a gallium phosphide (GaP ) substrates, aluminum nitride (AlN) substrates, copper (Cu) substrates, etc.
[0043] The second step: if Figure 4As shown, metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) is used to form an epitaxial layer on the substrate, and the epitaxial layer stacks a first semiconductor layer 301, a light emitting layer 302 and a second semiconductor layer 303 sequentially from bottom to top, wherein the first semi...
Embodiment 2
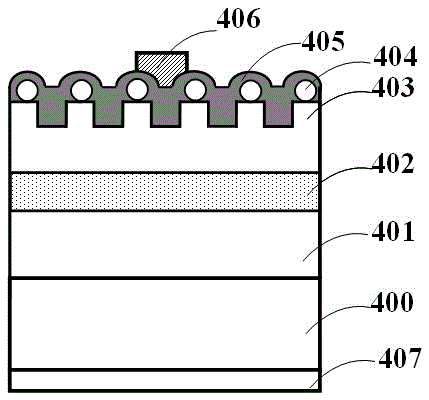
[0051] Such as Figure 11 As shown, different from Embodiment 1, this embodiment discloses a light-emitting diode chip with a vertical structure. In this embodiment, a silicon (Si) substrate is used as the conductive substrate 400, and the N electrode 407 is formed on the back surface of the conductive substrate 400, forming a vertical LED device structure. In addition, the patterned first current spreading layer 404 uses a ZnO nanowire structure, and the cross-sectional diameter of the nanowire is 10-500 nm, preferably 200 nm in this embodiment; the material of the second current spreading layer 405 is a ZnO continuous film, that is Keeping the same refractive index as the patterned first current spreading layer 404, the light path diagram of this embodiment is the same as Figure 10 Similar, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 2 is that this embodiment uses a copper (Cu) substrate as the conductive substrate 500, and the patterned first current spreading layer 504 uses an ITO nano-column structure. The height of the nano-column is 10-1000 nm, and the width It is 10~10000nm, and in the present embodiment, the height of the preferred nanocolumn is 500nm, and the width is 200nm; The refractive index of the expansion layer, so that the relationship of the refractive index of each material layer is: epitaxial layer > first current spreading layer > second current spreading layer > air, which can further reduce the occurrence probability of total reflection, thereby increasing the light emitting layer. Extraction probability, improve chip brightness and luminous efficiency.
[0054] It should be pointed out that the above-mentioned second current spreading layer 505 material can also be selected from indium tin oxide (ITO), by adjusting I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com