Core-shell structure electroactive composite fibers and preparation method of tissue engineering scaffold
A tissue engineering scaffold and composite fiber technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of serious decline, difficulty in stabilizing current, phase separation, etc., and achieve the effects of stable product quality, simple and feasible preparation method, and simple steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
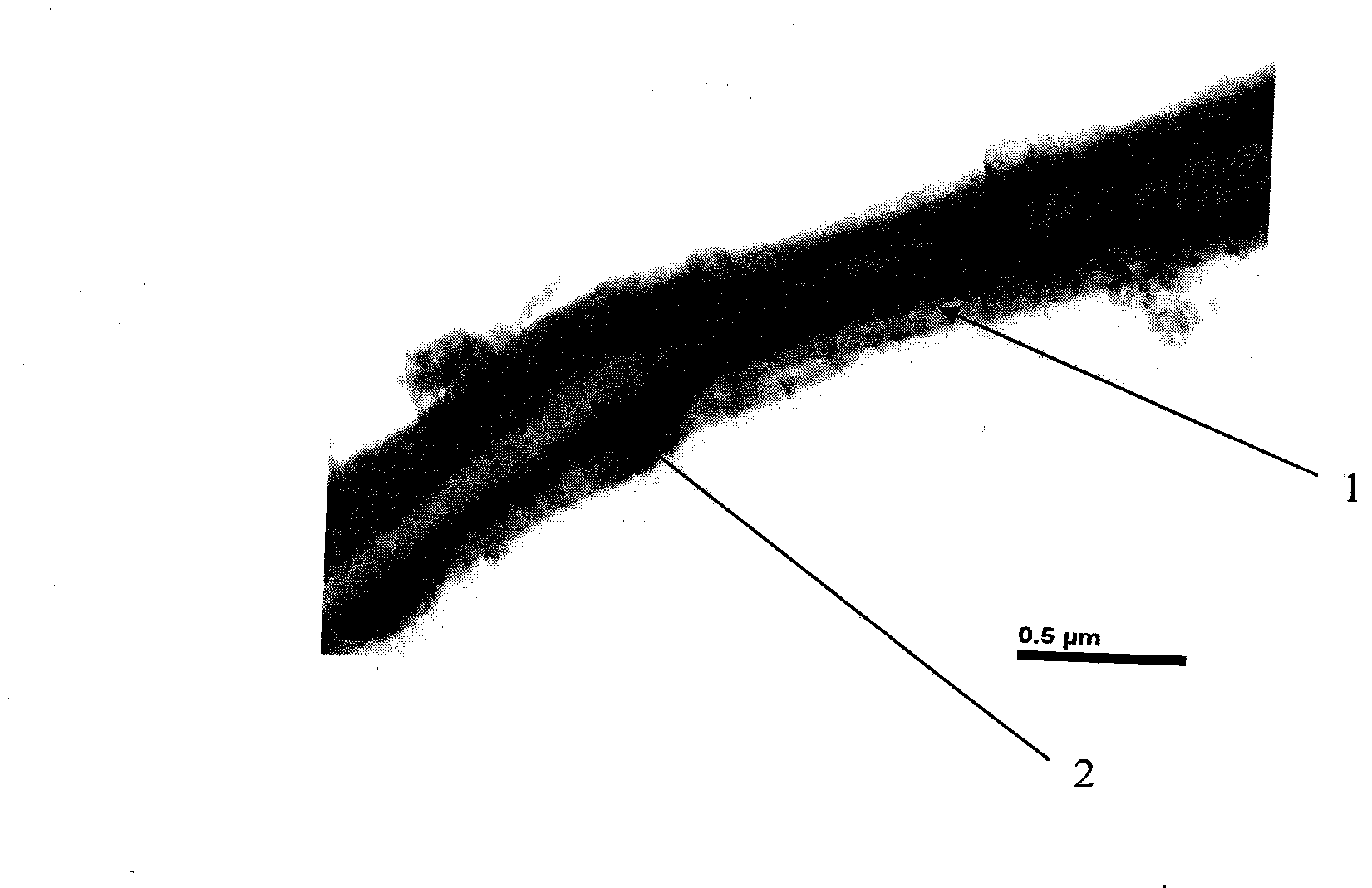
[0026] A method for preparing electroactive composite micro / nanofibers with a core-shell structure and a scaffold thereof with a spider silk protein as a shell and a polypyrrole as a core, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) Preparation of nuclear spray liquid
[0028] Dissolve dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid-doped polypyrrole in dichloromethane to prepare a nuclear spray solution with a concentration of 10 wt%.
[0029] (2) Preparation of shell spinning solution
[0030] Dissolve natural spider silk (collected outdoors) in hexafluoroisopropanol to prepare a shell spinning solution with a concentration of 12 wt%.
[0031] (3) Using the spider silk protein spinning solution as the shell and the polypyrrole spinning solution as the core, a coaxial co-spinning device (NEU-COAXIAL, Japan Kado Corporation) was used to combine the el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com