Papermaking technology and paper
A papermaking process and papermaking filler technology, which is applied in paper, papermaking, textiles and papermaking, etc., and can solve the problems of poor binding force, small improvement, and inability to improve filler retention rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
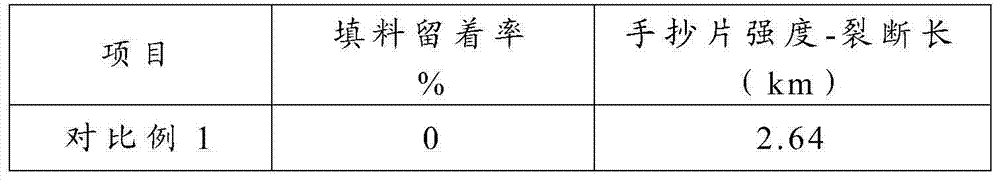
[0028] Make cationic starch into 5% aqueous suspension, mineral filler into 15% aqueous suspension, glutaraldehyde into 12.5% aqueous solution, wherein the dry-dry ratio of cationic starch to mineral filler is 1:500, The mass ratio of glutaraldehyde to cationic starch is 0.2:100, then mix the three together, stir evenly, adjust the pH to 4.0, raise the temperature of the mixture to 80°C, and make the cationic starch undergo cross-linking and gelatinization reactions. Finally, a cationic starch-filler composite system is formed.
[0029] The mechanism of crosslinking reaction is that under the catalysis of acid, the aldehyde group of glutaraldehyde can react with the hydroxyl group of cationic starch to form hemiacetal, and the unstable hemiacetal will continue to react with the hydroxyl group on another cationic starch molecule to form stable The product acetal, glutaraldehyde is equivalent to playing the role of "bridge" between cationic starch molecules, so that the cross-...
Embodiment 2
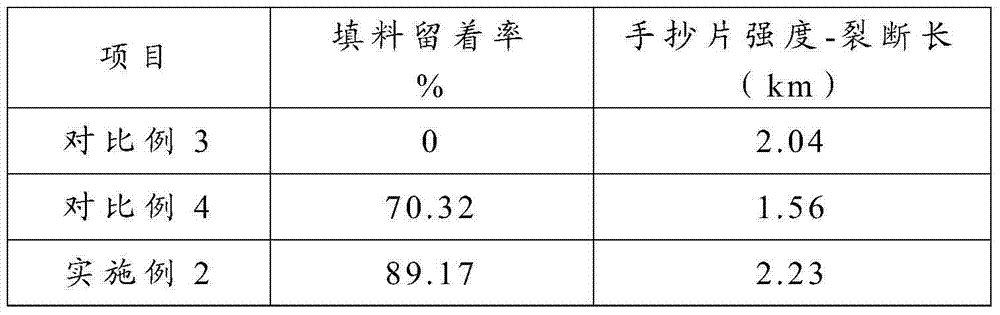
[0039] Make cationic starch into 2% water suspension (temperature is 35 degrees); calcium carbonate into 10% water suspension (temperature is 90 degrees), and the dry-dry ratio of cationic starch to calcium carbonate is 1:250 , sodium trimetaphosphate is formulated into a 5% aqueous solution, the mass ratio of sodium trimetaphosphate to cationic starch is 2:100; then the three are mixed together, stirred evenly to adjust the pH to 10.5, so that the cationic starch can be cross-linked and pasted Cationic starch-filler composite system is finally formed. (Note: Since the single suspension has a relatively high temperature, there is no need for an additional increase after mixing to ensure that the three have a higher temperature after mixing, and the temperature range is usually between 50 degrees and 90 degrees.)
[0040] Mix the cationic starch-filler composite system with the wood pulp fiber after pulping treatment, wherein the absolute dry mass ratio of the filler contained ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com