Recombinant human bivalent diabody against rabies virus and uses thereof
A rabies virus and double-chain antibody technology, applied in the field of immunology, can solve complex biological processes, expensive and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Human X mouse heterohybridoma producing human anti-rabies virus monoclonal antibody
[0065] The rabies virus strain used in the present invention is a Pasteur virus (PV) strain described in the literature.
[0066] Human X mouse heterohybridomas were generated by fusing human immune B cells with human X mouse heteromyeloma (Champion et al. (2000); The development of monoclonal human rabies virus-neutralizing antibodies as a substitute for pooled human immune globulin in the prophylactic treatment of rabies virus exposure, Journal of Immunological Methods 235(1-2):81-90). Heterohybridomas were developed by fusing naive peripheral blood B cells with the heteromyeloma cell line K6H6 / B5 (Carroll et al. (1986); Mouse x human heterohybridomas as fusion partners with human B cell tumors. Journal of Immunological Methods 89( 1):61-72)). The K6H6 / B5 cell line was chosen because it has been successfully used to clone human antiviral antibodies (Siemoneit et al. (1994). Isolati...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Screening of 8 novel human IgG antibody (huMab) clones
[0071] Clones were screened for specific human Mab secretion by indirect ELISA using purified inactivated rabies virus antigen (PV strain).
[0072] Antibody purification
[0073] Human monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) secreted by heterohybridoma clones have been affinity purified on protein A sepharose columns. Check the purified antibody on a gel ( Figure 7 ). Lane 1 shows BSA as a standard with a molecular weight of 66Kda. Lanes 2-5 show purified R16E5 human monoclonal antibody with a molecular weight of 160 KDa. The main criterion for selecting 4 of the 8 clones was the rabies virus neutralization profile as determined by RFFIT.
[0074] Assay to confirm production of human anti-rabies virus monoclonal antibody by heterohybridoma cells
[0075] Several assays such as indirect ELISA, cellular ELISA, RFFIT and MNT were performed to confirm the rabies virus specificity of huMabs secreted by heterohybridoma...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Construction of diabody fragments
[0086] RNA extraction and amplification of antibody variable domain sequences
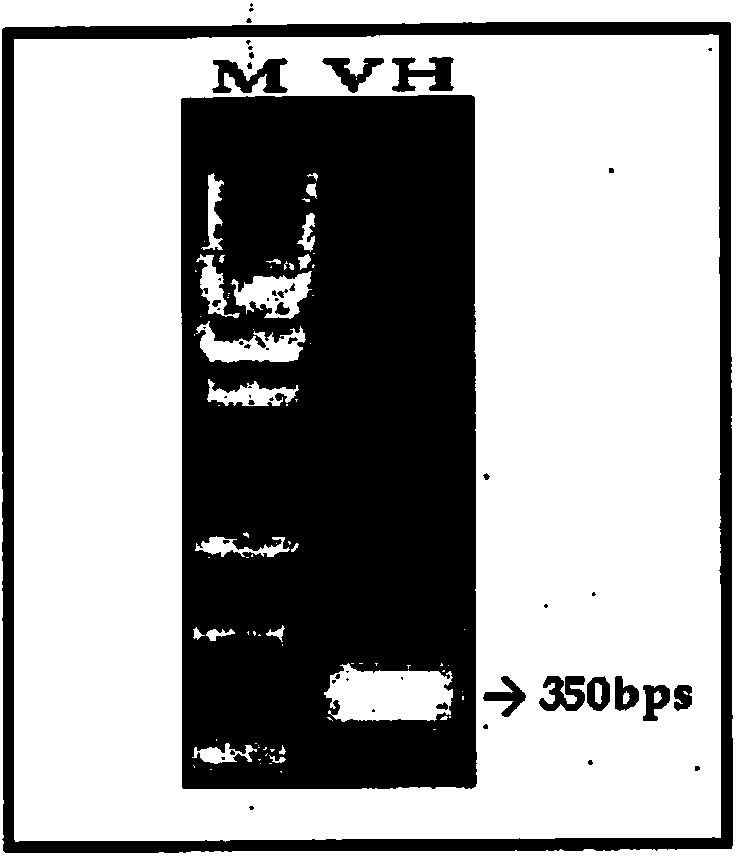
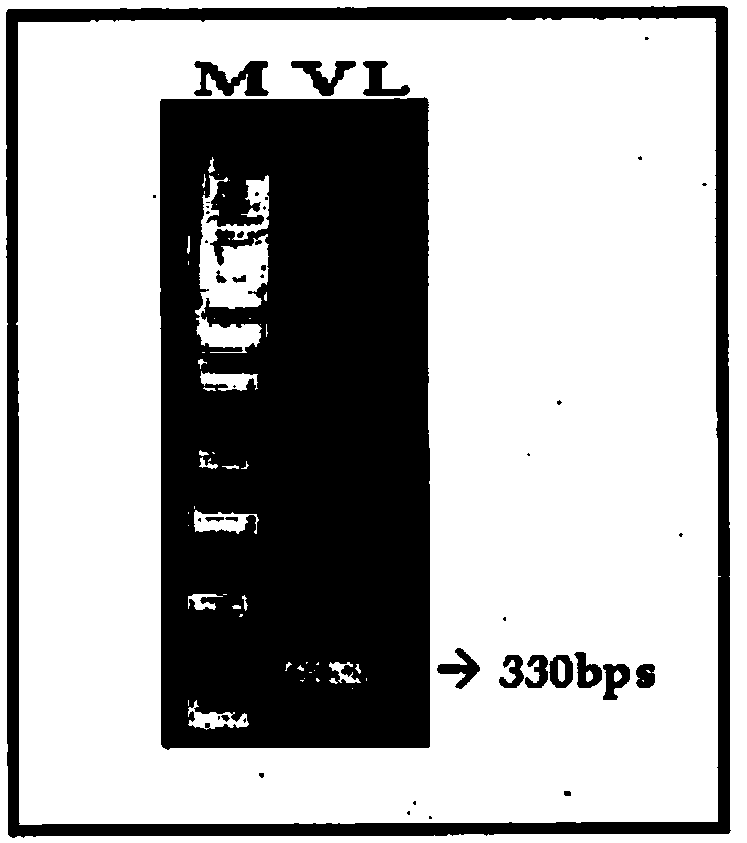
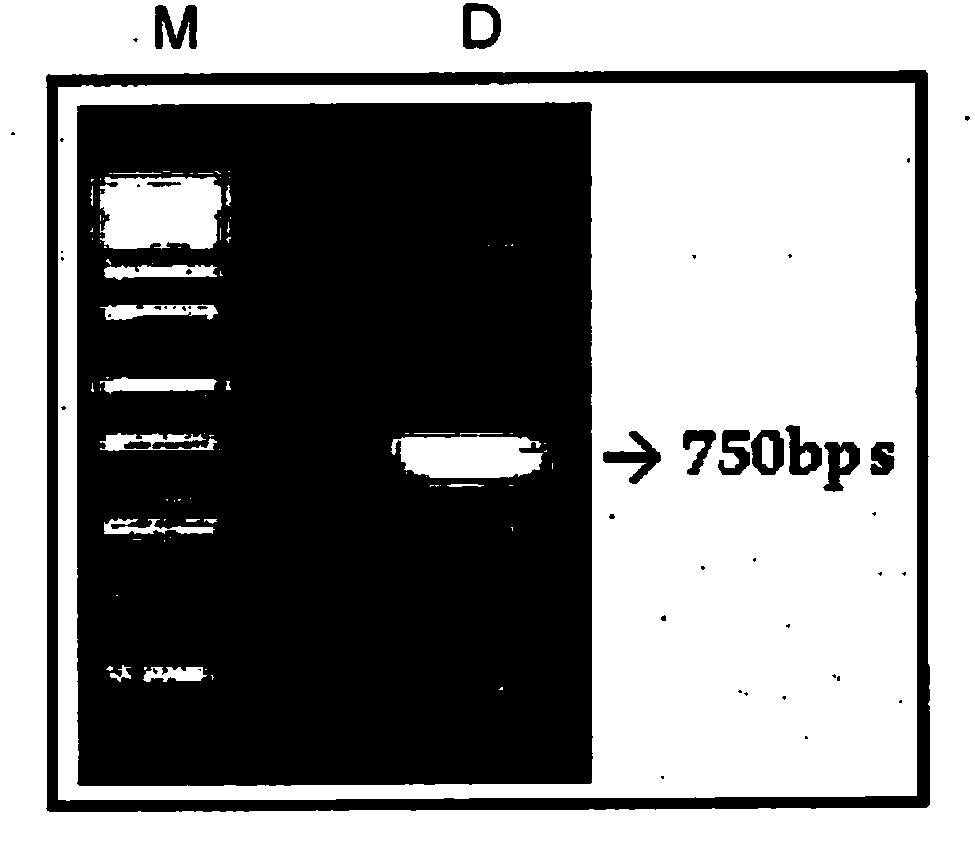
[0087] Total RNA was isolated from rabies resistant heterohybridoma (R16E5) and DNA was synthesized by RT-PCR. The nucleotide sequence of the amplified c-DNA is shown in SEQ ID NO:25. The cDNA amplified by RT-PCR was used as a template to amplify variable domains of antibodies using universal primers having the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:20. The amplified variable domains were assembled by splicing using overlap extension PCR to form diabodies and cloned into TOPO vectors for sequence verification ( Figure 1A , Figure 1B with Figure 1C ).
[0088] Primers used to amplify the variable domains of the heavy and light chains were as follows:
[0089] Forward primer for human variable heavy chain
[0090] HuVH1a: SEQ ID NO: 1
[0091] GGCGGCGGCGGCTCCGGTGGTGGTCAGGTGCAGCTGGTGCAGTCTGG
[0092] HuVH2a:SEQ ID NO:2
[0093...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com