Synthetic method of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide
A technology of acetylpyridine adenine and adenine nucleoside, which is applied in the field of synthesis of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide, can solve the problems of high cost and product enzymatic hydrolysis, and achieve low total cost and high product yield , cheap effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 15-T
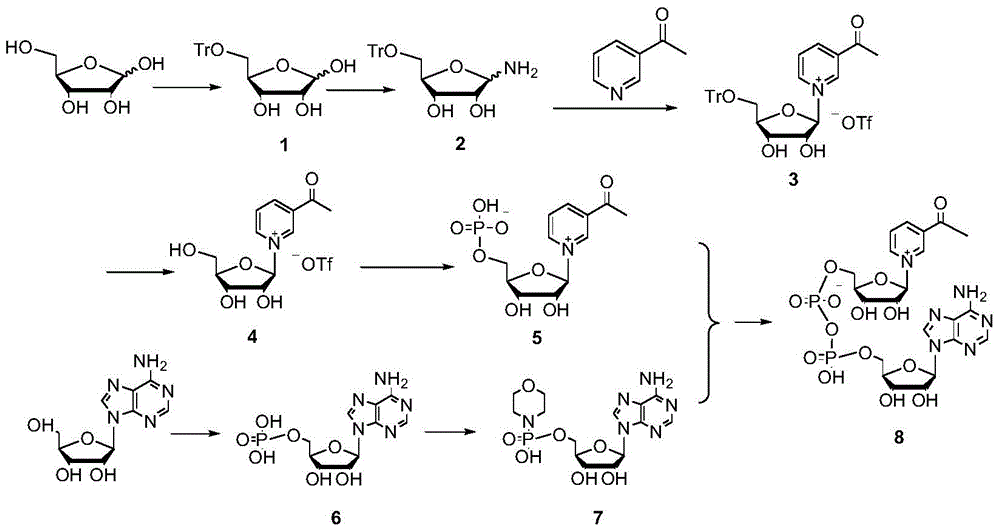
[0038] Example 15-Synthesis of Tr-D-Ribose (Compound 1).
[0039] Add 15.0g of D-ribose to a 250ml three-necked flask, add 100ml of anhydrous pyridine, and start stirring. Add 27.8 g of triphenylchloromethane. Heat to 75°C, stir and react for 4 hours. Most of the pyridine was distilled off under reduced pressure, then stripped with toluene three times, and dried to obtain a brown syrupy product. Then dissolve with 200ml chloroform, and wash three times with ice water and saturated brine in turn. The organic phase was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, spin-dried, and recrystallized from ethanol to obtain 39.4 g of product. It is 5-Tr-D-ribose.
[0040] LC-MS: [M+Na] + =415. HNMR (MeOH-d4): δ: 7.605-7.104 (m, 15H); 6.260 (d, 1H); 5.832 (d, 1H); 5.201 (d, 1H); 5.006 (d, 1H) ppm.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Synthesis of 5-Tr-1-amino-D-ribose (Compound 2).
[0042] Dissolve 39.4g 5-Tr-D-ribose in 200ml anhydrous methanol, place it in a constant temperature and low temperature water bath, and keep it at 0°C. Under stirring, dry ammonia gas was continuously introduced. After 20 hours, the detected raw material disappeared and it was almost quantitatively converted into 5-Tr-1-amino-D-ribose. 39.2 g of yellow solid is obtained, which is the product.
[0043] LC-MS: [M+H] + =392. HNMR (MeOH-d4): δ: 7.523-7.078 (m, 15H); 5.891 (d, 1H); 5.755 (d, 1H); 4.568 (d, 1H); 4.306 (d, 1H) ppm.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Synthesis of 3-acetylpyridine-5-Tr-α-D-nucleoside (compound 3).
[0045] At room temperature, add 50ml of anhydrous methanol to a 250ml three-necked flask, and add 6.0g of 3-acetylpyridine dropwise with stirring. 11.6g of trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) was slowly added dropwise. After half an hour, a methanol solution of 5-Tr-1-amino-D-ribose was added (19.6 g of 5-Tr-1-amino-D-ribose dissolved in 50 ml of methanol). After the addition is complete, stir at room temperature for 5 hours. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. Dissolve with as little volume of methanol as possible, add anhydrous ether slowly, and a solid will precipitate. Filter and dry to obtain crude product. Column chromatography eluted with dichloromethane and methanol system to obtain 9.65 g of 3-acetylpyridine-5-Tr-α-D-nucleoside.
[0046] LC-MS: [M] + =496 (after deducting trifluoromethanesulfonate). HNMR (DMSO-d6): δ: 9.472 (s, 1H); 9.387 (s, 1H); 9.165 (d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com