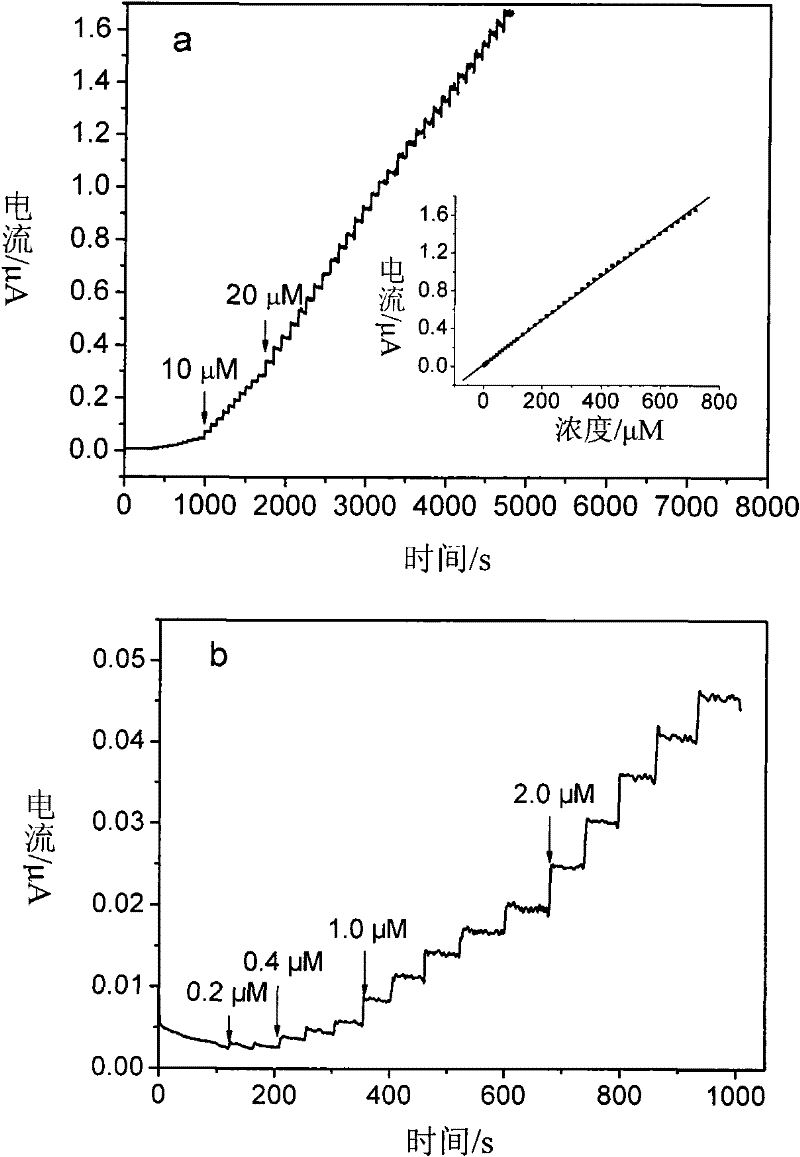
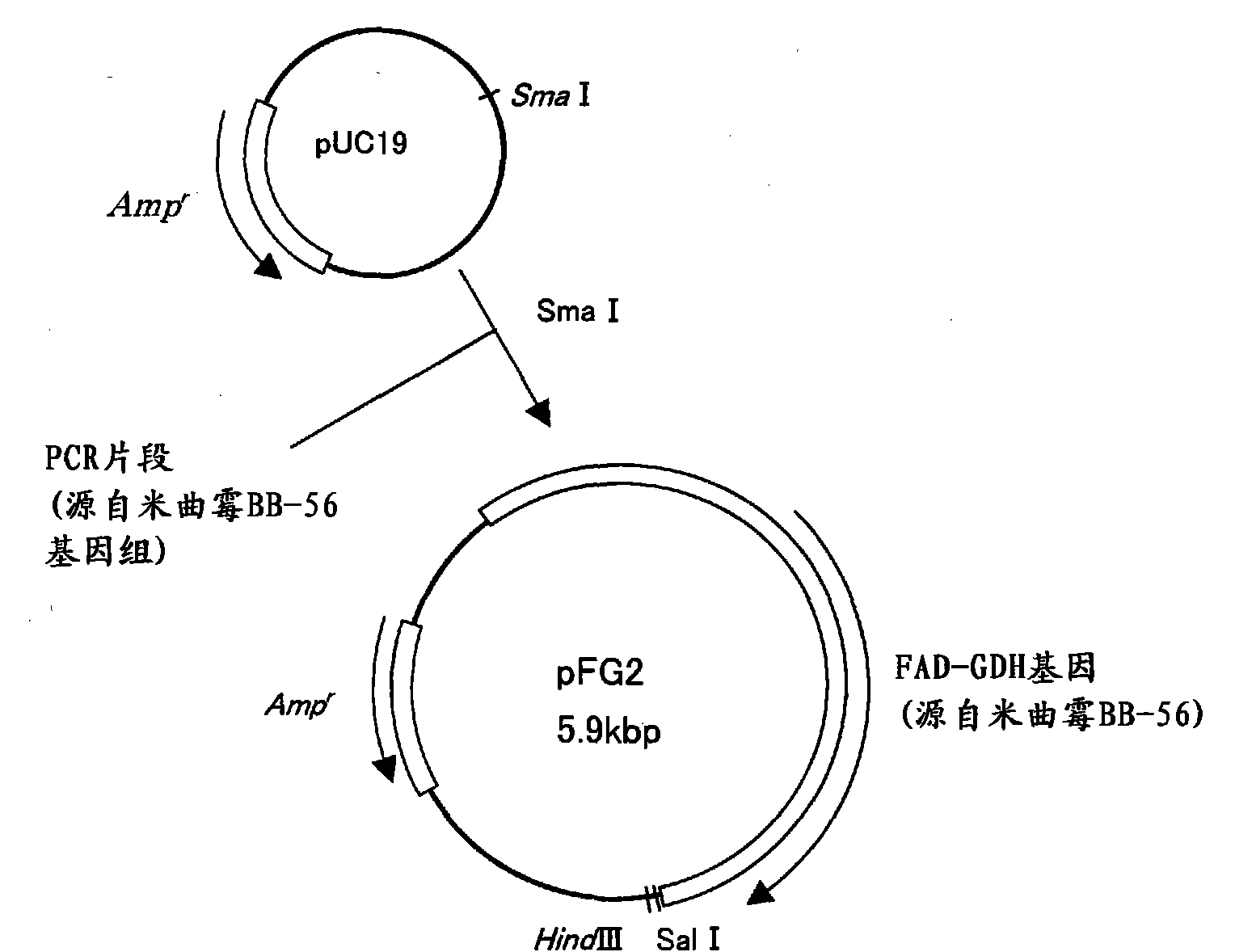
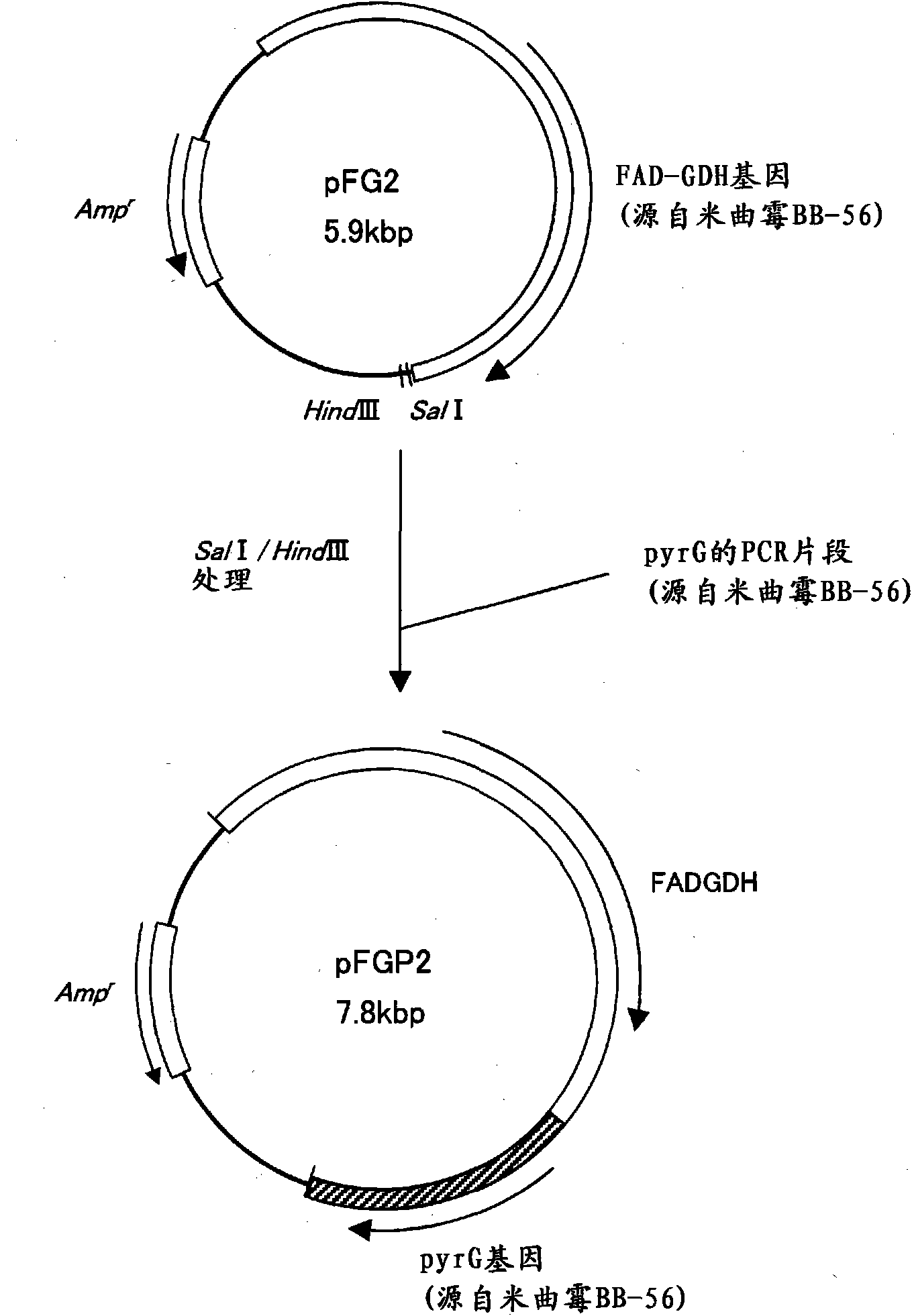
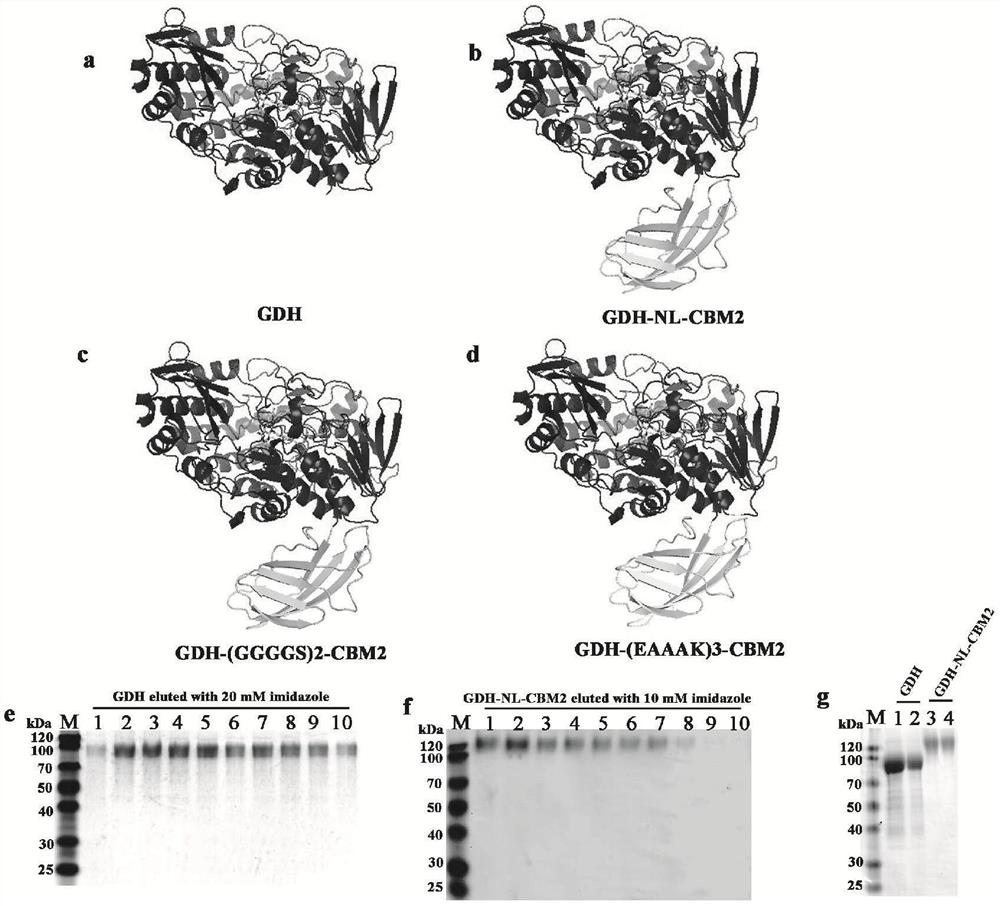
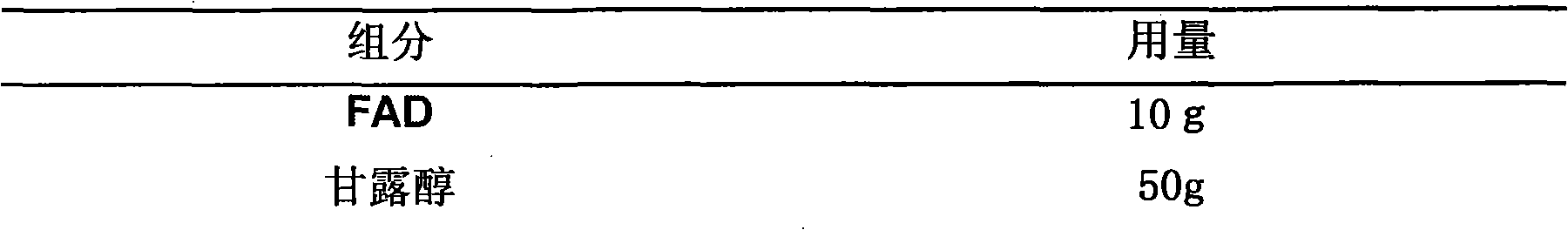Patents
Literature
53 results about "Adenine dinucleotides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
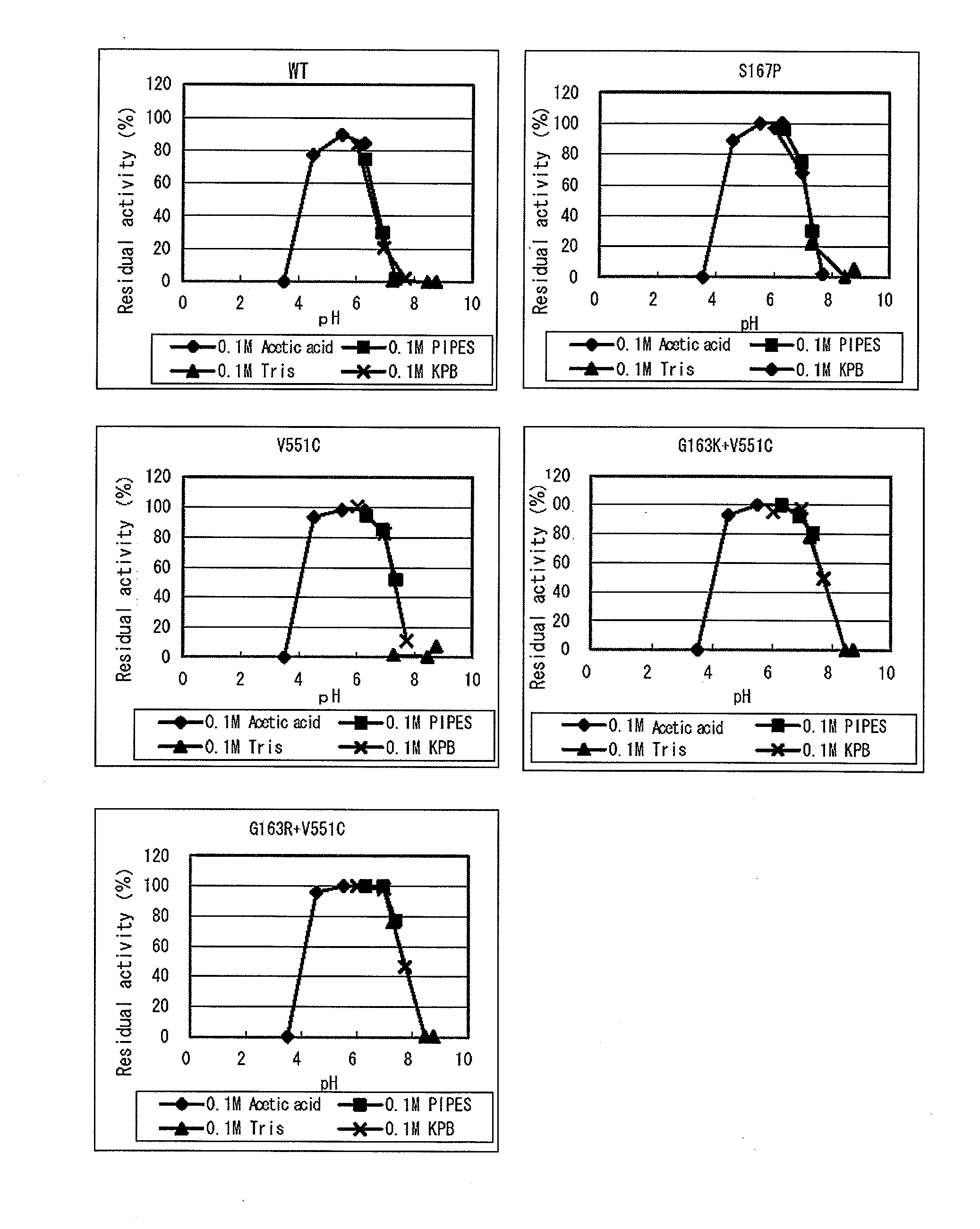
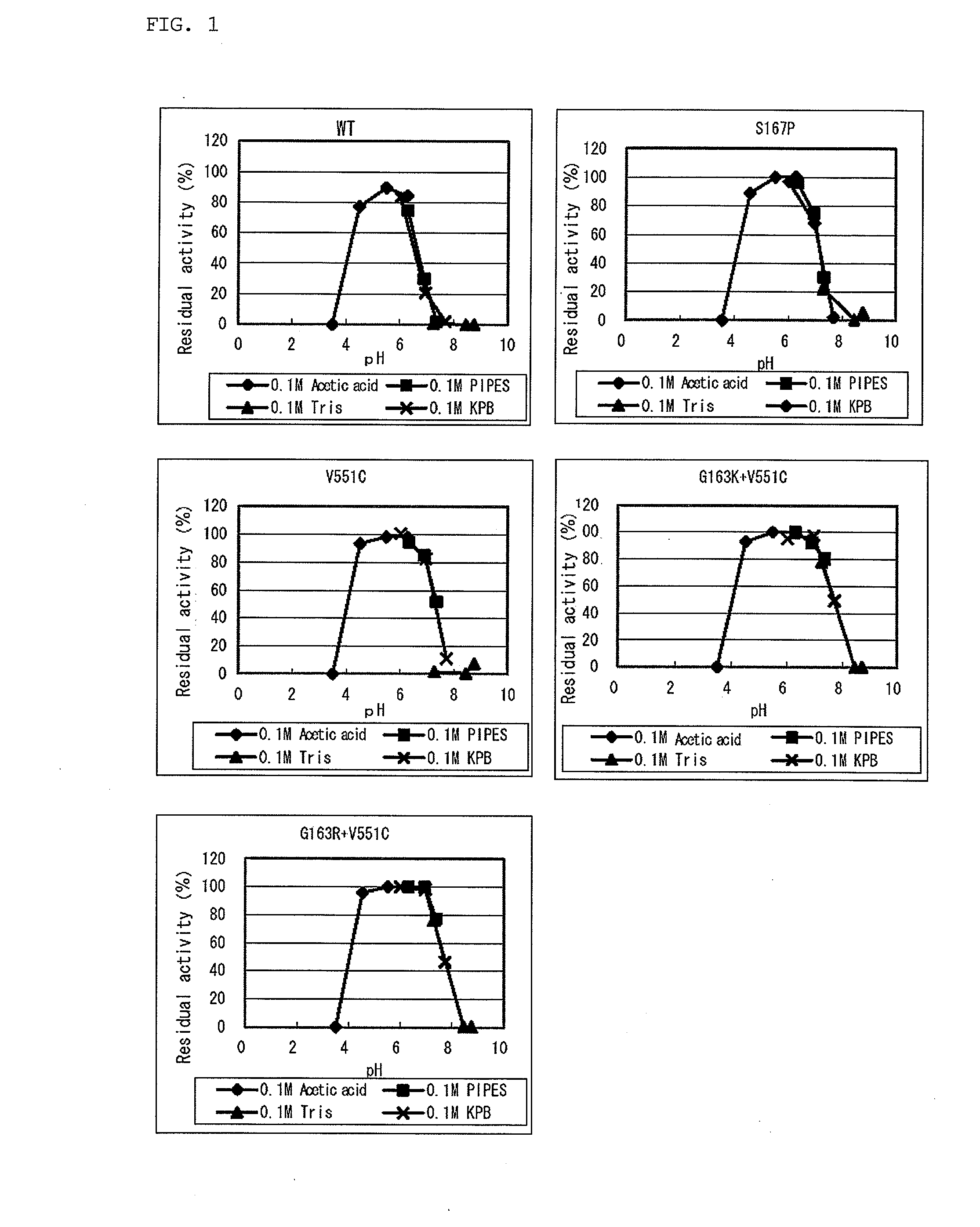
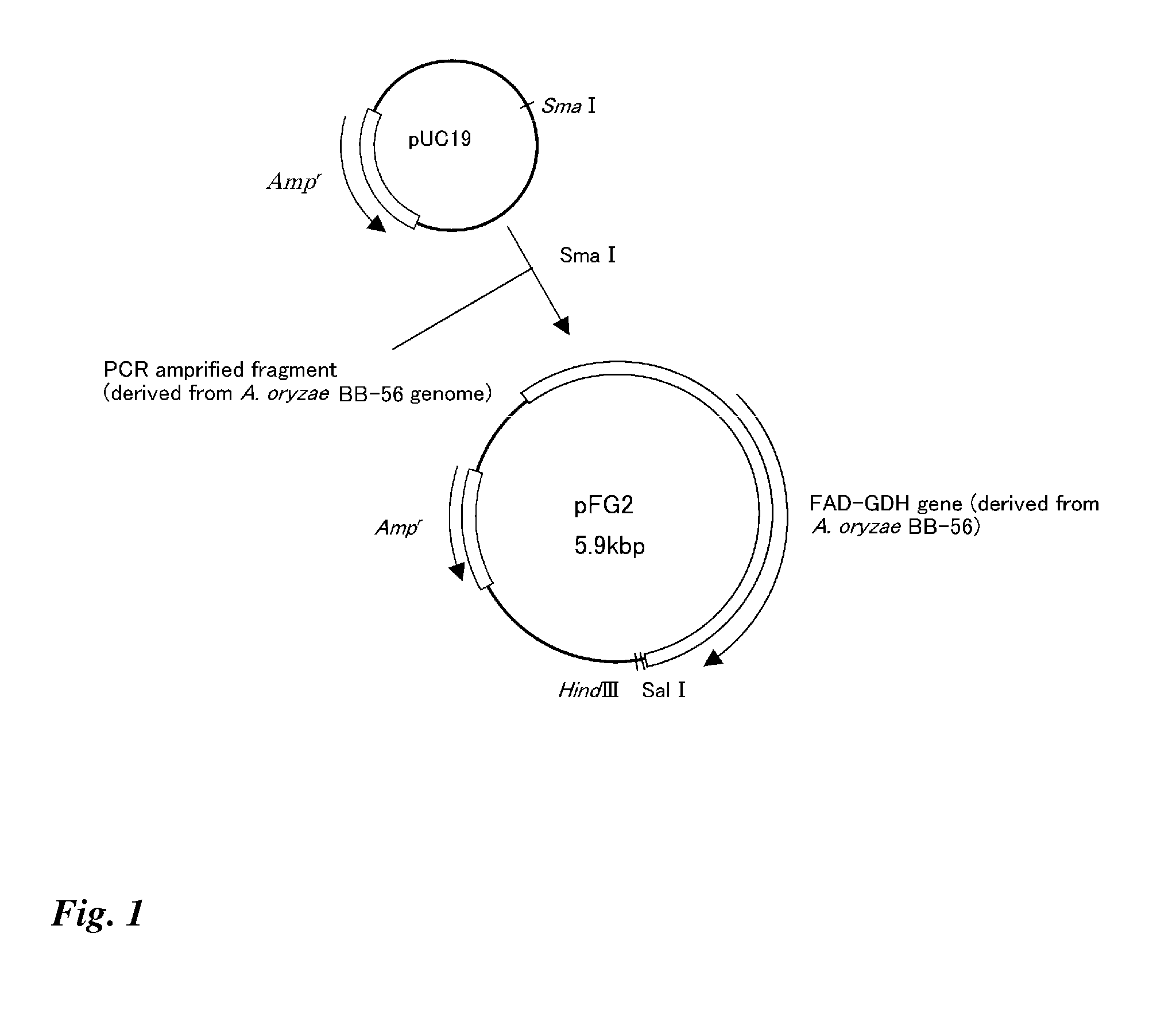
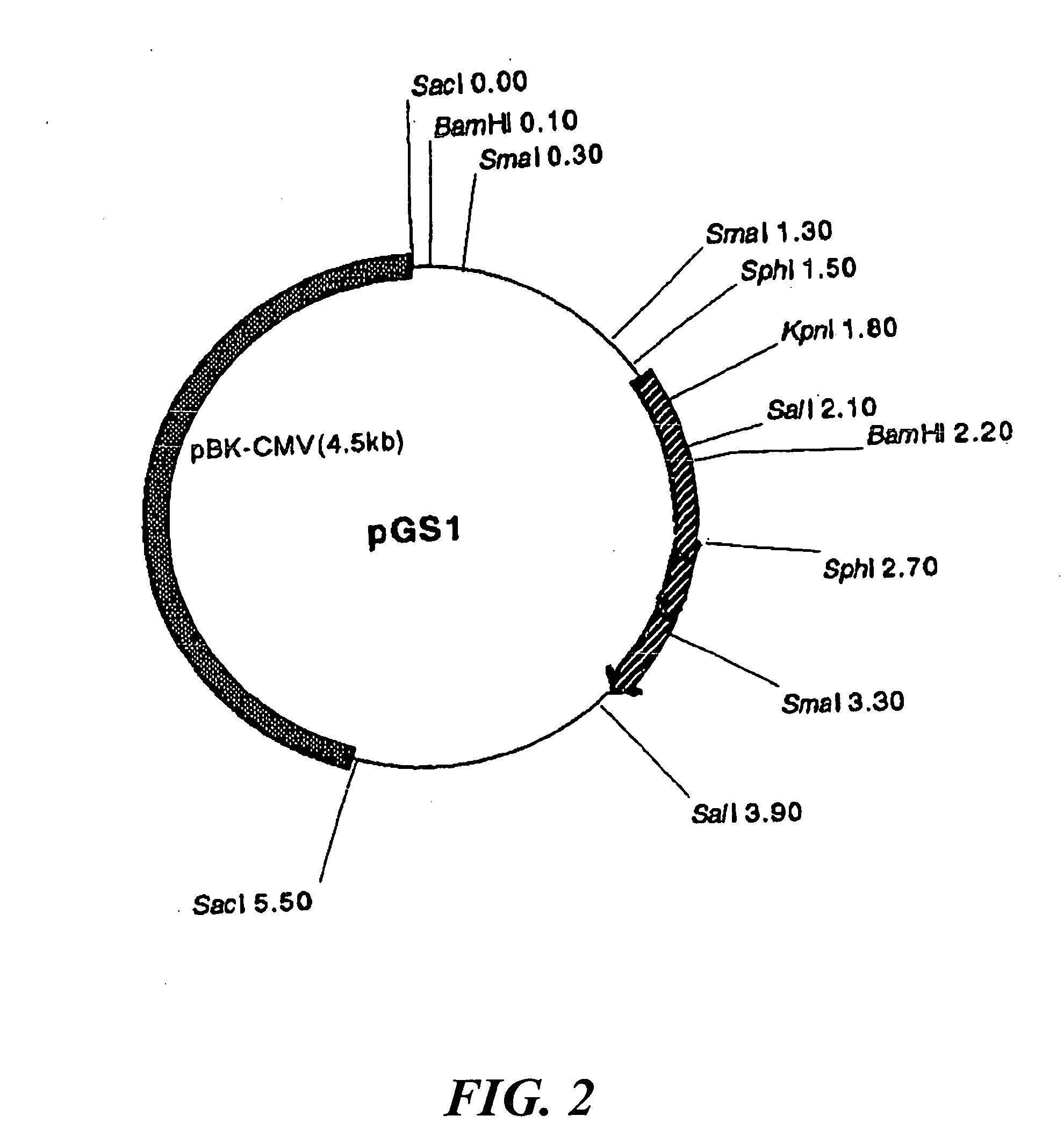
Modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20080220460A1Reduce heat-inactivationDecreasing amount of usedFungiBacteriaFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose sensors
Object: An object of the present invention is to provide a more practically advantageous enzyme usable as a reagent for measuring blood glucose than the known enzymes used as blood glucose sensors.Method for Achieving the Object: A modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase (FADGDH) with more improved heat stability than FADGDH derived from wild-type FADGDH, the modified FADGDH being derived from preferably a eukaryote, more preferably a filamentous fungus, and furthermore preferably an Aspergillus fungus, and, for example, those having a primary structure with at least one amino acid substituted, deleted, inserted or added to FADGDH having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID Nos. 2 or 46 in the sequence table.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
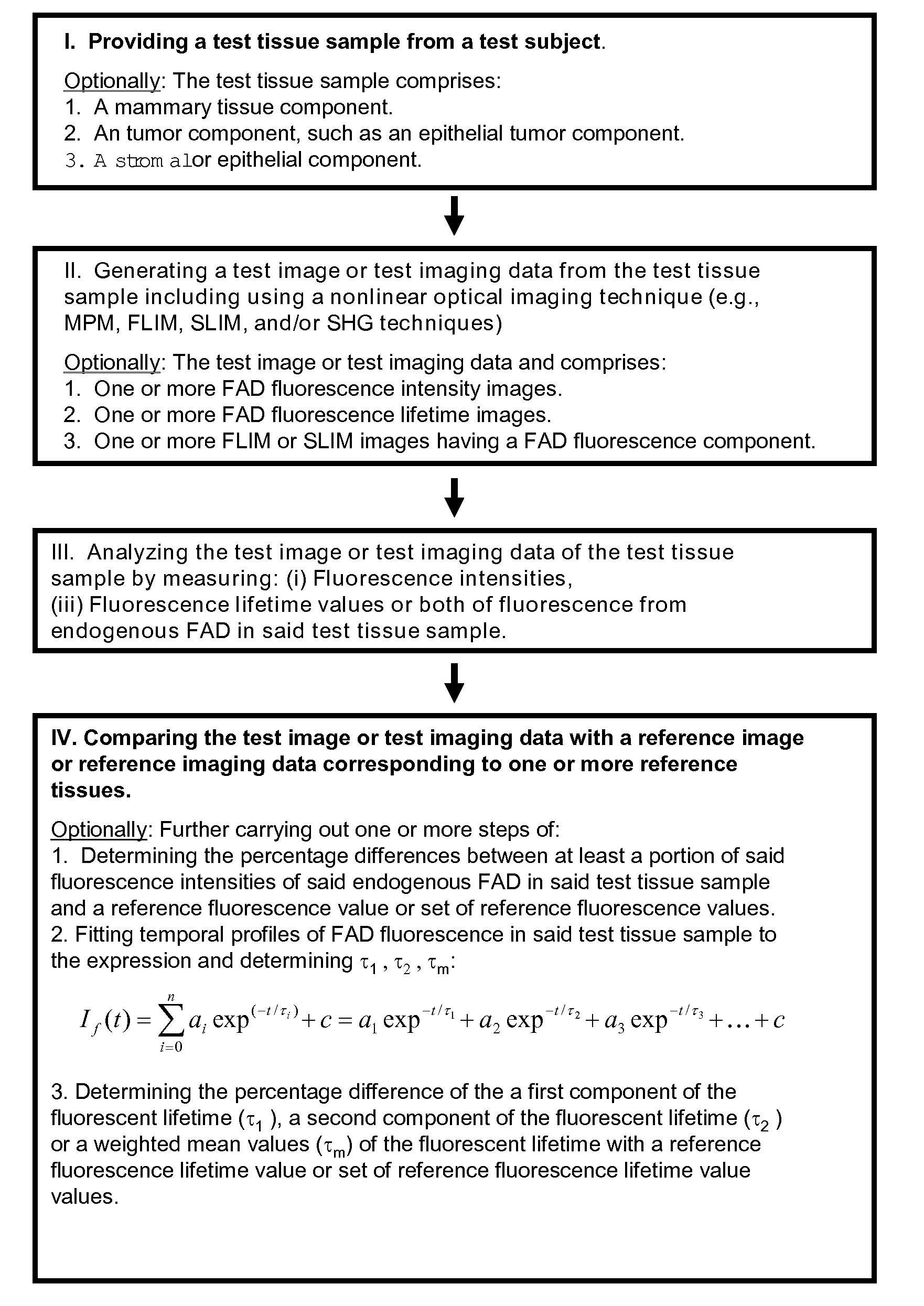
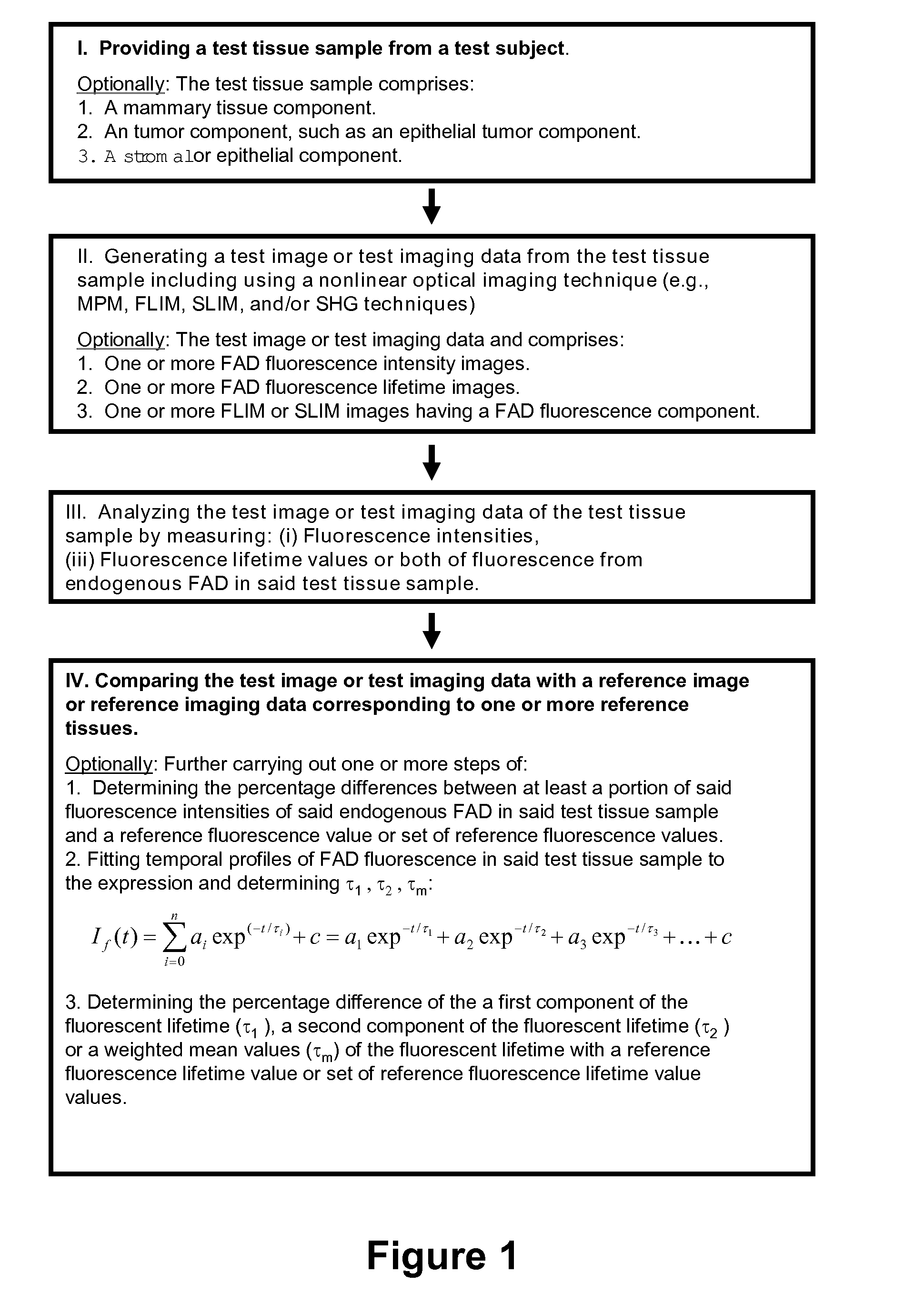
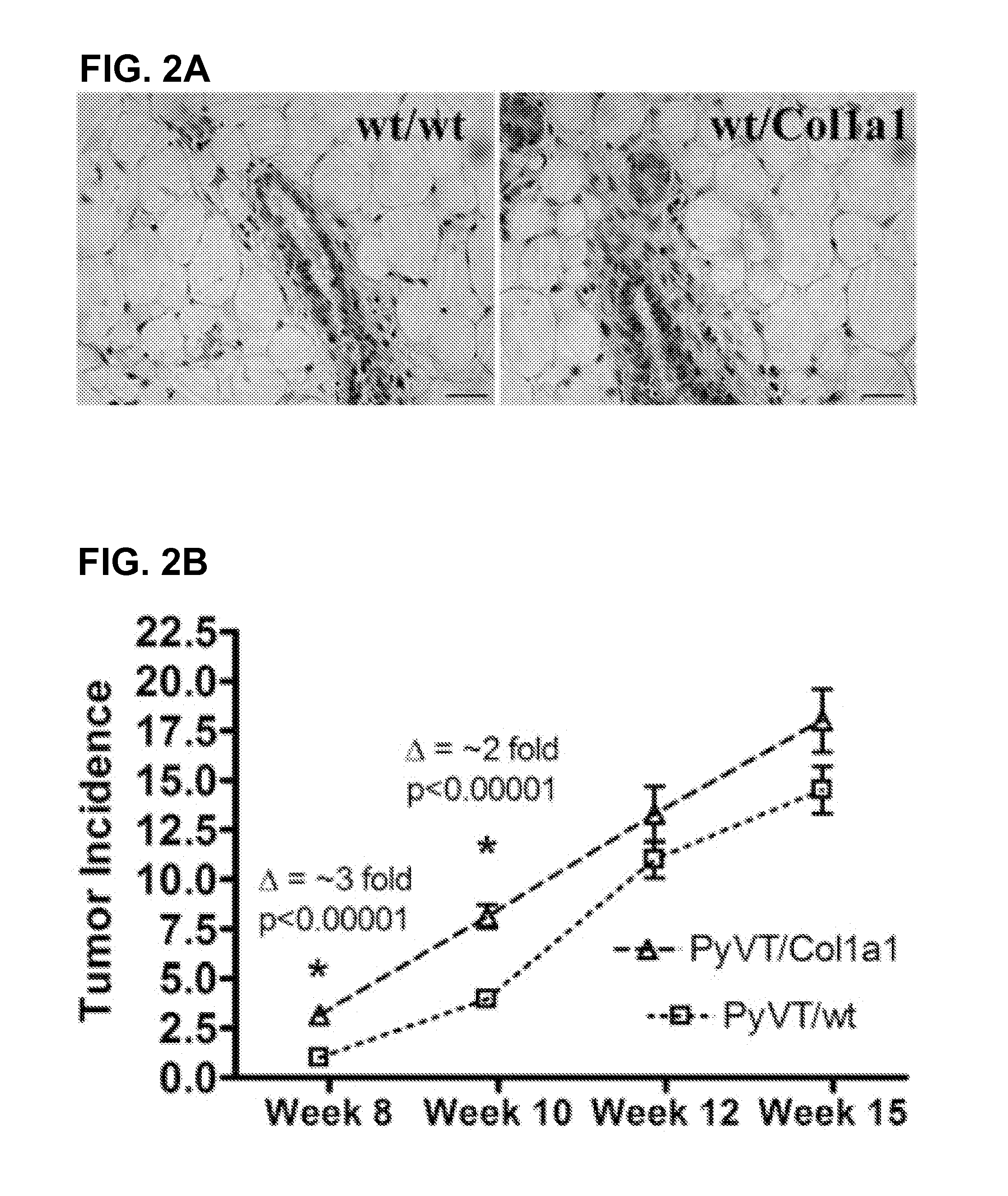
Use of Endogenous Fluorescence to Identify Invading Metastatic Breast Tumor Cells
ActiveUS20080212867A1Accurate representationEliminate needDiagnostics using lightCharacter and pattern recognitionFlavin adenine dinucleotideAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention broadly provides methods and systems for detecting, identifying, and characterizing conditions, including diseases and other disorders in human or other animal subjects, by analyzing fluorescence from endogenous flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) fluorophors present in biological materials and samples. In particular embodiments, the invention relates to conditions of the human breast including cancers such as carcinoma. Methods and systems are provided for detecting, locating, and characterizing tumors and precancerous tissue via nonlinear optical imaging techniques capable of accurately characterizing fluorescence intensities and fluorescent lifetime parameters from endogenous FAD fluorophors present in a test tissue sample.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
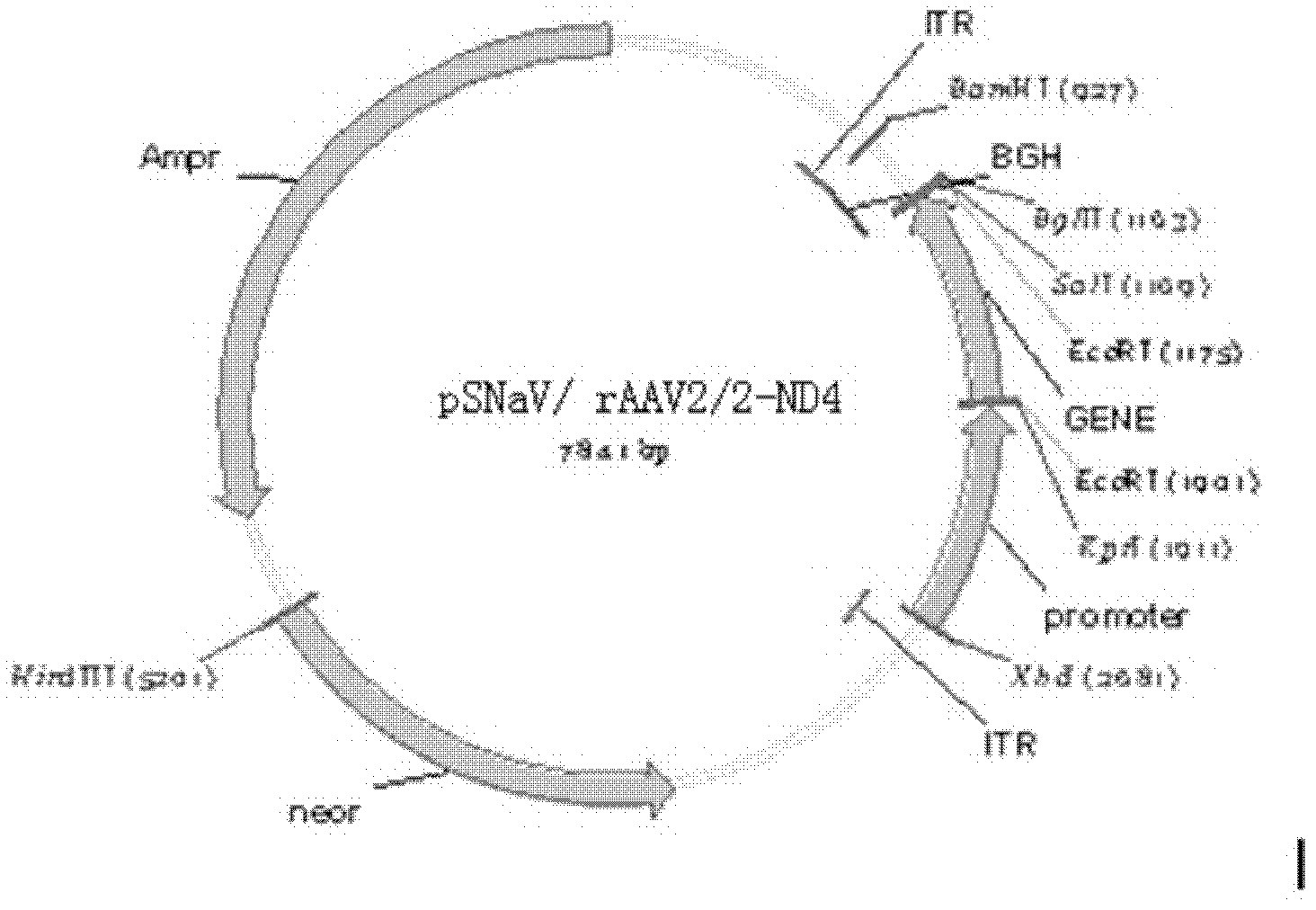
Recombinant human NADH (nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide) dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene and constructing method of expression vector thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant human NADH (nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotid) dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene and a constructing method of an expression vector thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the size of the nucleotide sequence is 2889 bp. The constructing steps of adeno-associate virus vectors are as follows: firstly constructing a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing the human NADH dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene, and then coating, infecting, purifying, concentrating and identifying the recombinant adeno-associated virus. According to the method, the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector with the recombinant human NADH dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene can be quickly and simply constructed, and is packaged to obtain the adeno-associated virus vector with complex defects. The gene can be used for gene therapy of LHON (leber's hereditary optic neuropathy).
Owner:WUHAN NEUROPHTH BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD CO
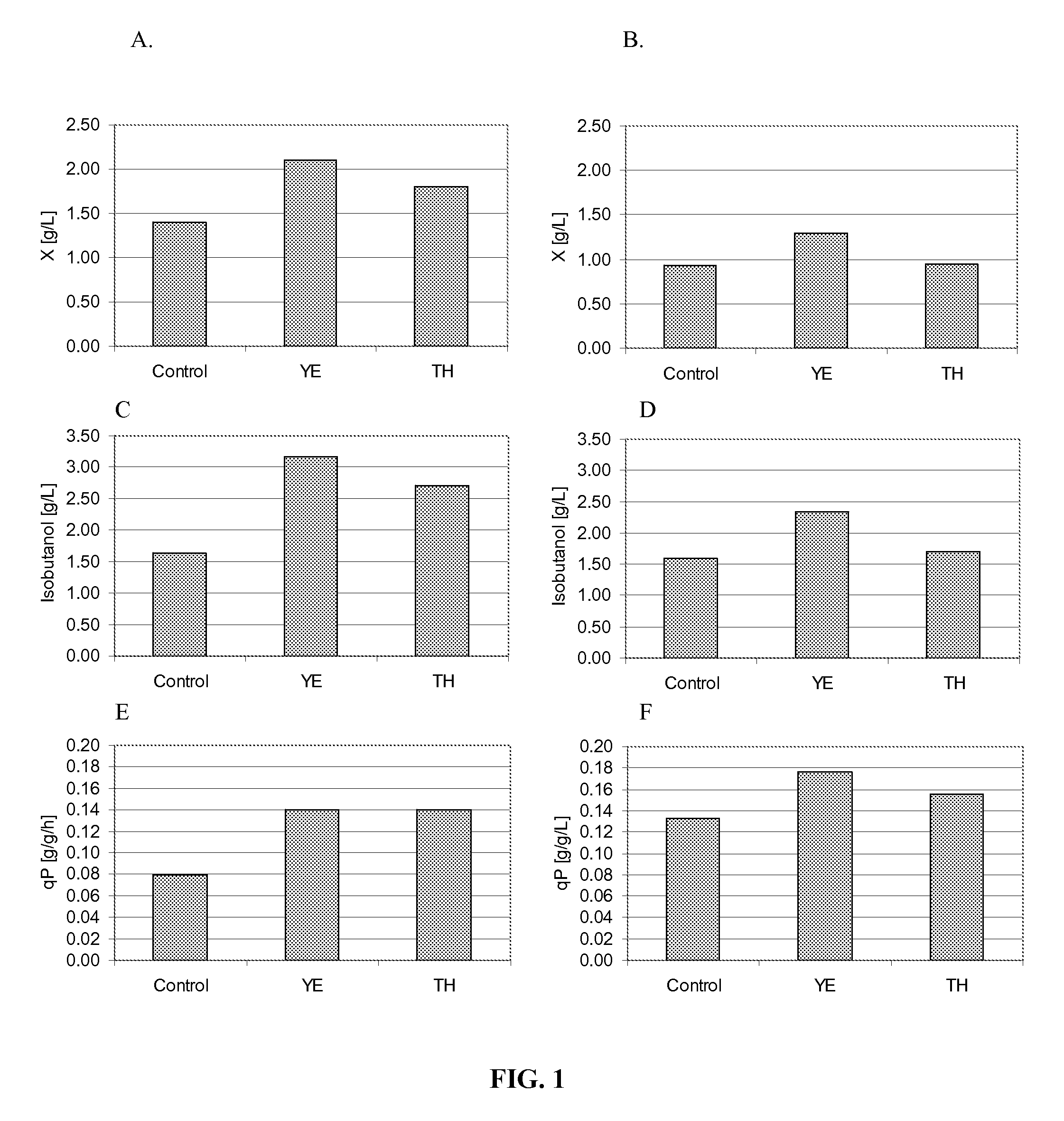
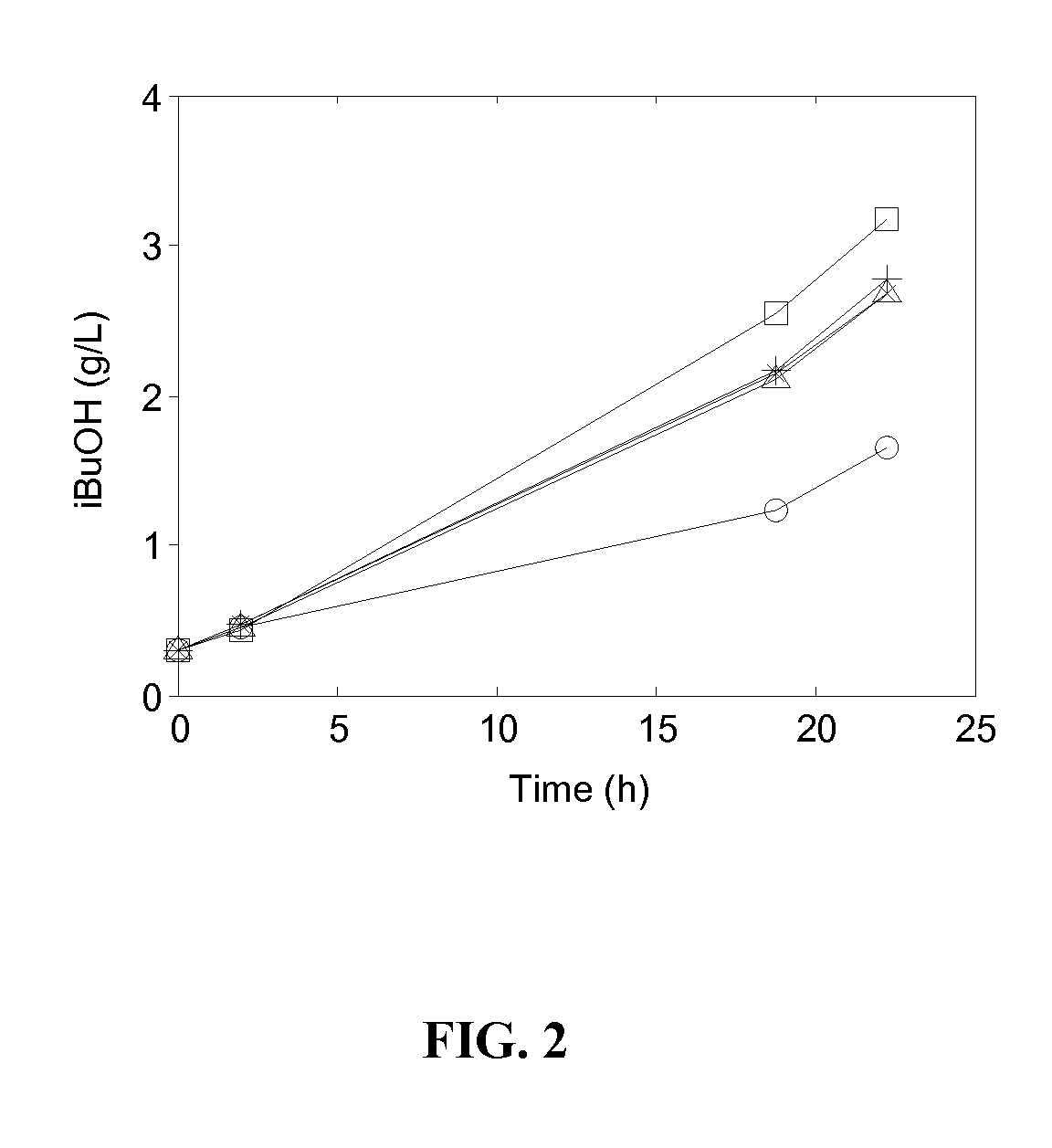
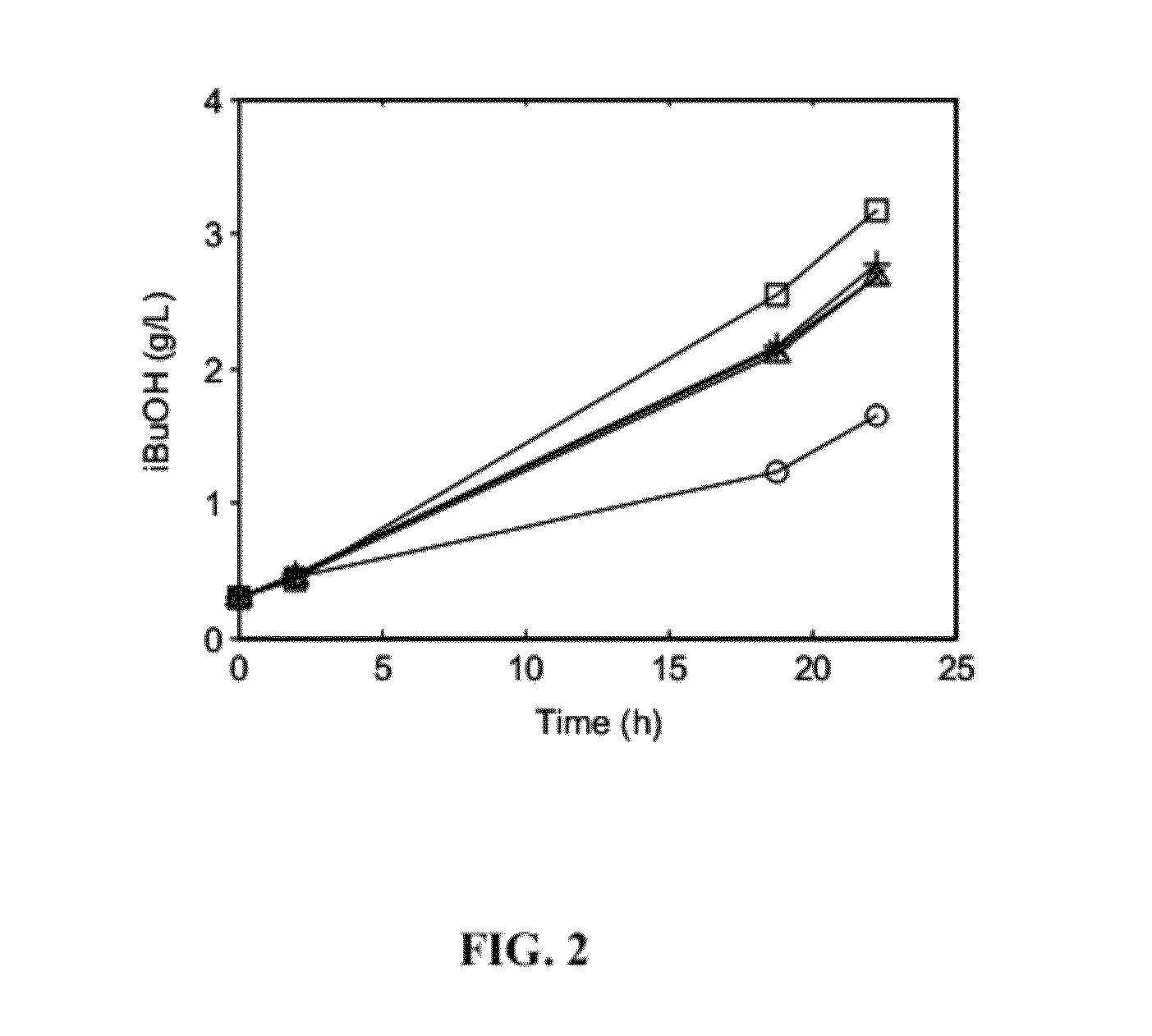
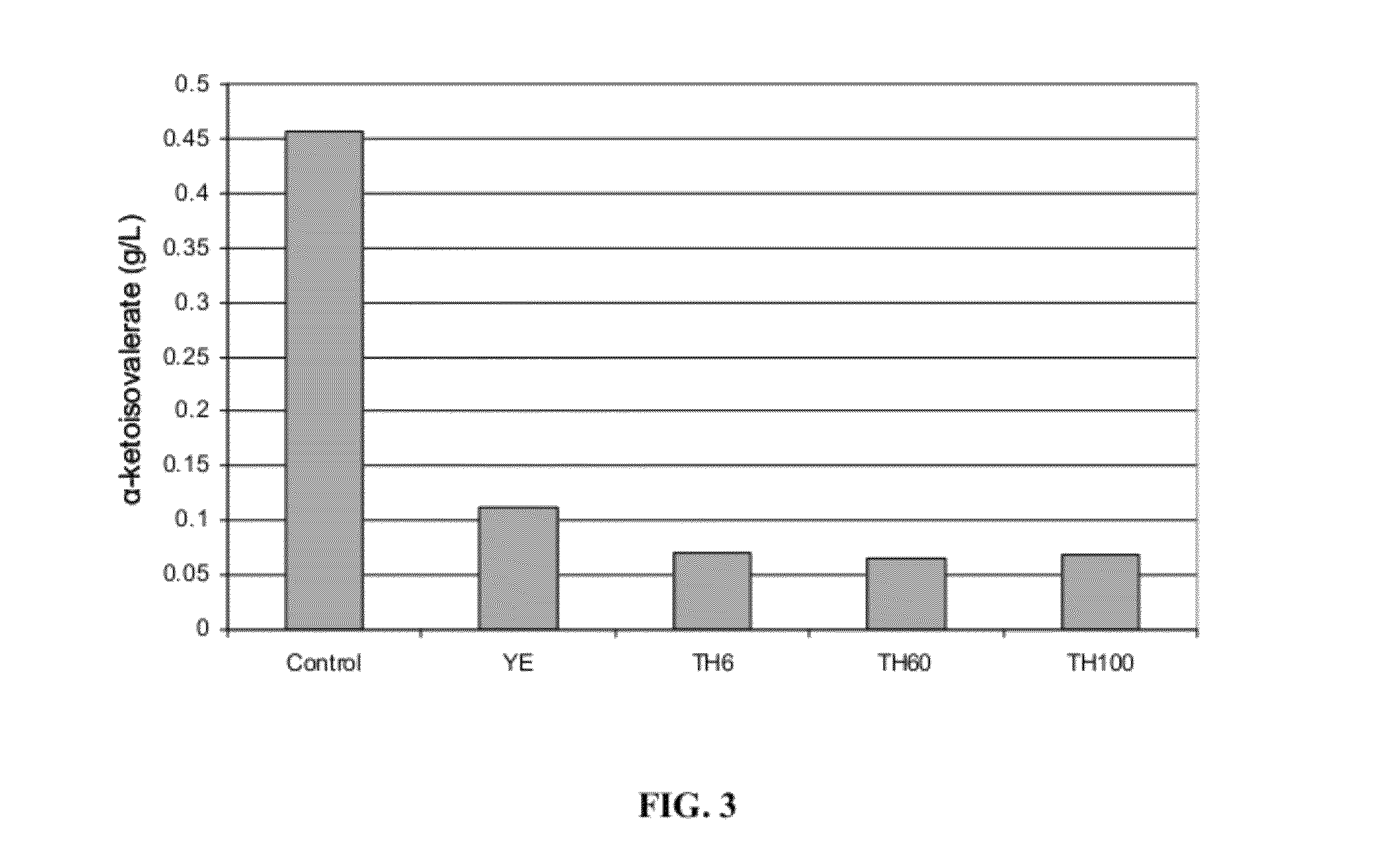
Use of thiamine and nicotine adenine dinucleotide for butanol production
The invention relates generally to the field of industrial microbiology and alcohol production. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to improve butanol production. Butanol production can be improved by providing sufficient amounts of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) in the production media.
Owner:GEVO INC
Resetting biological pathways for defending against and repairing deterioration from human aging
PendingCN108290059ADispersion deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsS-Adenosyl-l-methionineNicotinamide riboside
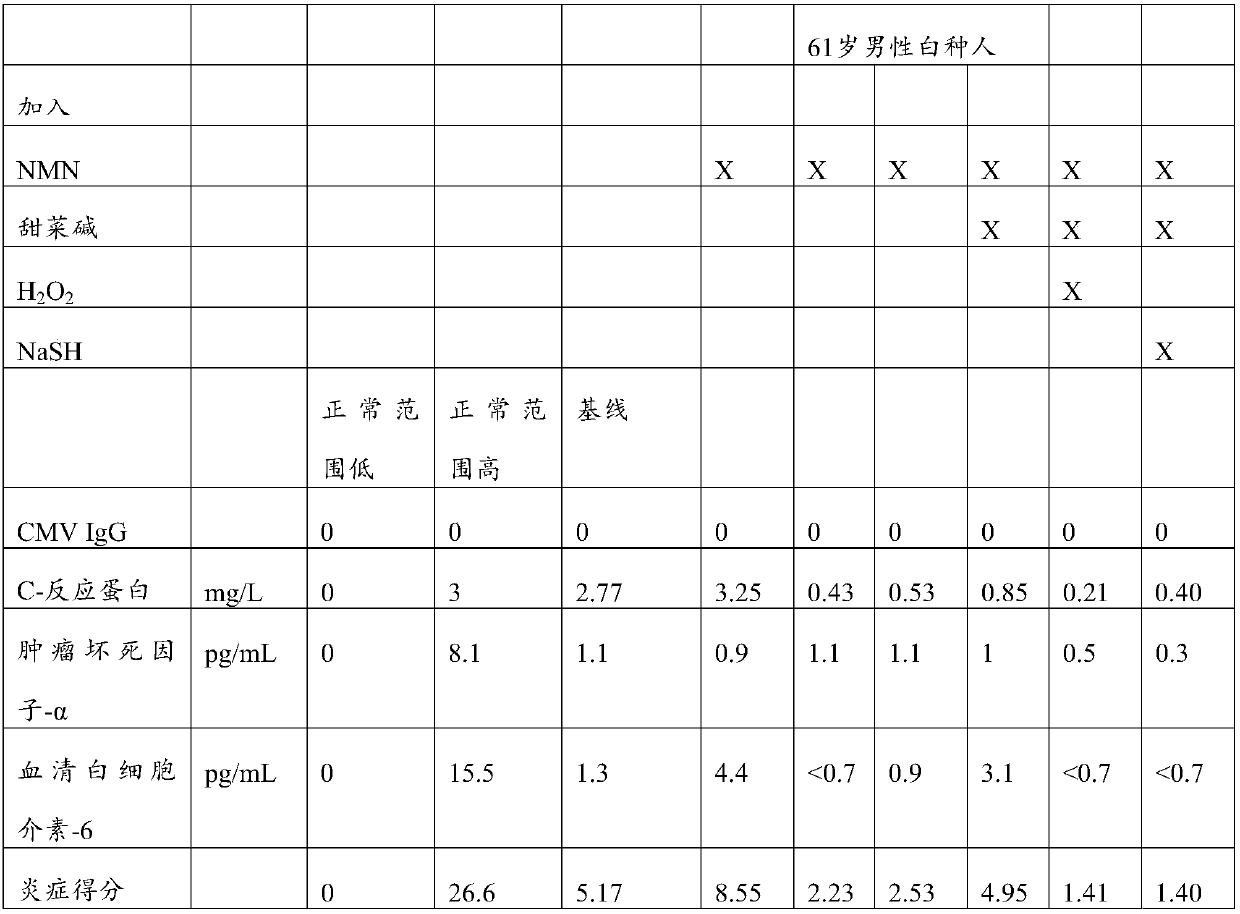
Compositions for addressing one or more of the effects of aging are described. The compositions comprise a first component comprising repair system activator(s) such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide riboside (NR), nicotinic acid adenine mononucleotide (NaMN), nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD), nicotinic acid riboside (NAR), 1-methylnicotinamide (MNM), cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and combinations thereof; a second component comprising methyl donor(s), such as S-5'-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM), methionine, betaine, choline, folate, vitamin B12, or combinations thereof; and a third component comprising antioxidant defense activators, such as H2O2, N2S, NaSH, Na2S, and several others, including combinations thereof.Methods of administering the disclosed compositions or separate formulations of repair system activator, methyl donors, and antioxidant defense activators are also disclosed.
Owner:乔尔胡伊赞加
Palladium nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber compound, preparation method and application thereof in electrocatalysis
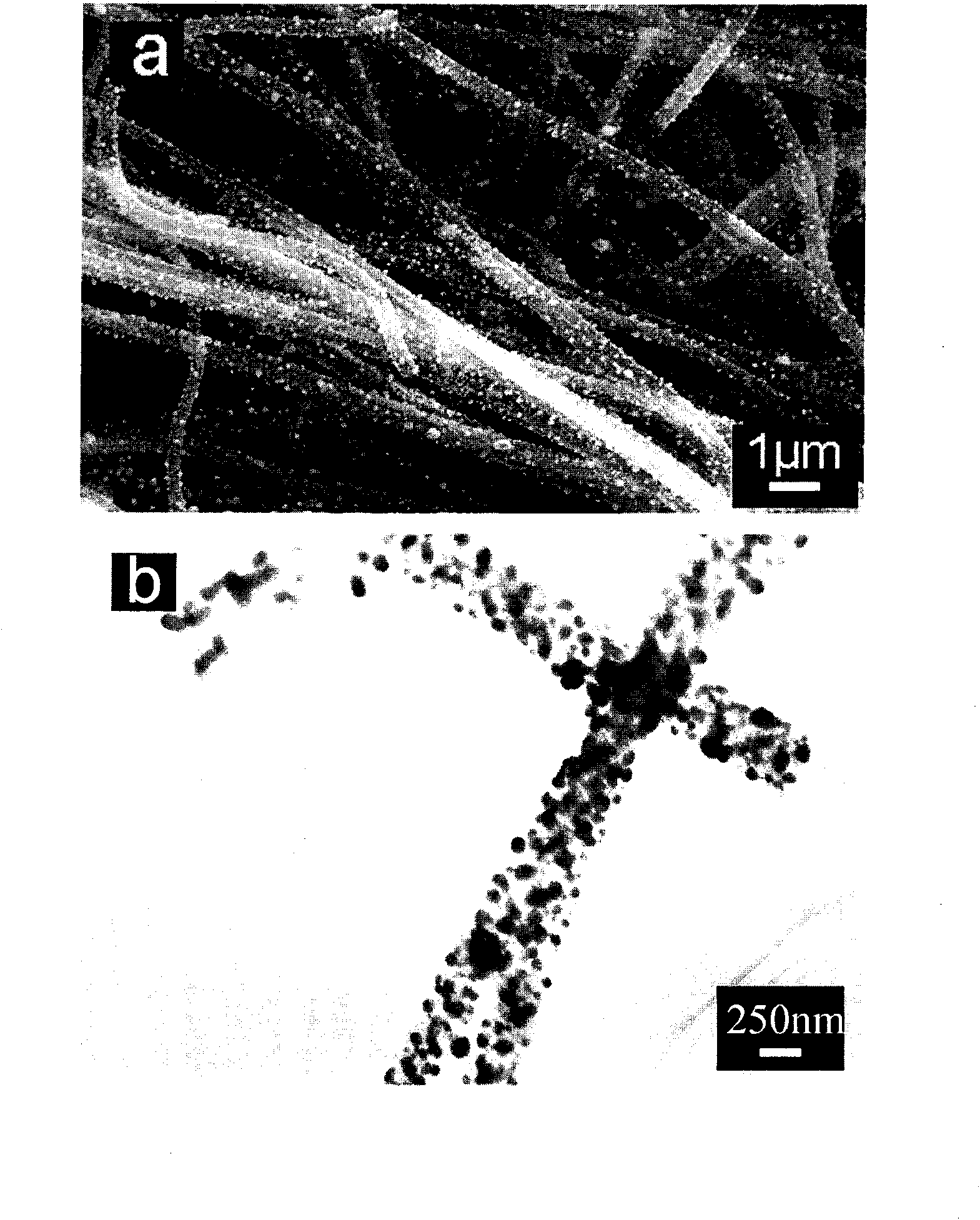
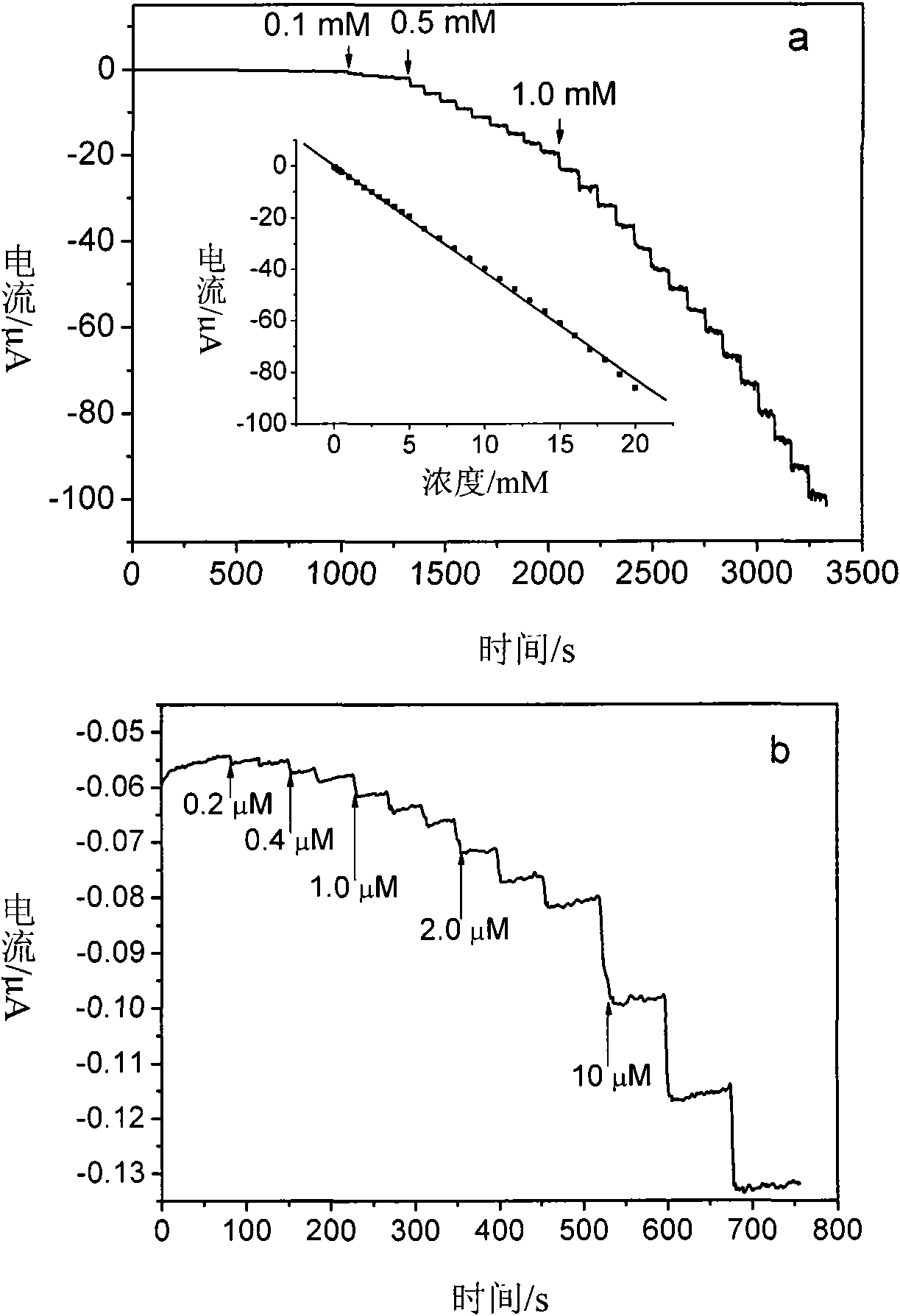
ActiveCN101665232AGood dispersionImprove stabilityIndividual molecule manipulationMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanofiberPalladium nanoparticles
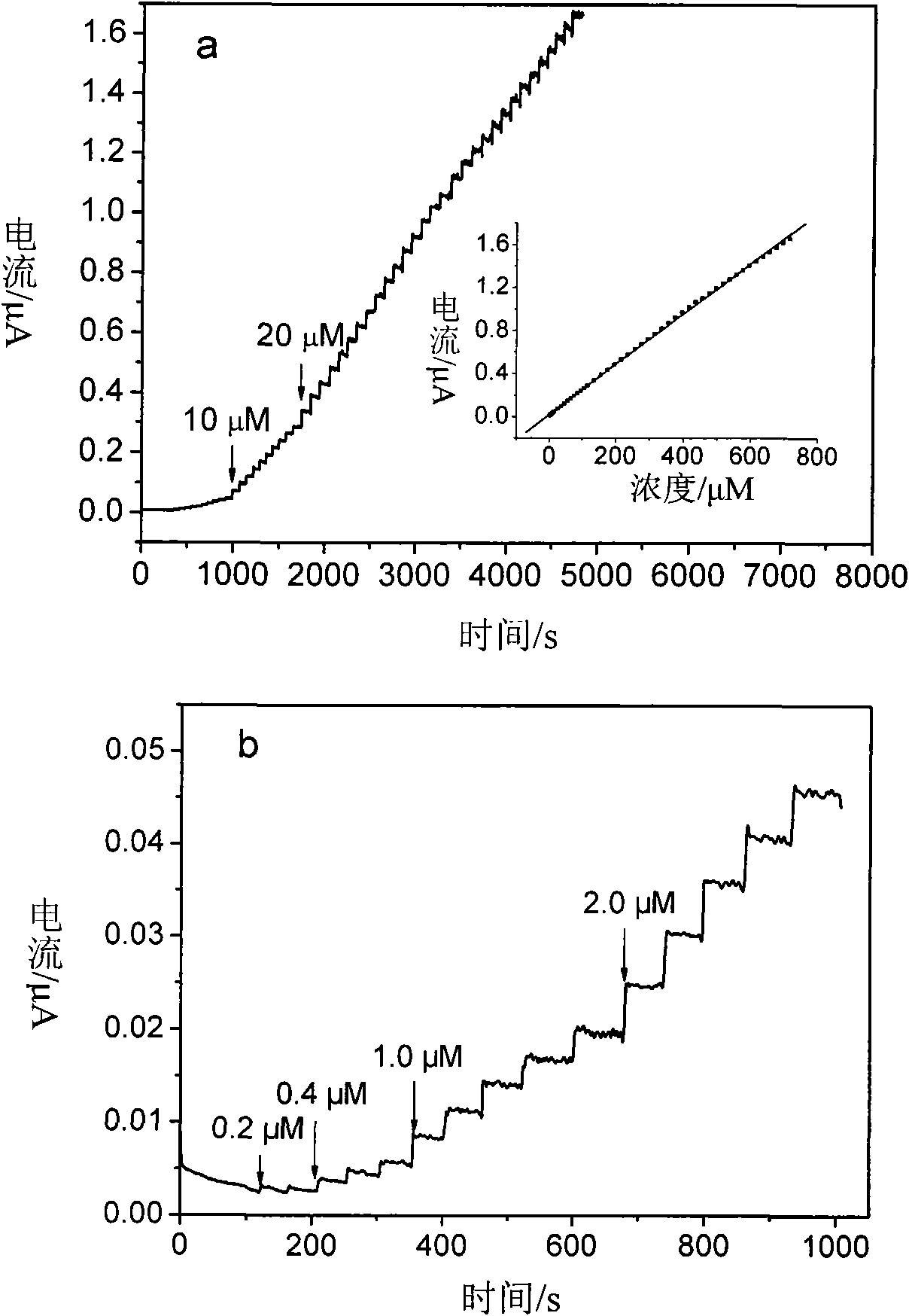
The invention relates to a palladium nanoparticle / carbon nanofiber compound, a preparation method and an application thereof in electrocatalysis. The compound is directly prepared by a one-step electrospinning method. An electrode modified by the compound is used for direct eectrochemical detection on hydrogen peroxide, beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dopamine, ascorbic acid and lithic acid. The electrode modified by the compound has the linear range from 0.2 micrometer to 20 millimetres and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the hydrogen peroxide and has the linear range of 0.2-716.6 micrometers and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the beta- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and the peak-peak potential differences between the ascorbic acid and the dopamine, the dopamine and the lithic acid as well as the ascorbic acid and the lithic acid are respectively 244mV, 148 mV and 392 mV, thereby showingthat the modified electrode can be used for simultaneous eectrochemical detection of three substances. The compound can be used in the fields of catalysis, fuel cells and sensing.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
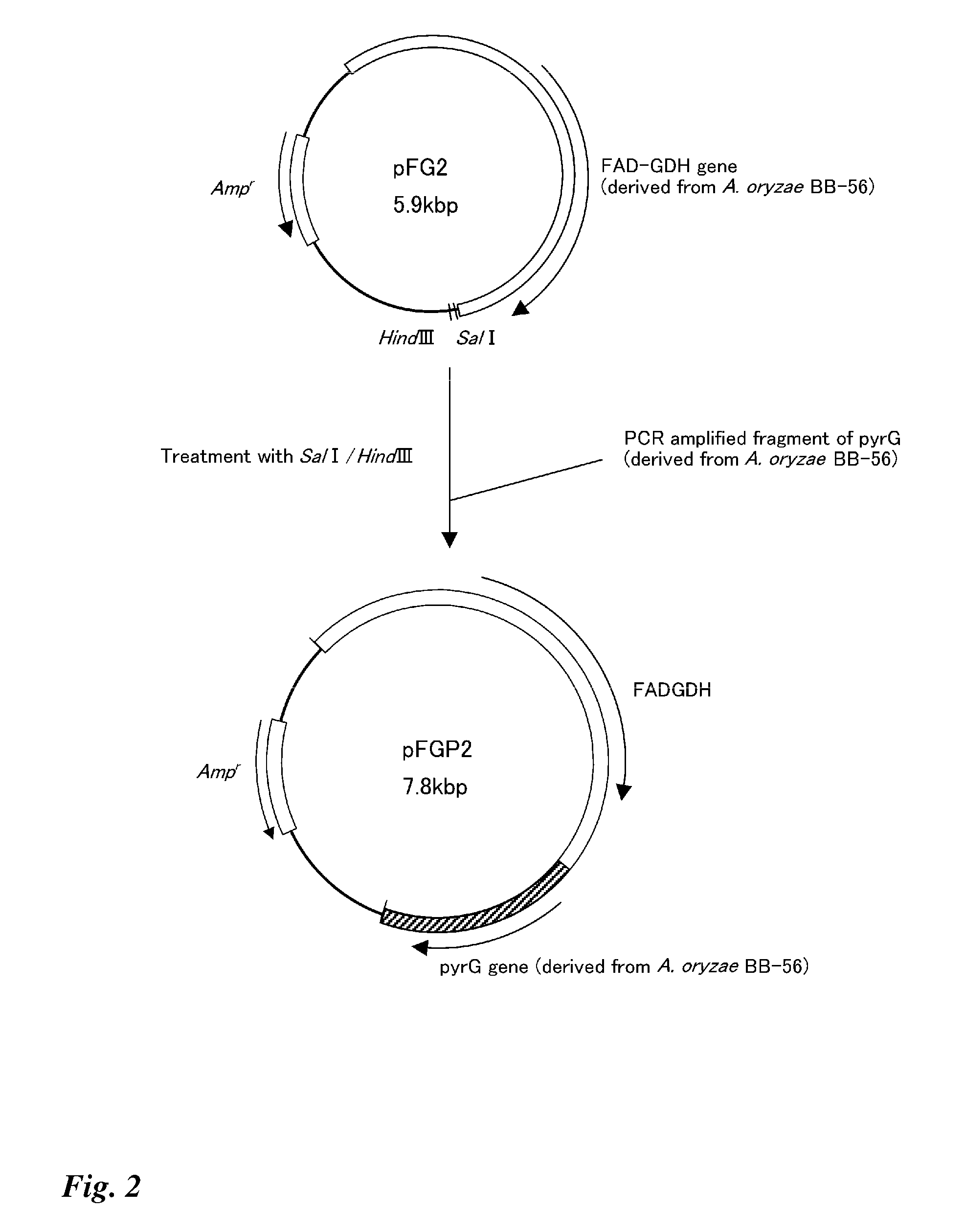
Transformant transfected with flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase gene and method for producing flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the same
InactiveUS20110053194A1Accurate measurementIncrease production capacityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideA-DNA
It is intended to highly efficiently produce a large amount of novel FAD-GDH capable of more accurately measuring a glucose level. Provided is a transformant in which a DNA encoding a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase selected from the group consisting of (a) a DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 20; (b) a DNA consisting of the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 19; (c) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 19 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase activity; (d) a DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 34; (e) a DNA consisting of the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 33; and (f) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence of SEQ ID NO: 33 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase activity has been introduced. Further, a method for producing a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the transformant is provided.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Use of thiamine and nicotine adenine dinucleotide for butanol production
The invention relates generally to the field of industrial microbiology and alcohol production. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to improve butanol production. Butanol production can be improved by providing sufficient amounts of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) in the production media.
Owner:GEVO INC
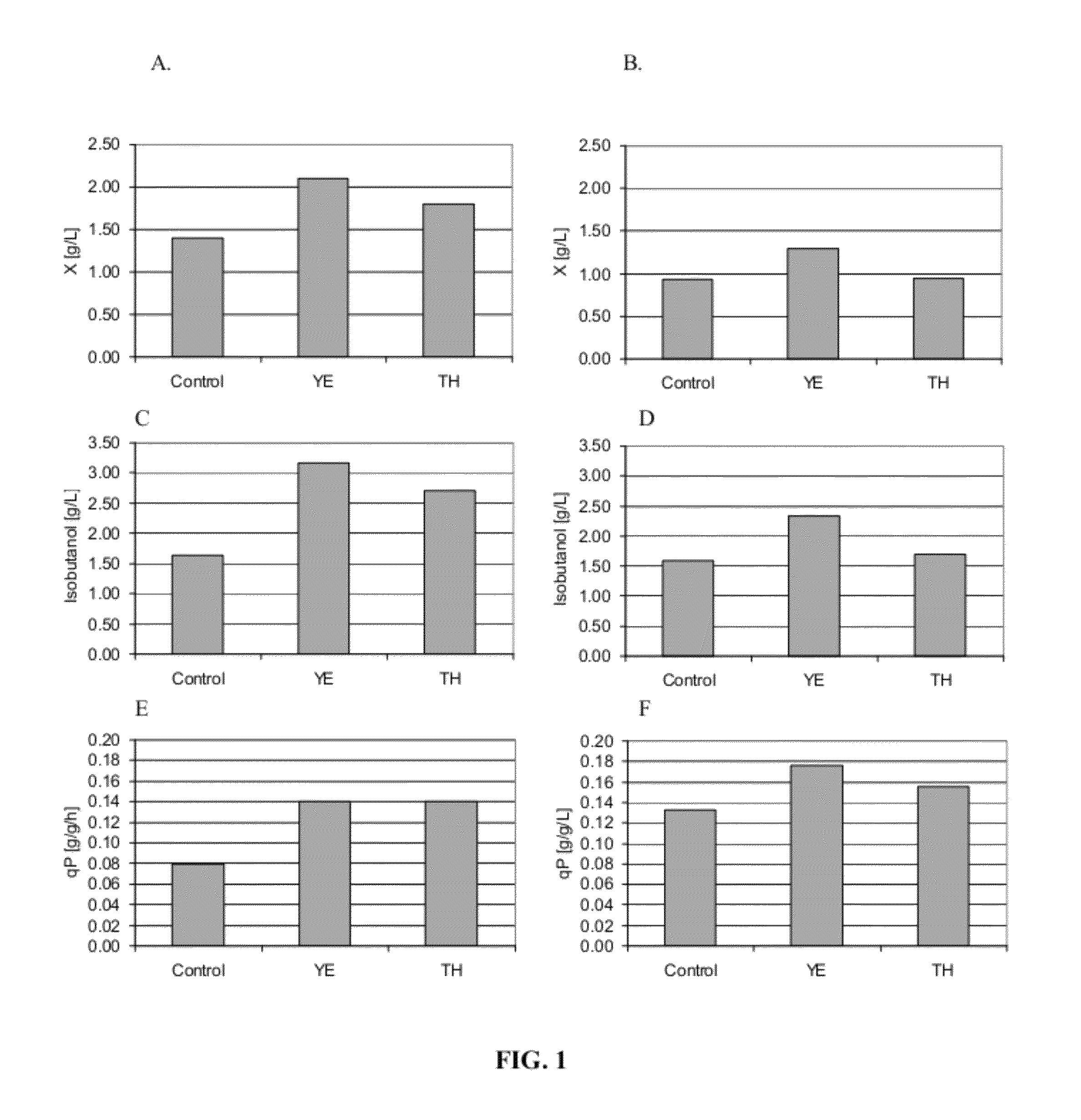
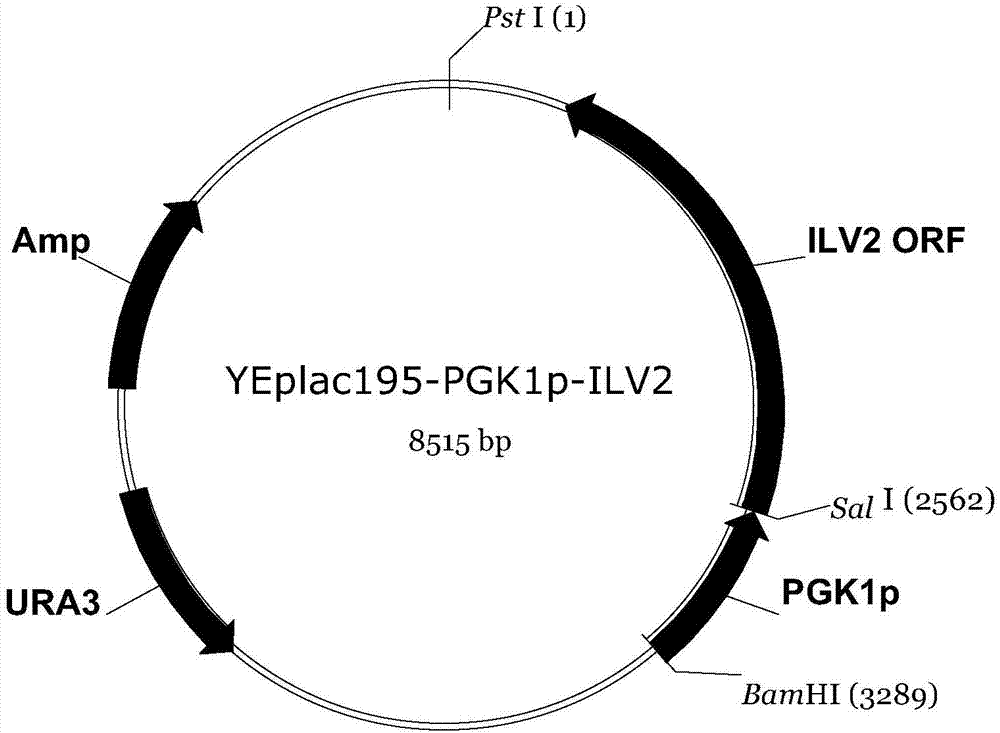
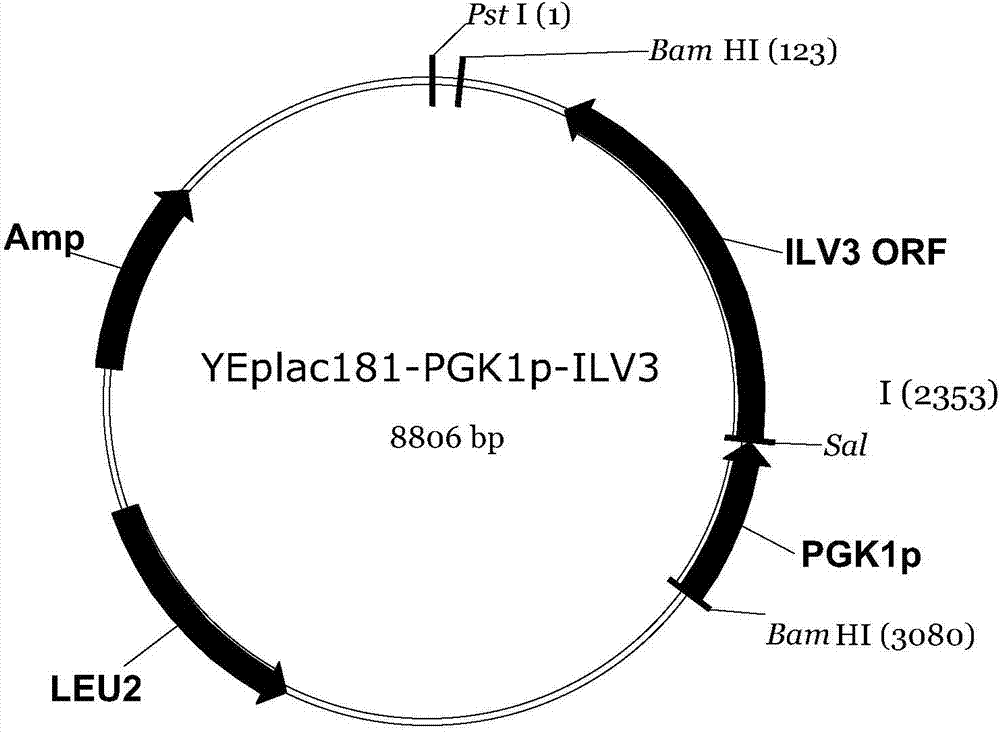
Construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of isobutanol
ActiveCN103789341AIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionIsobutanolBiotechnology
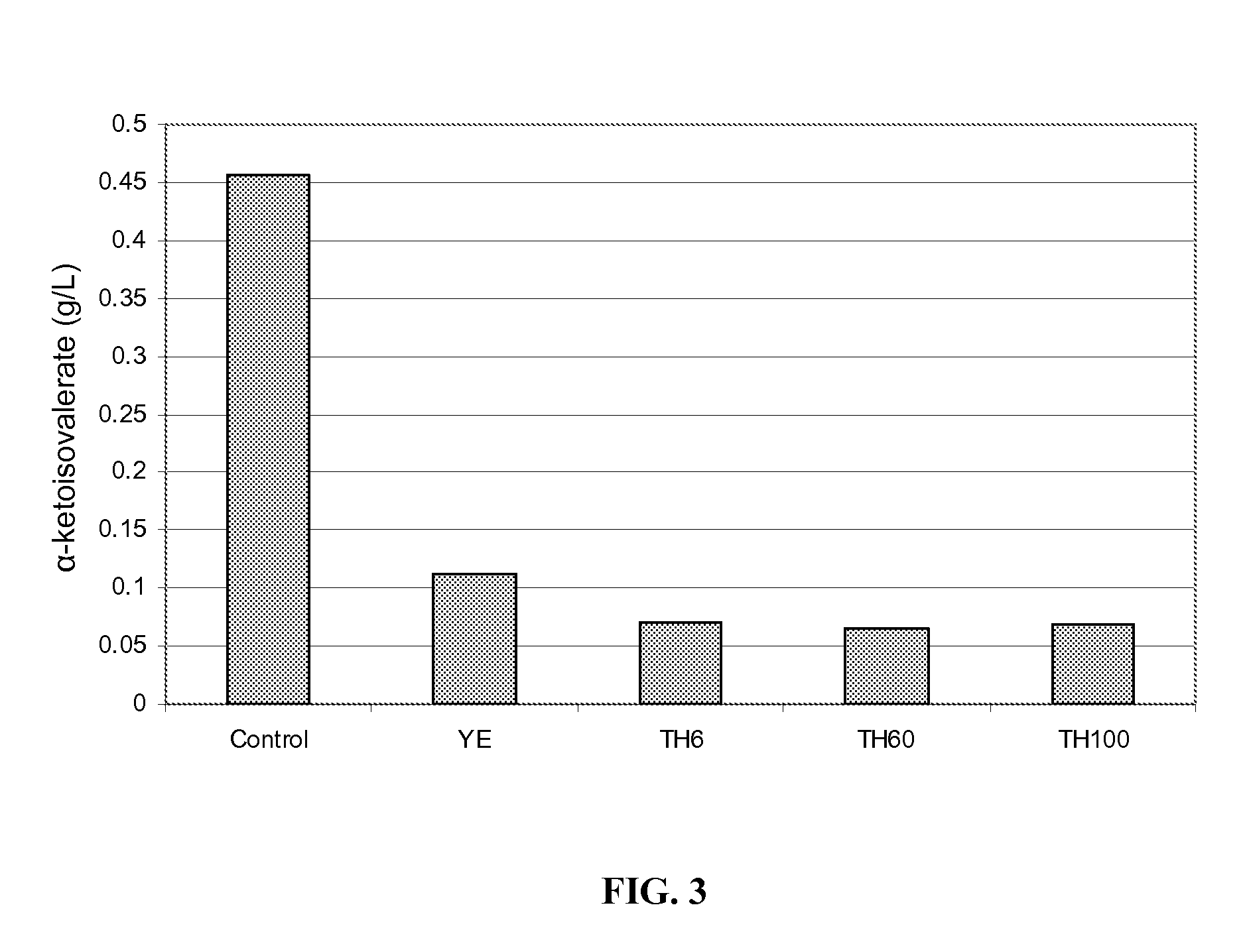
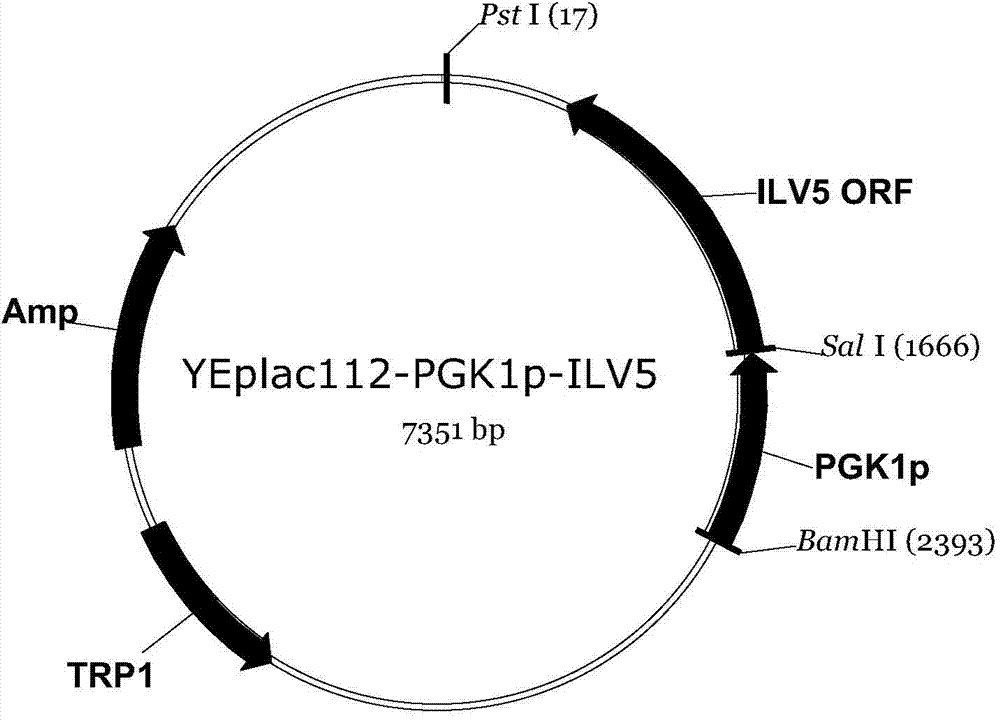
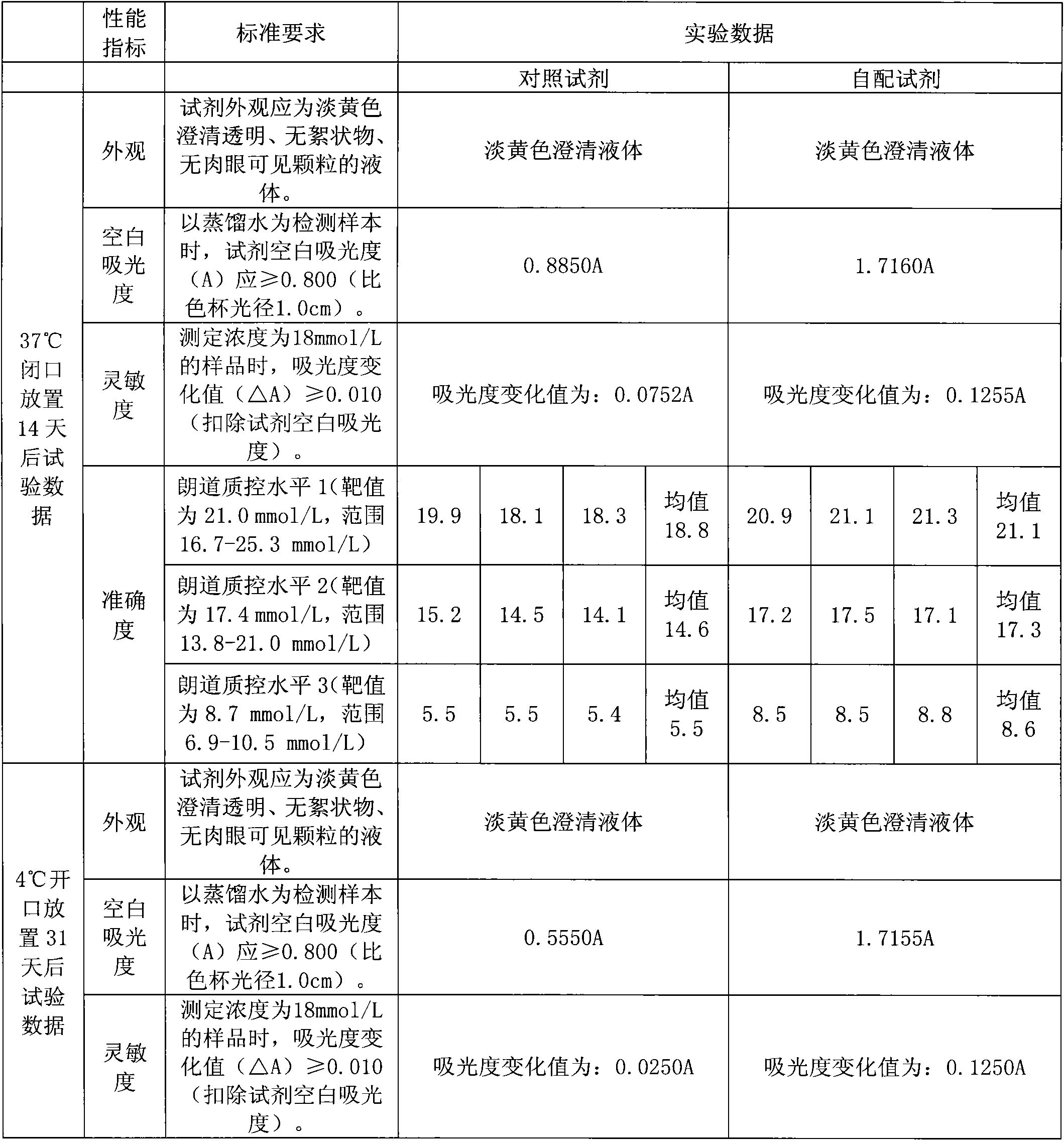
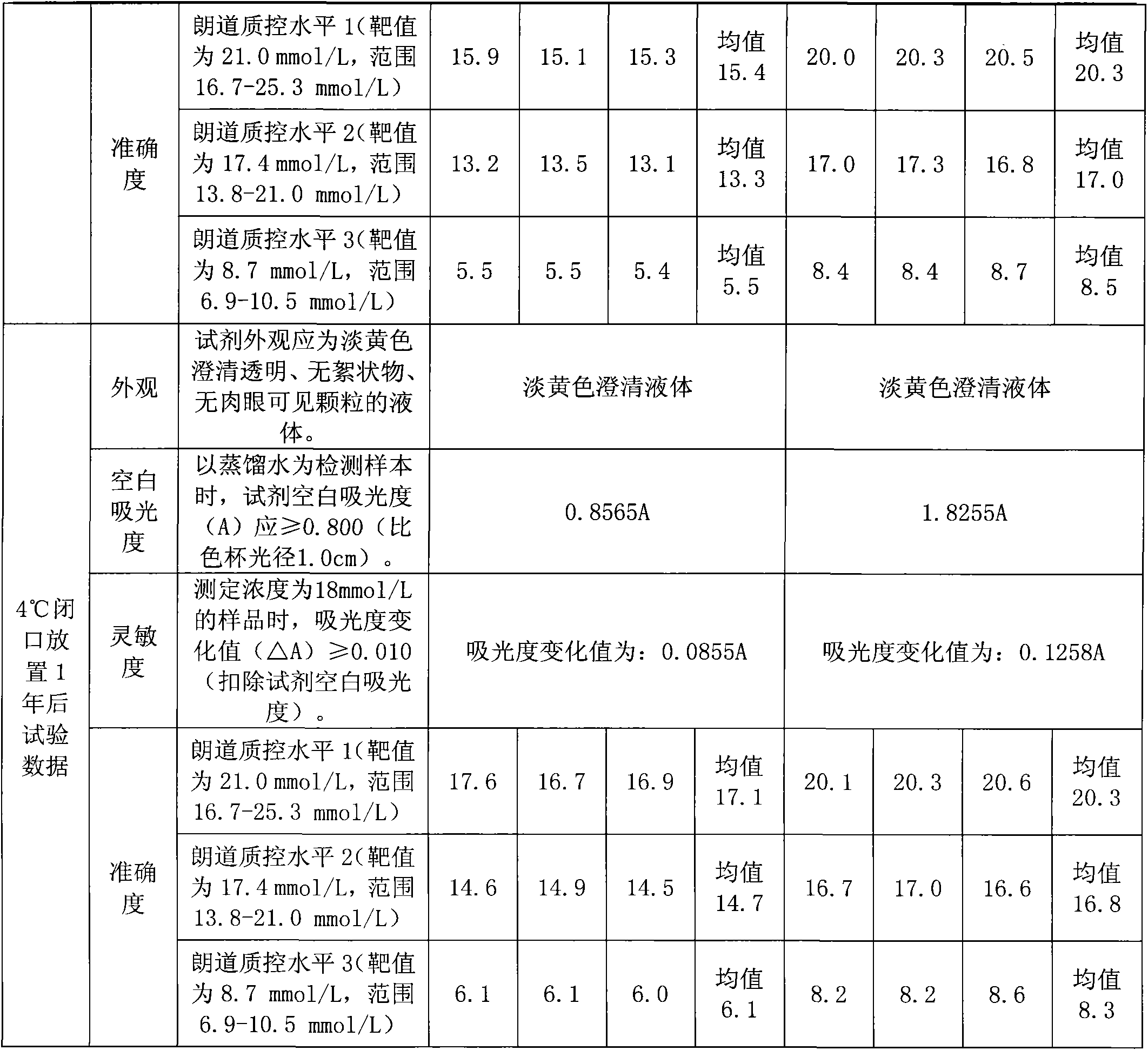
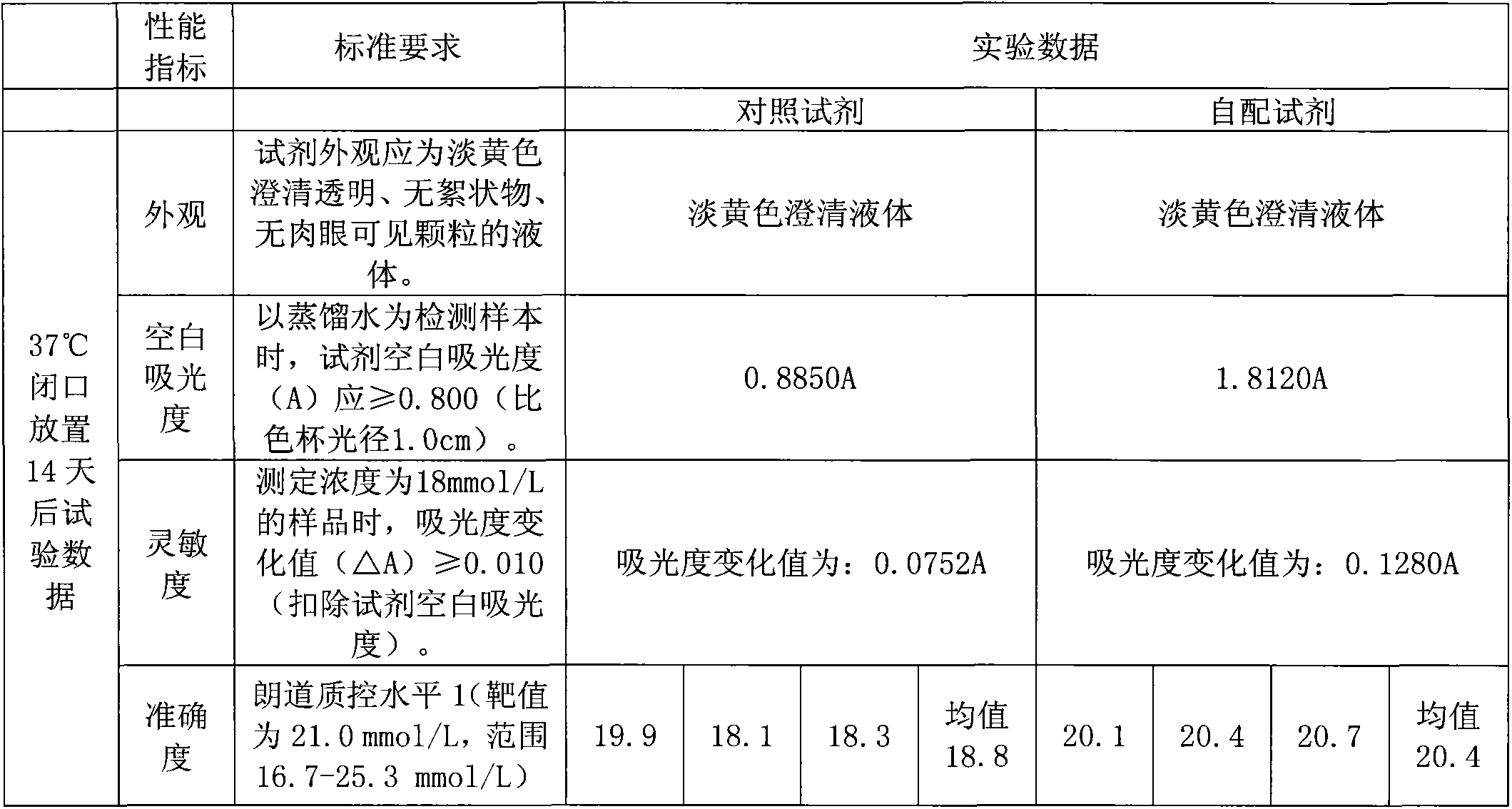
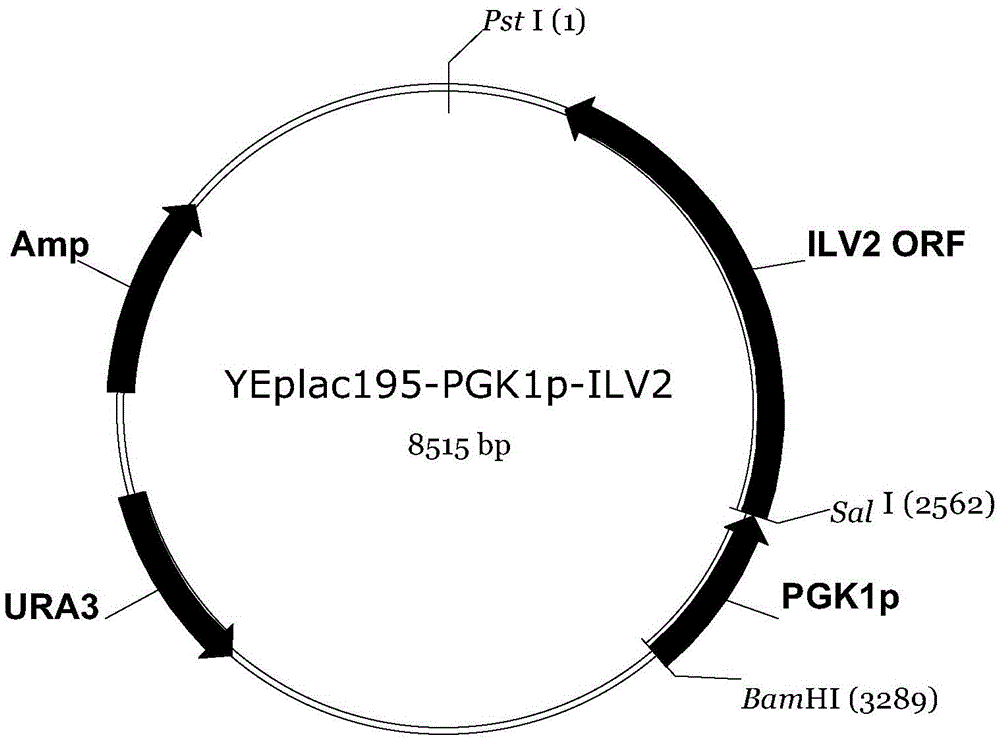
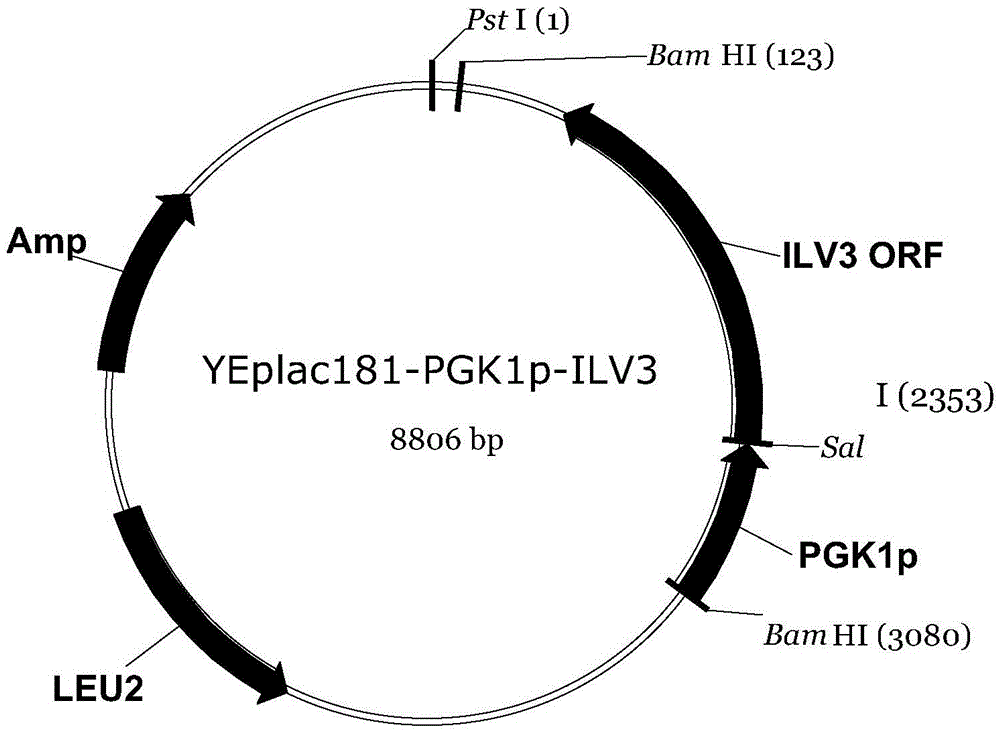
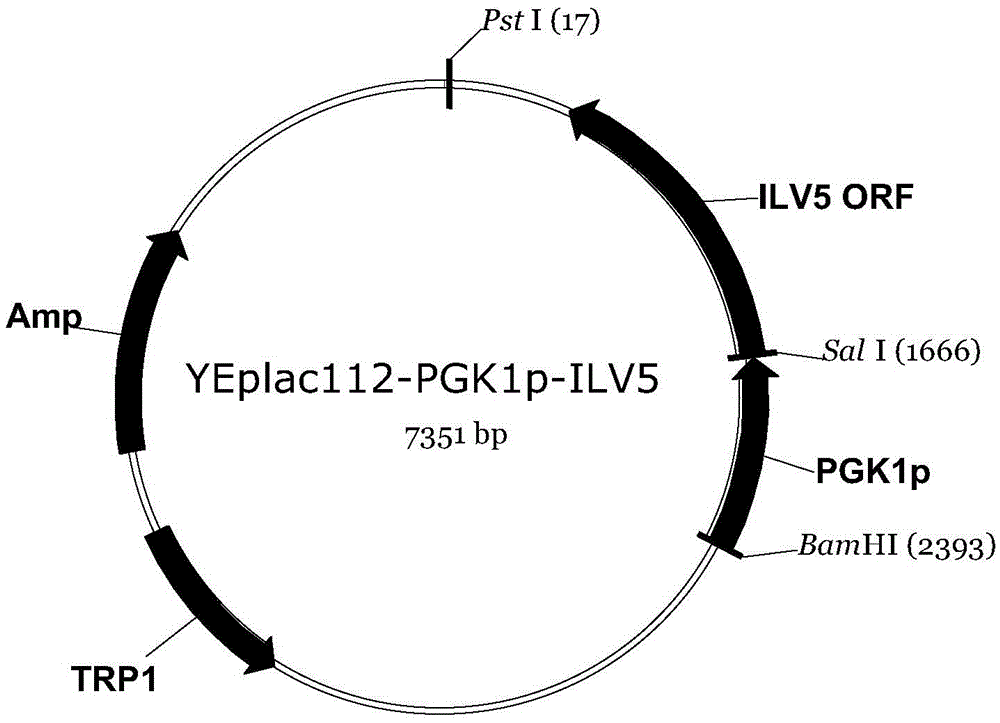
The invention discloses a construction method of a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with a high yield of isobutanol and relates to preparation of microorganism by a recombinant DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) technology. According to the method, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with the high yield of isobutanol is constructed by reforming saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using molecular biology and the gene recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing plasmids of over-expressing ILV2 (Induced Leukemia Virus), ILV3, ILV5 and ZWF1 genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae; and S2, constructing a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain HBGDAL-103 with the high yield of isobutanol. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the deficiency that further improvement of the yield of isobutanol is restricted by factors such as imbalance of a coenzyme NADPH / NADP<+> (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) / (Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate<+>) from pyruvic acid to 2-one isovaleric acid due to over-expressed ILV2, ILV3 and ILV5 in the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells of yielding isobutanol in the prior art.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Enzyme composition and use therefore
InactiveUS20100151554A1Improve combustion efficiencyTransferasesOxidoreductasesFlavin adenine dinucleotideThiamine pyrophosphate
The present invention provides an enzyme composition and a method for treating coal using the enzyme composition. The enzyme composition includes at least one enzyme, coenzyme and ammonium acetate, wherein the enzyme can be laccase-isozyme, pyruvate dehydrogenase, dihydrolipoyl transacetylase, and dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, and the coenzyme can be CoA, CoA-SH, thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. In addition, the method of the present invention includes treating the coal with the enzyme composition for more than 72 hours.
Owner:EIN INTL
Carbon dioxide measurement kit
InactiveCN103558370AEasy to useEasy to operateBiological testingFlavin adenine dinucleotidePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides a carbon dioxide measurement kit. The carbon dioxide measurement kit mainly comprises the following components: 50 to 200mM of a buffer solution, 10 to 50% of a stabilizer, 0.1 to 5% of a surface active agent, 0.1 to 5g / L of a preservative, 1 to 20mM of a reaction accelerator, 2 to 10mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type), 5 to 50g / L of phosphoenolpyruvic acid, 50 to 500U / L of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, and 1 to 3KU / L of malate dehydrogenase; a recycling system of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide (reduction type) comprises (1) 2 to 20g / L of glucose substrate, (2) 100 to 2,000U / L of corresponding glucose dehydrogenase, and (3) 1 to 5mM of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide. The carbon dioxide measurement kit is convenient to use and simple to operate; the components participating in coupling reaction are extra added, so that no pollution caused by endogenous and allogenic substances are introduced; the rate of the recycling system is below the main reaction rate, thus the main reaction cannot be interfered; the carbon dioxide measurement kit is high in stability and can be used for a long time.
Owner:QINGDAO JINYANG BIOTECH
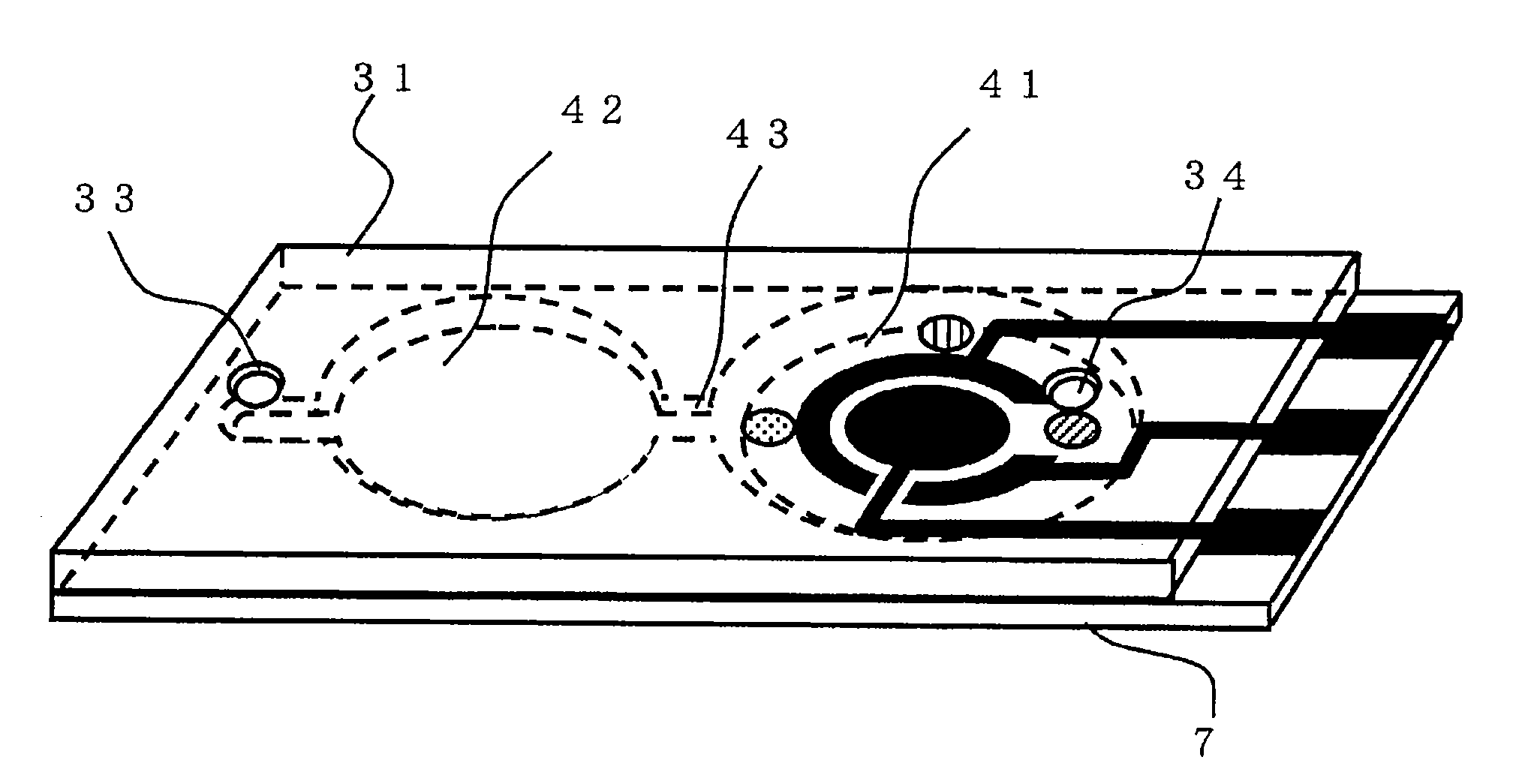
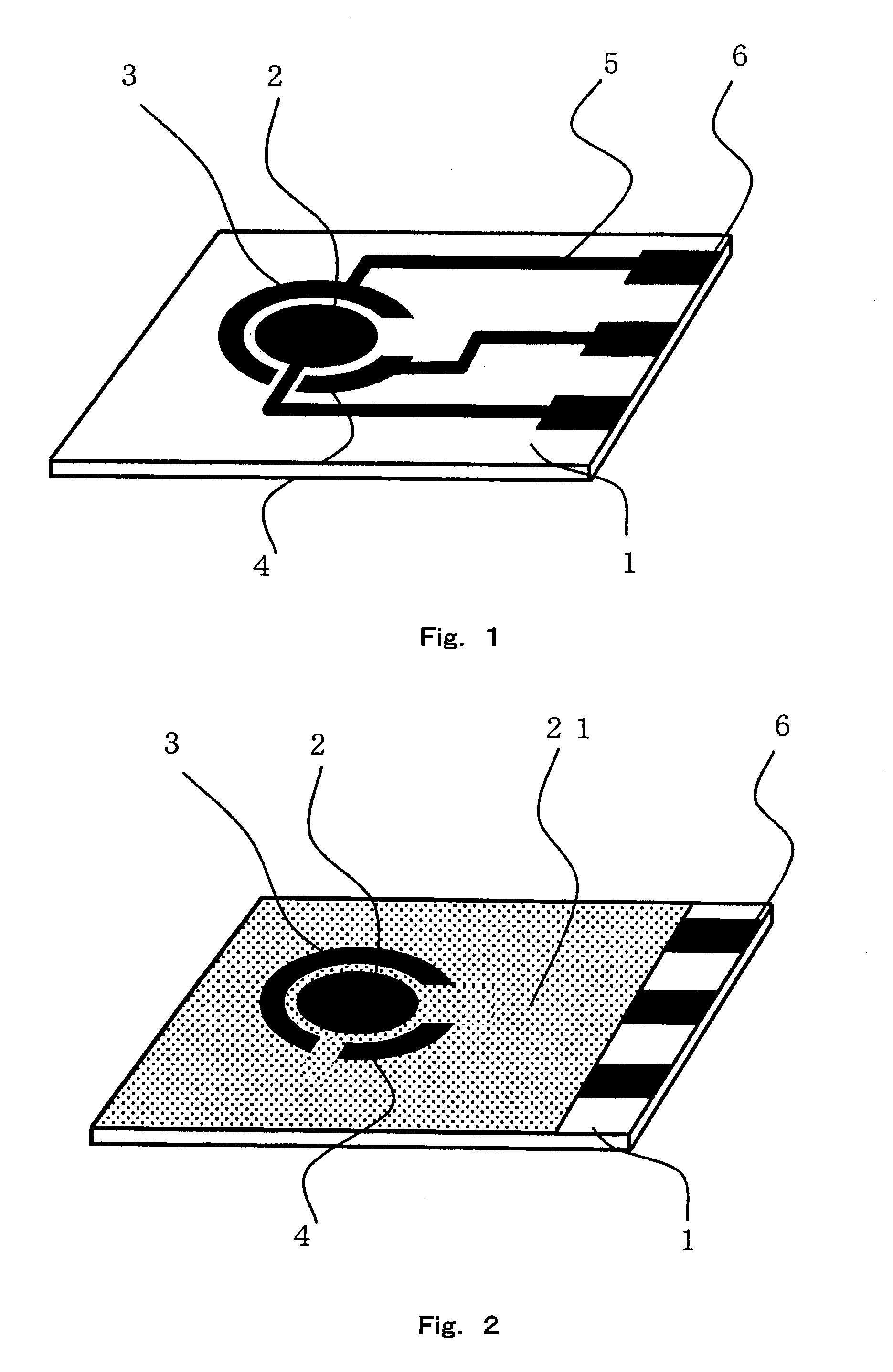
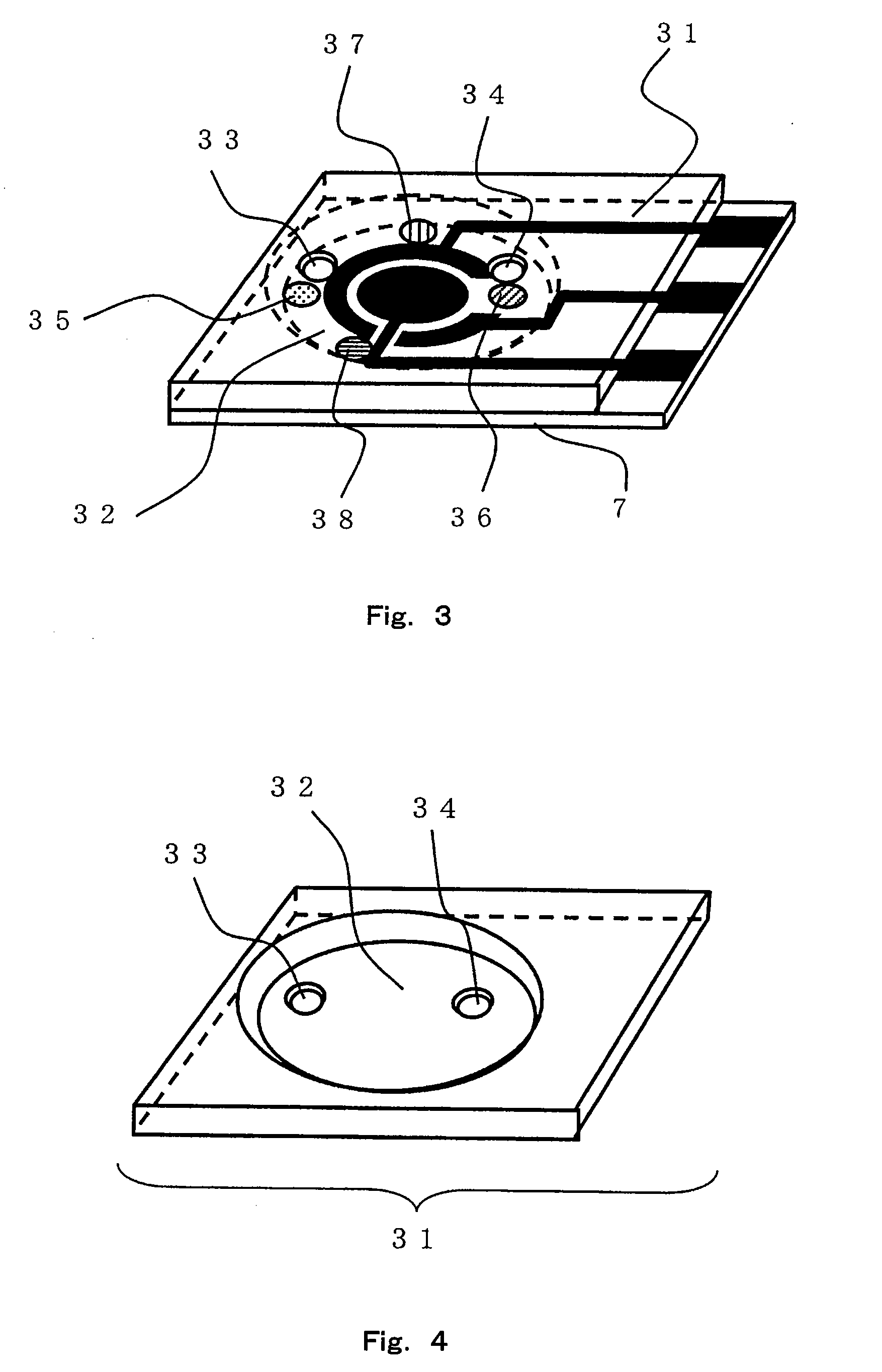
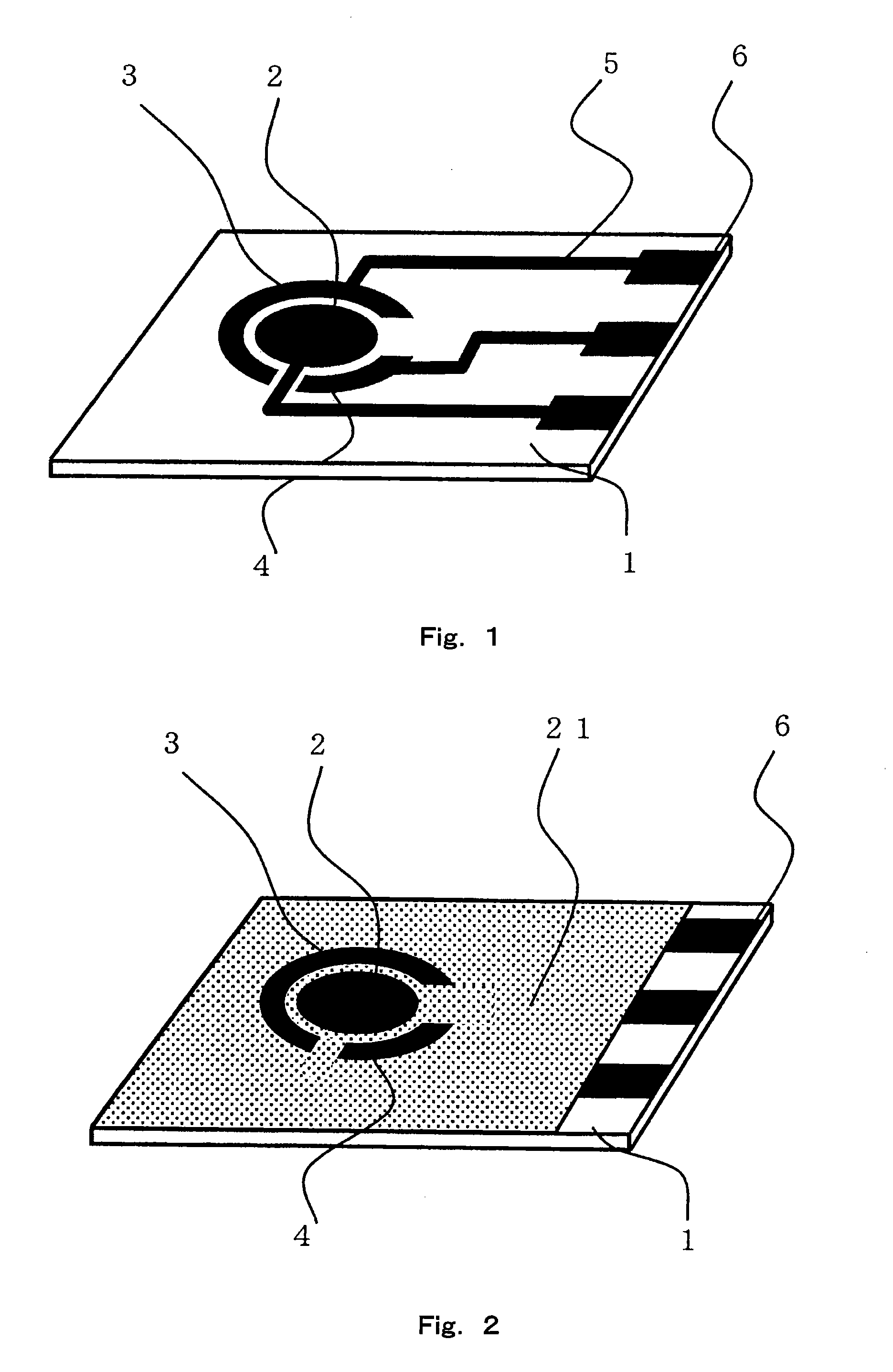
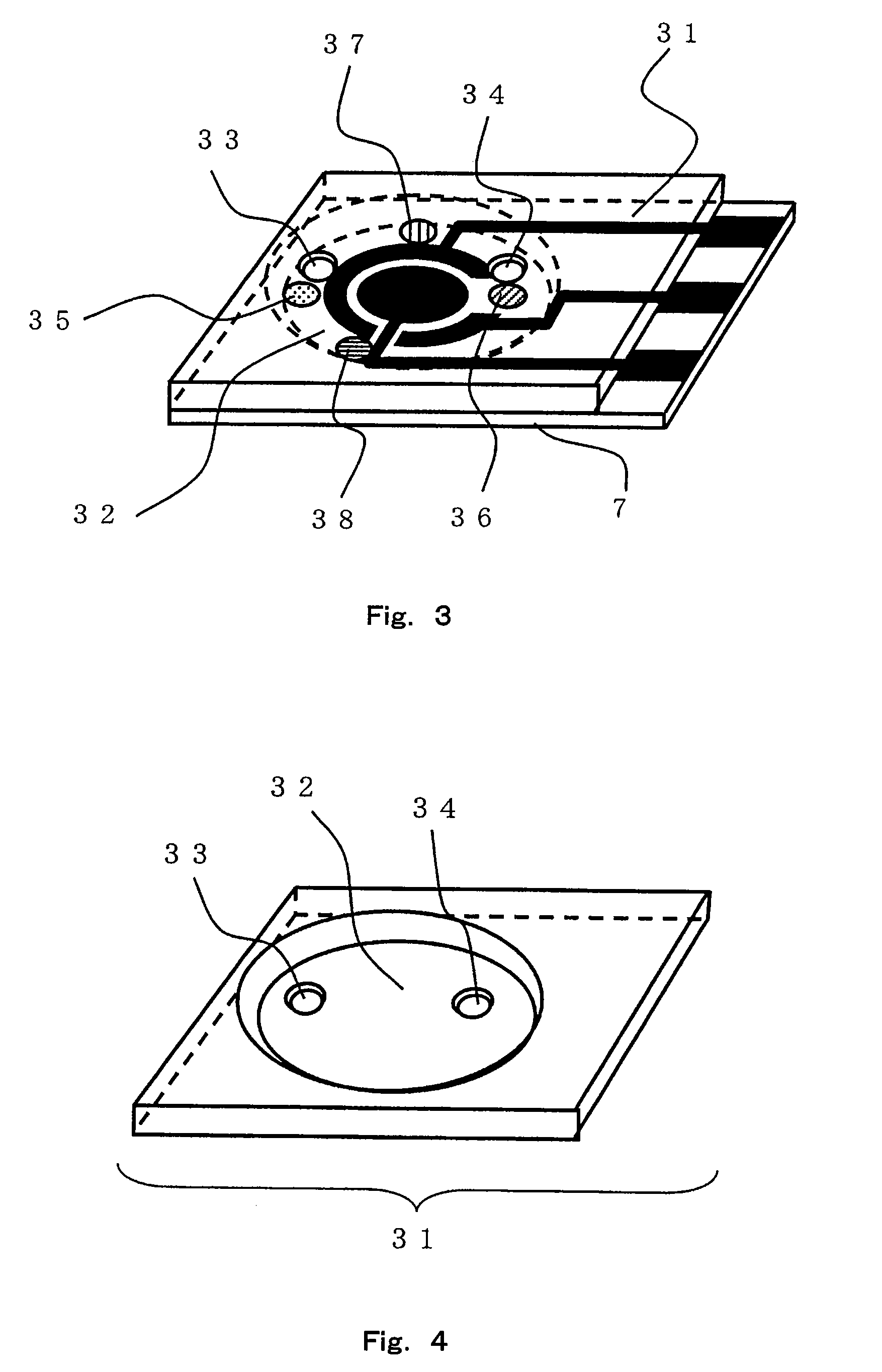
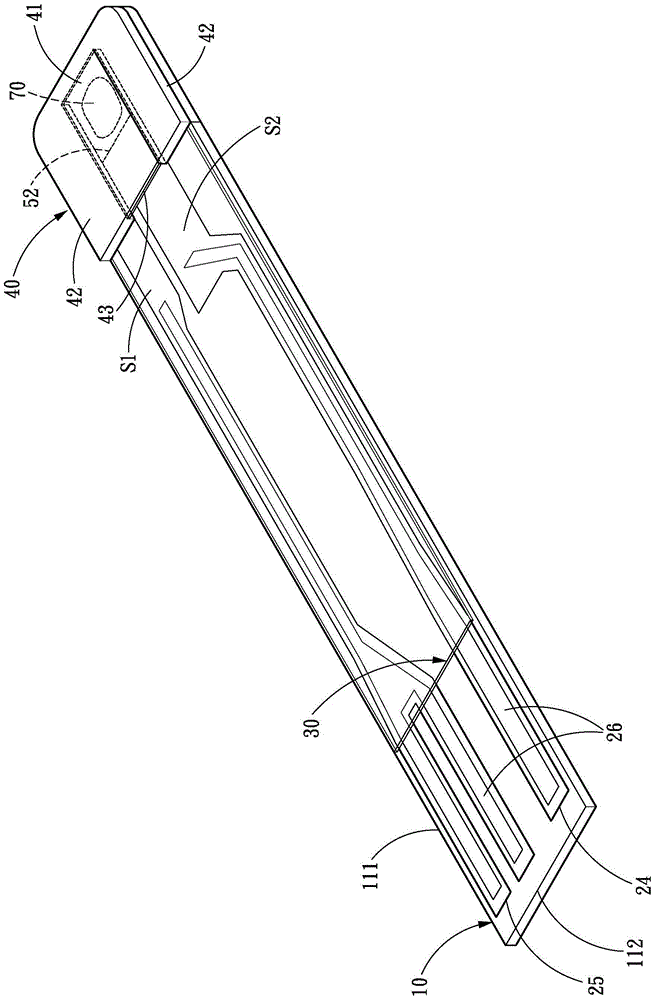
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
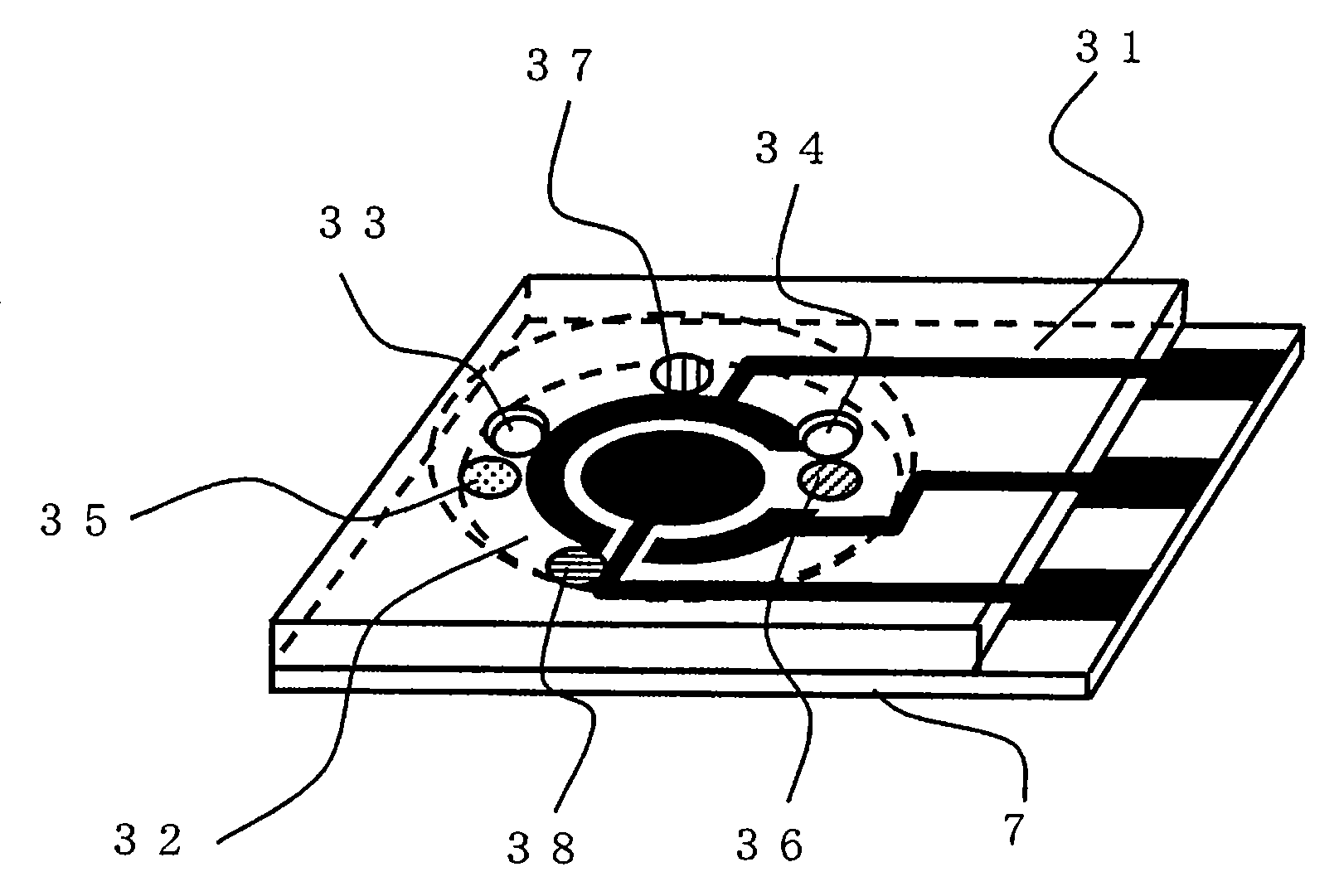
ActiveUS20080293128A1High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
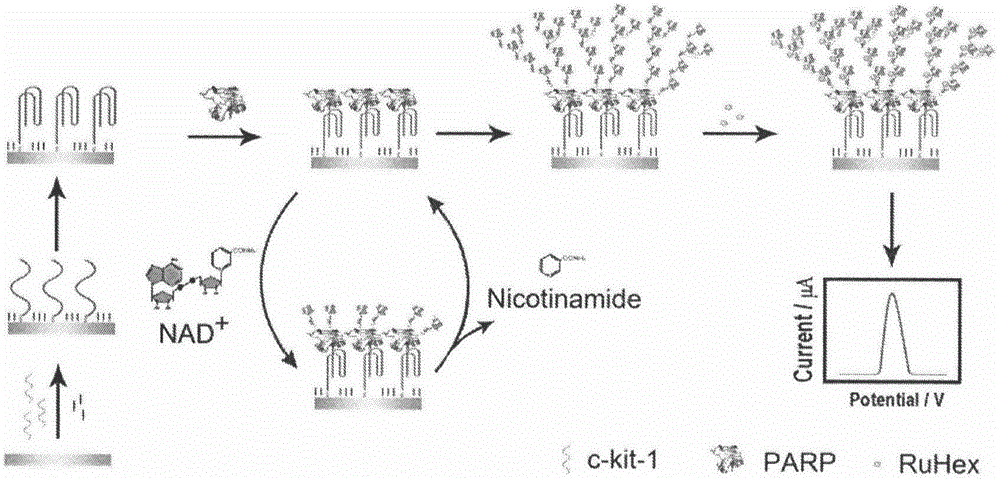
Detection method of poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase
InactiveCN105606671AEnable label-free detectionSimple methodMaterial electrochemical variablesSignalling moleculesPolyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase
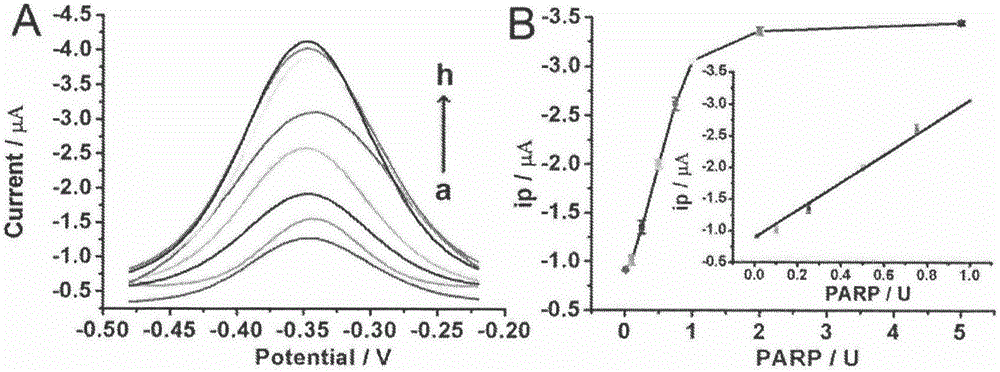
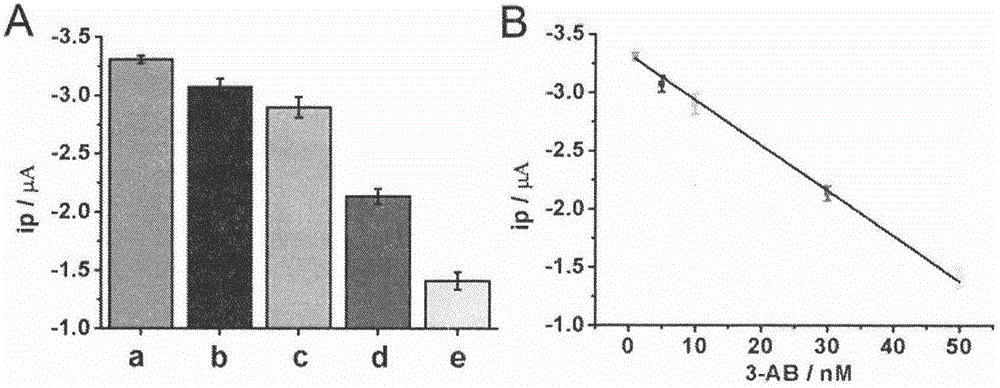
The invention belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and relates to a detection method and application of PARP [poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase]. The detection method mainly includes: modifying a single-stranded DNA (c-kit-1) capable of specifically binding with the PARP on the surface of a gold electrode in a classical mercapto self-assembly mode and enabling c-kit-1 to form a tetramer configuration through treatment; after the tetramer configuration is incubated with the PARP, adding a specific catalytic substrate, namely NAD (nicotinamide ademinedinucleotide) of the PARP, to enable the PARP to self-catalyze to produce PAR with high negative charges; using the negative charges of the PAR for adsorbing electrical signal molecules RuHex with positive charges, quantifying the RuHex adsorbed on the surface of the electrode through an electroanalysis method, and drawing a standard curve according to a relation between electrochemical signals and PARP concentration so as to achieve sensitive PARP detection by measuring the electrochemical signals of to-be-detected samples and calculating. The detection method is high in repeatability and sensitivity and can be applied to detection of the PARP and an inhibitor 3-AB (3-aminobenzamide) thereof.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cyclophorase detection method for quantitative detection of thio-nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (Thio-NAD) and kit
The invention discloses a cyclophorase detection method for quantitative detection of thio-nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (Thio-NAD). The cyclophorase detection method comprises the following steps of: preparing Tris-HCl buffer solution with pH of 8.5 to 10.50, wherein the Tris-HCl buffer solution includes a certain amount of coenzyme I (NADH), a sodium deoxycholate solution, 3Alpha-hydroxysteroiddehydrogenase (3Alpha-HSD) and trehalose, and adding a Thio-NAD-containing sample to be tested; dehydrogenizing and oxidizing sodium cholate or sodium deoxycholate by 3Alpha-HSD to form 3Alpha-ketosteroid; meanwhile, reducing Thio-NAD into reduced-type thio-nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (Thio-NADH); re-reducing 3Alpha-ketosteroid into sodium cholate or derivatives thereof by 3Alpha-HSD in the presence of NADH in the solution; meanwhile, dehydrogenating and oxidizing the NADH into NAD<+>, wherein the Thio NADH generated in the reaction has maximum absorption at a 405 nm place; and computing content of THE Thio-NADH of the sample to be tested by measuring optical density of the solution under a specific wavelength after reacting at 37 DEG C for some time. The cyclophorase detection method, provided by the invention, has the advantages of environmental friendliness, and stable test reagent, and is particularly suitable for bulk detection of Thio-NAD.
Owner:浙江夸克生物科技有限公司
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
ActiveUS7632392B2High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sensor used for detecting lactic dehydrogenase
InactiveCN105987938AWide range of applicationsJudging the test resultsMaterial electrochemical variablesPotassium ferricyanideDiaphorase
A sensor for detecting lactate dehydrogenase, used for detecting a lactate dehydrogenase content of a biological sample, comprising a substrate, an electrode group, a hydrophobic insulating layer, a cover and a reaction drug membrane. The electrode group includes a working electrode and a reference electrode and is located on the substrate, the hydrophobic insulating layer is arranged on the substrate and includes a gap, the cover covers the gap and is connected to the substrate A sample channel is formed between them to accommodate the reaction drug film, the reaction drug film is selected from the group consisting of lactic acid, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, diaphorase and potassium ferricyanide. The reaction drug film is in contact with the lactate dehydrogenase in the biological sample to generate a bioelectrochemical reaction, so that the electrode group undergoes an electrical signal change reflecting the content of the lactate dehydrogenase.
Owner:EUMED BIOTECH
Method for improving bacillus glycerin metabolism to increase yield of poly gamma-glutamic acid
ActiveCN109913515ATo promote metabolismIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFAD synthesis
The invention discloses a method for improving bacillus glycerin metabolism to increase yield of poly gamma-glutamic acid by enhancing synthesis of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Three FAD enhanced synthetic strains are respectively built by enhancing expression of three key genes ribE, ribF and ribH in bacillus in a FAD synthesis path. In different liquid fermentation conditions, overexpression of ribE, ribF and ribH enables glycerin metabolic capacity to be improved by at least 22.02%, 20.62% and 23.92% respectively when compared with that of a comparison strain, and poly gamma-glutamicacid yield of these recombinant strains are at least 1.20, 1.18 and 1.27 times of that of the comparison strain. It shows that enhancing of FAD synthesis can remarkably improve bacillus glycerin metabolism and increase synthesis of poly gamma-glutamic acid. The method can improve glycerin utilization to enhance synthesis of a target produce and has wide application value in the aspect of utilizingglycerin as a raw material for microbial fermentation to synthesize a bio-based compound, and a new strategy is provided for microorganisms to efficiently utilize glycerin to synthesize bio-based chemicals.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
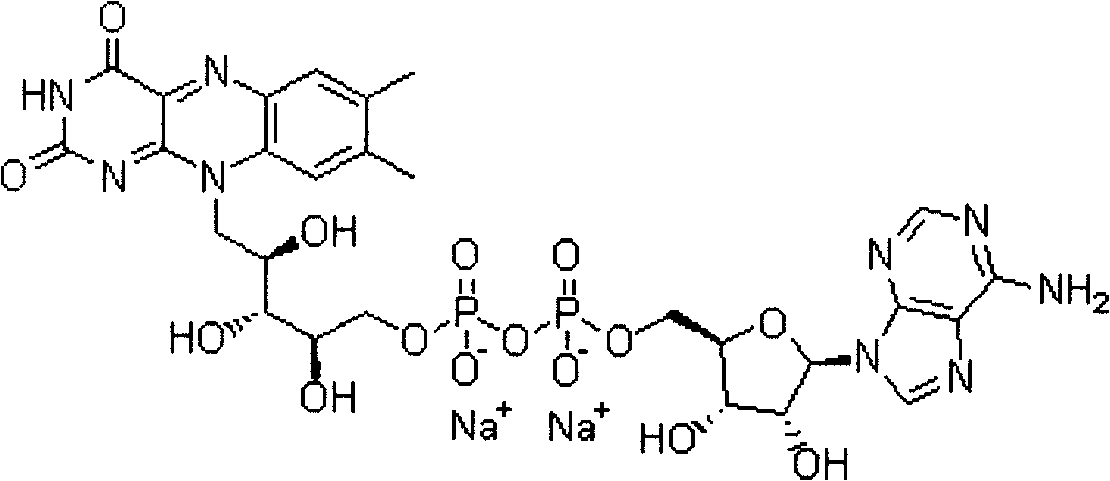
Flavin adenine dinucleotide disodium salt freeze-dried powder needle preparation and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a FAD-Na2 freeze-dried acanthopanax powder spasmolytic preparation and a method for preparing the same. The FAD-Na2 freeze-dried acanthopanax powder spasmolytic preparation is a drug composition made by mixing FAD-Na2 serving as medicinal active ingredients and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The preparation method is as follows: the FAD-Na2 is used as raw material and added with certain spices of excipients according to certain proportions; the mixture is prepared and developed by a technical means provided by the invention into freeze-dried acanthopanax powder spasmolytic agent which can be used for subcutaneous injection, intramuscular and intravenous injection and used to cure a variety of diseases caused by lacks of vitamin B2.
Owner:BEIJING RUNDEKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
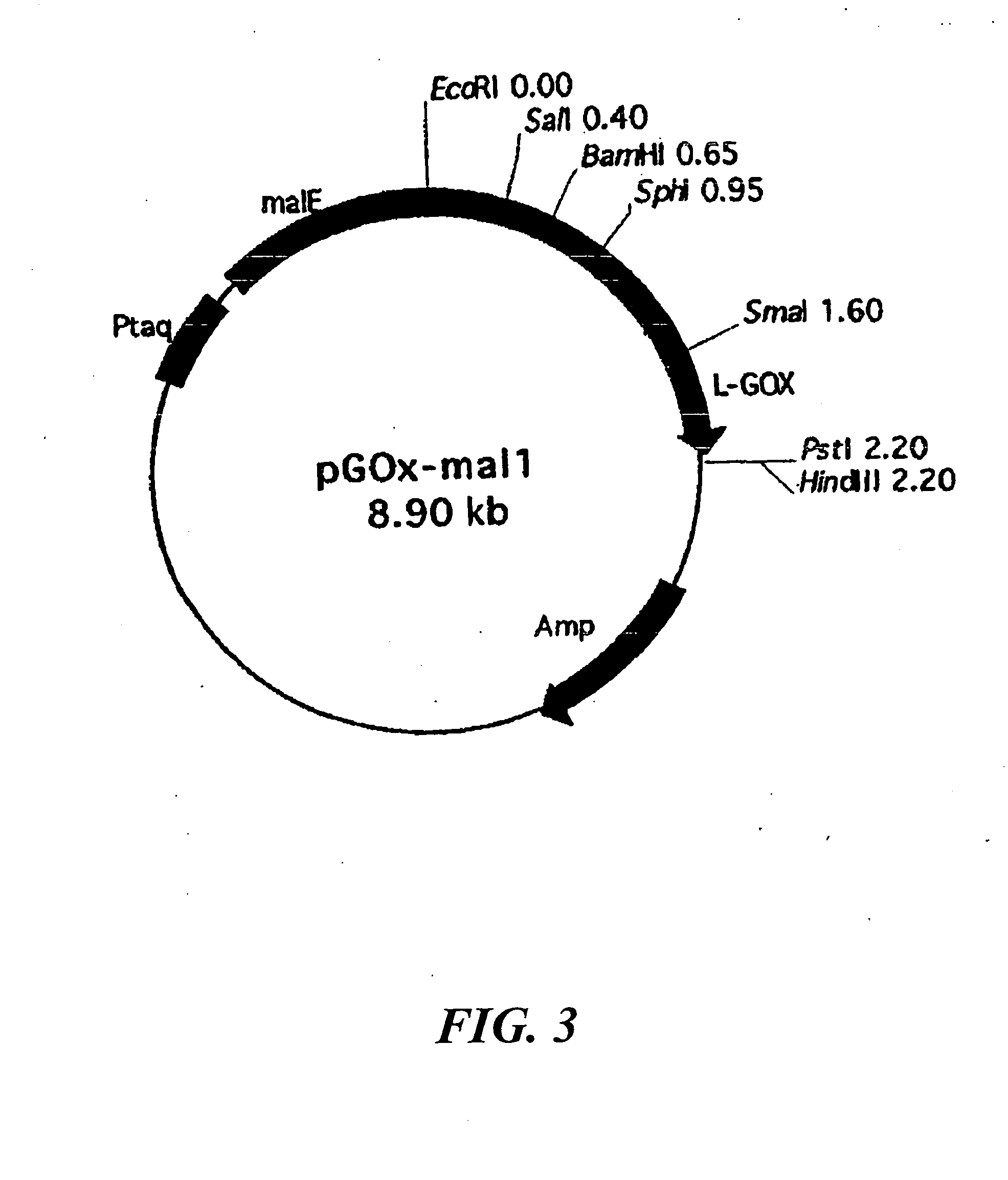
L-glutamate oxidase
The present invention provides a novel L-glutamate oxidase, a gene encoding the enzyme, and a method for producing the enzyme. By use of a gene encoding the enzyme, L-glutamate oxidase can be readily prepared at low costs through a recombinant DNA technique. The novel L-glutamate oxidase has the following physicochemical properties: (A) action: catalyzing the following reaction: L-glutamic acid+O2+H2O→α-ketoglutaric acid+H2O2+NH3; (B) substrate specificity: being specific to L-glutamic acid; (C) molecular weight and subunit structure: molecular weight as determined through SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 70,000±6,000, molecular weight as determined through gel filtration of 140,000±10,000, and being a dimer formed of the same subunits having a molecular weight of 70,000±6,000; (D) optimum pH: around pH 6.0 to 8.5; (E) heat stability: being stable up to 60° C. at a pH of 7.4 for 30 minutes; and (F) coenzyme: flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD).
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU CO LTD
A kind of construction method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae isobutanol high-yielding strain
ActiveCN103789341BIncrease productionHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismMother cells
The invention discloses a construction method of a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with a high yield of isobutanol and relates to preparation of microorganism by a recombinant DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) technology. According to the method, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with the high yield of isobutanol is constructed by reforming saccharomyces cerevisiae cells by using molecular biology and the gene recombination technology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing plasmids of over-expressing ILV2 (Induced Leukemia Virus), ILV3, ILV5 and ZWF1 genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae; and S2, constructing a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain HBGDAL-103 with the high yield of isobutanol. The method disclosed by the invention overcomes the deficiency that further improvement of the yield of isobutanol is restricted by factors such as imbalance of a coenzyme NADPH / NADP<+> (Reduced Form of Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) / (Nicotinamide-Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate<+>) from pyruvic acid to 2-one isovaleric acid due to over-expressed ILV2, ILV3 and ILV5 in the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells of yielding isobutanol in the prior art.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
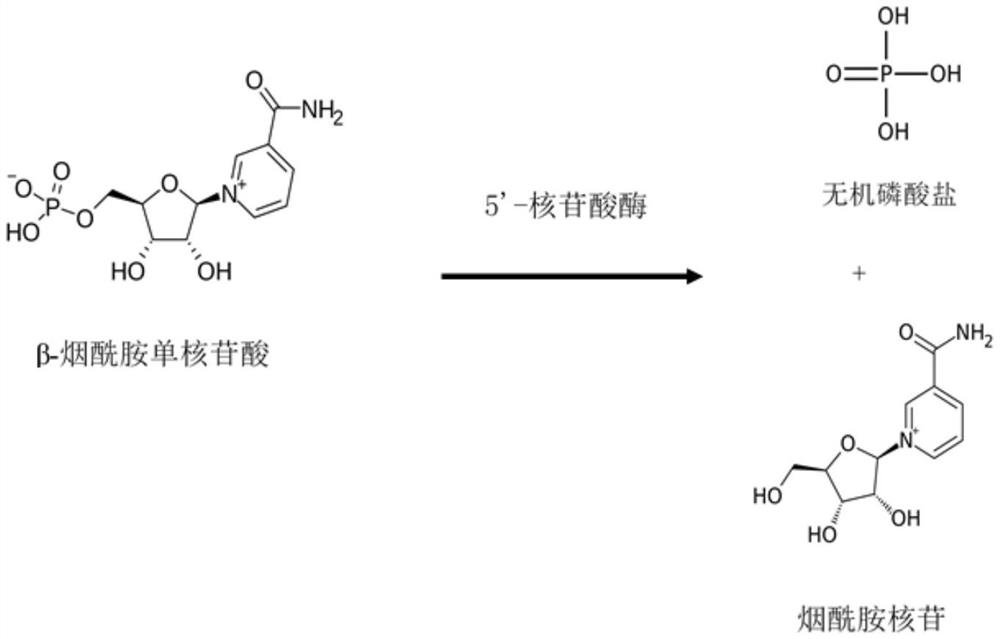
Method for preparing nucleosides of nicotinic acid or derivatives thereof, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide and nicotinic acid mononucleotide, enzyme composition and application
ActiveCN113151378AReduce usageEfficient responseHydrolasesTransferasesChemical synthesisNucleotidase
The invention provides a method for preparing nucleosides of nicotinic acid or derivatives thereof, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide and nicotinic acid mononucleotide, an enzyme composition and application. The method for preparing the nucleosides of the nicotinic acid or the derivatives thereof comprises the step of carrying out reaction by using 5'-nucleotidase and mononucleotide of the nicotinic acid or the derivatives thereof or salt of the mononucleotide as a substrate, wherein the amino acid sequence of the 5'-nucleotidase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. Compared with a chemical synthesis method, the method is safer and more reliable, and is more environment-friendly because the use of an organic solvent can be avoided. Nicotinamide nucleoside can be more effectively produced so as to meet increasing demands.
Owner:BIORIGHT WORLDWIDE
Transhydrogenase-1 activity determination kit and use method thereof
InactiveCN107727589AEliminate distractionsStrong detection specificityColor/spectral properties measurementsInner mitochondrial membraneSucrose
The invention discloses a transhydrogenase-1 activity determination kit and a use method thereof. The kit comprises a mixed solution of a Tris-HCl buffer solution, sucrose and EDTA, a Tris-HCl buffersolution, NADH and AcPyADP. The method is based on the detection principle of replacing the NADP<+> with a synthetic substrate 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (APADP<+>) and calculating TH-1 activity through measuring a light absorption increasing speed at 375nm of APADPH generated by the reduction of APADP<+> catalyzed by TH-1, can effectively eliminate the interference of NAD andhas high detection specificity. Through a simple work liquid, only through adding a sample and a work liquid into a microcuvette or a 96-well plate, the determination is finished and detection is convenient. The kit can effectively isolate cytoplasmic proteins and mitochondrial proteins and accurately determine TH-1 located in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
Owner:SUZHOU COMIN BIOTECH
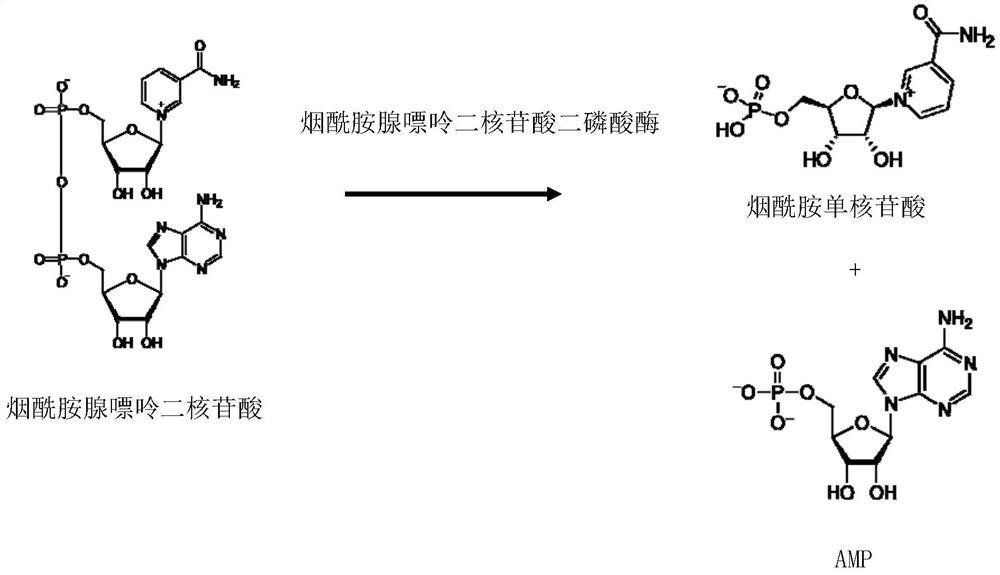
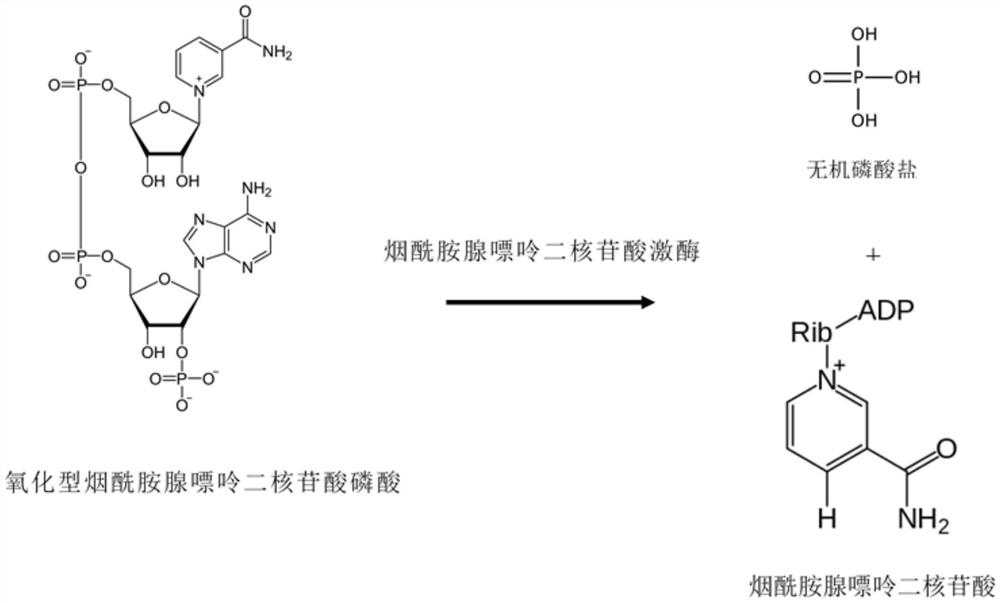
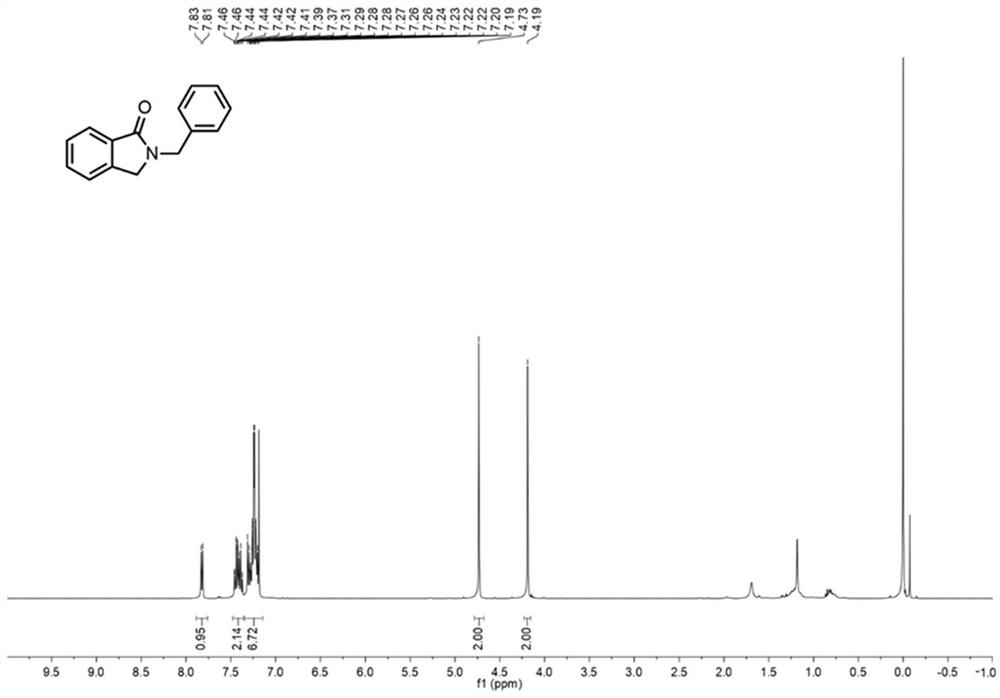
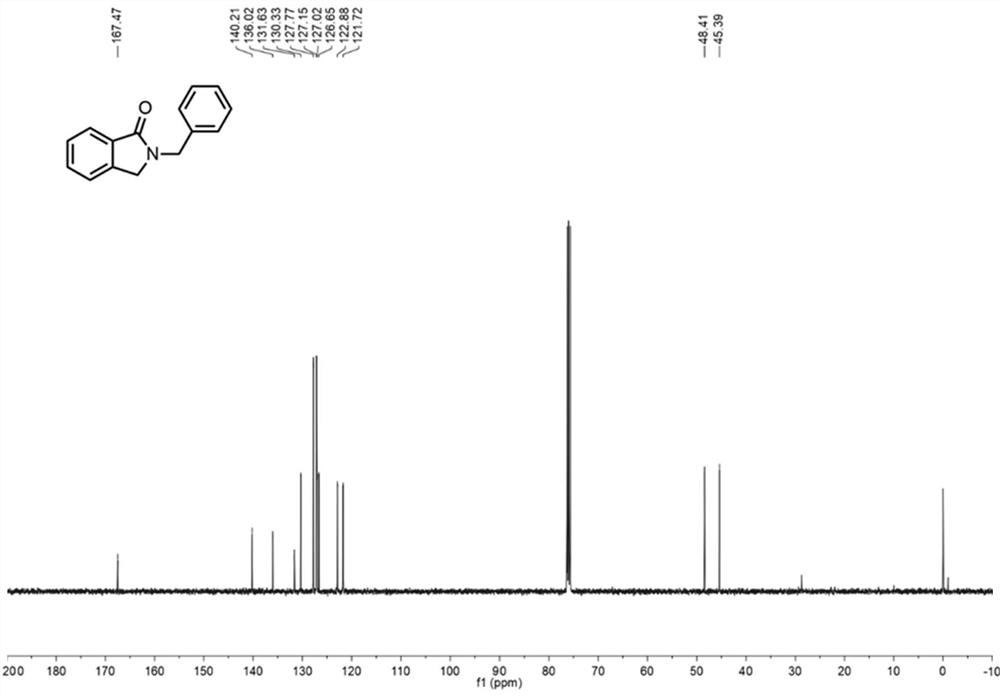
Method for continuously preparing 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound by adopting microchannel reactor
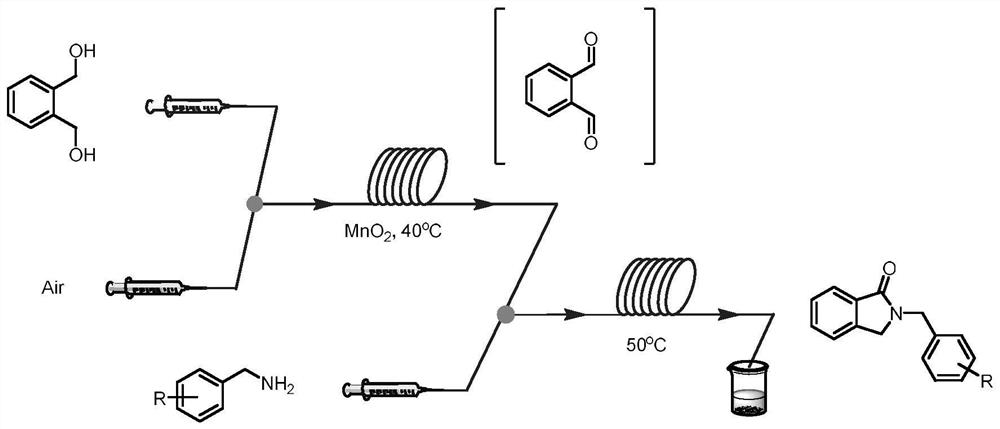
PendingCN113444752AShort reaction timeHigh reaction conversion rateOrganic chemistryFermentationFlavin adenine dinucleotidePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing a 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound by adopting a microchannel reactor, which comprises the following steps: (1) respectively and simultaneously pumping a mixed solution containing 1,2-Benzenedimethanol, alcohol oxidase, flavin adenine dinucleotide and hydrogen peroxide reductase and air into a microchannel reaction device; carrying out a first reaction in a first microreactor containing nano MnO2; and (2) respectively and simultaneously pumping the first reaction effluent and a benzylamine compound solution into a second microreactor, and carrying out a second reaction to obtain the 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound as shown in a formula IV. The method has the advantages of short reaction time, high reaction conversion rate, few side reactions, small toxicity and pollution, low production cost, good product quality and the like, does not use noble metal catalysis in the reaction process, is green, environment-friendly, energy-saving and efficient, is suitable for popularization and application, and solves the problems of long reaction time, harsh reaction conditions and need of noble metal catalytic catalyst in the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Novel weedicide
InactiveCN103749474AInhibition of photophosphorylationDelay drug resistanceBiocideAgriculture gas emission reductionPhosphateSimazine
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural weeding chemicals, and particularly relates to a novel weedicide which is mainly applicable to weeding of sugarcane, corn and sorghum fields. The novel weedicide is characterized by comprising the following active ingredients in percentage by weight: 20-80% of simazine, 20-80% of atrazine, 3-15% of auxiliaries, and the balance of fillers. The novel weedicide belongs to uptake and translocation type weedicide, and inhibits the photophosphorylation action in a plant body through the uptake and translocation of stem leaves and roots of plants, the processes of NADP (nicotinamide - adenine dinucleotide phosphate) reduction and CO2 fixation and the like, damages the photosynthesis of plants, and influences the absorption of nutrients in weeds so as to stop the growth of plants. According to the novel weedicide, two ingredients have synergistic interaction, the weedicide controlling spectrum can be effectively extended, various weeds can be prevented through once application, the application amount of the weedicide can be greatly decreased, the cost can be lowered and the adverse effect on the environment can be reduced, the drug resistance of the weeds can be postponed, and the defects that the drug resistance of the weeds due to long-time use of one weedicide is increased, weedicide effect is decreased, and the like can be overcome.
Owner:DALIAN ZHAOYANG SOFTWARE TECH
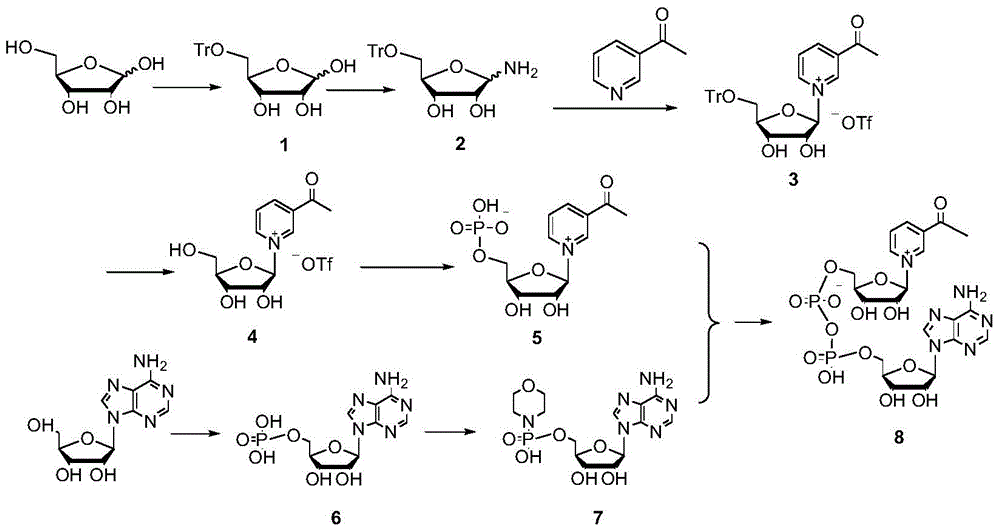
Synthetic method of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide
InactiveCN103601780ALow priceEasy to buySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical synthesisMorpholine
The invention discloses a chemical synthesis method of 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide, comprising the following steps: (1) D-ribose is used as a starting material to prepare monophosphate-3-acetylpyridine-alpha-D-nucleoside; (2) adenosine is used as a main raw material to prepare morpholine adenosine monophosphate; and (3) a docking reaction between morpholine adenosine monophosphate and monophosphate-3-acetylpyridine-alpha-D-nucleoside is carried out to prepare 3-acetylpyridine adenine dinucleotide. According to the chemical synthesis method, a commercial industrial product D-ribose is used as the starting raw material; any enzyme is not used during the preparation process of an intermediate; price of raw materials is low and the raw materials are easy to purchase; and production cost of the product is reduced greatly. In addition, by the chemical synthesis method, yield of the product is high, and total yield of the reaction is 4.2% and is remarkably higher than product yield of a present biosynthesis method.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
Nicotinamide ribose derivative cosmetic raw material and application thereof in cosmetics
PendingCN110934768AAvoid damageAnti agingCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsNicotinamide ribosideNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a nicotinamide ribose derivative cosmetic raw material and an application thereof in cosmetics. The nicotinamide ribose derivative cosmetic raw material comprises the followingcomponents in parts by weight: 15 to 20 parts of nicotinamide ribose chloride; 10 to 14 parts of dihydronicotinamide ribose, 10 to 12 parts of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide, 4 to 7 parts of NAD4,3 to 5 parts of NADH, 4 to 6 parts of oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide sodium salt, 4 to 6 parts of thiooxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and 4 to 6 parts of oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide lithium salt, and the nicotinamide ribose derivative cosmetic raw material relates to the technical field of cosmetics. The invention discloses the nicotinamide ribose derivative cosmetic raw material and the application thereof in cosmetics, the nicotinamide ribose and derivatives thereof can improve the mitochondrial function in cells; mitochondrial function decline is closely related to human aging, functions of sirtuin are activated, mitochondrial activity is improved, and cell damage caused by free radicals is prevented, so that the effect of delaying cell aging is achieved, functions of epidermal cells and other cells in a human body are improved, skin health can be maintained, and skin aging is delayed.
Owner:深圳市龙格生技术有限公司
Palladium nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber compound, preparation method and application thereof in electrocatalysis
ActiveCN101665232BGood dispersionImprove stabilityIndividual molecule manipulationMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanofiberPalladium nanoparticles
The invention relates to a palladium nanoparticle / carbon nanofiber compound, a preparation method and an application thereof in electrocatalysis. The compound is directly prepared by a one-step electrospinning method. An electrode modified by the compound is used for direct eectrochemical detection on hydrogen peroxide, beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dopamine, ascorbic acid and lithic acid. The electrode modified by the compound has the linear range from 0.2 micrometer to 20 millimetres and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the hydrogen peroxide and has the linear range of 0.2-716.6 micrometers and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the beta- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and the peak-peak potential differences between the ascorbic acid and the dopamine, the dopamine and the lithic acid as well as the ascorbic acid and the lithic acid are respectively 244mV, 148 mV and 392 mV, thereby showing that the modified electrode can be used for simultaneous eectrochemical detection of three substances. The compound can be used in the fields of catalysis, fuel cells and sensing.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Transformant transfected with flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase gene and method for producing flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the same
It is intended to highly efficiently produce a large amount of novel FAD-GDH capable of more accurately measuring a glucose level. A transformant transfected with a DNA encoding a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase selected from the group consisting of (a) a DNA encoding an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 20; (b) a DNA composed of a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 19; (c) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 19 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenaseactivity; (d) a DNA encoding an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 34; (e) a DNA composed of a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 33; and (f) a DNA having a base sequence homologous to the base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 33 and encoding a protein having a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase activity is provided. Further, a method for producing a flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding glucose dehydrogenase using the transformant is provided.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Fusion enzyme and application of fusion enzyme in paper-based biosensor
ActiveCN112851821AImprove performanceHigh detection sensitivityPolypeptide with affinity tagOxidoreductasesFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose sensors
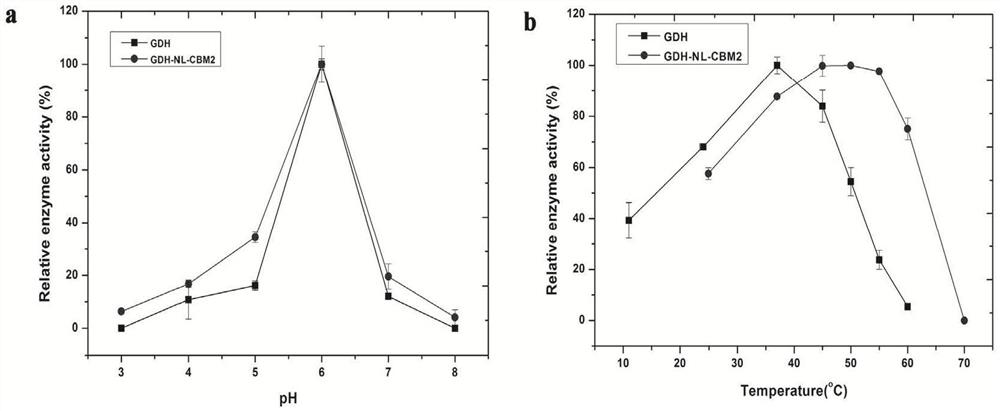
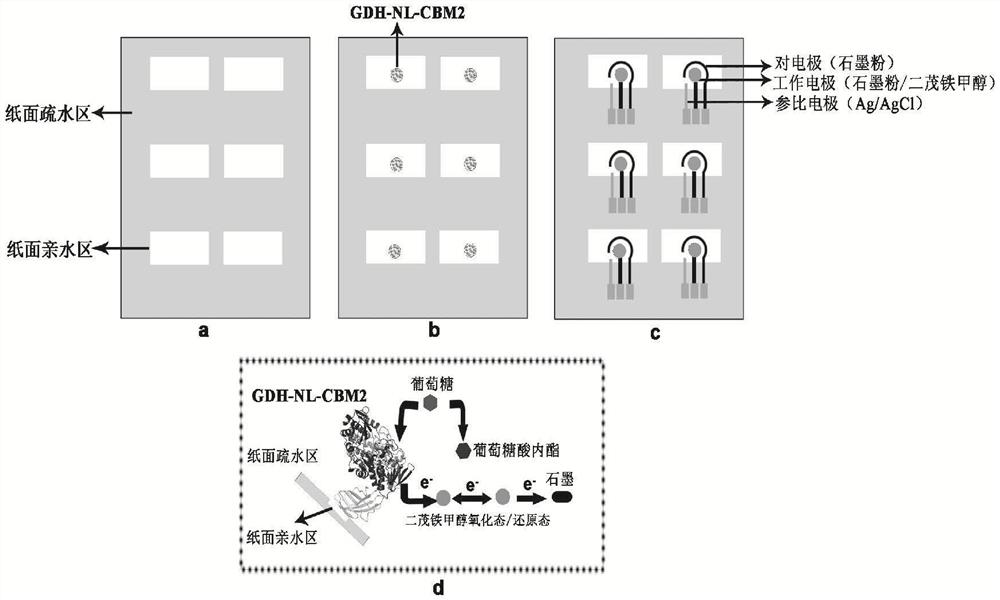
The invention particularly relates to a fusion enzyme and application of the fusion enzyme in a paper-based biosensor. Glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) taking flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) as a coenzyme has good stability, is developed into a portable glucose sensor and has a good application prospect. The invention provides a GDH-linker-CBM fusion enzyme constructed by a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) dependent glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) gene and a carbohydrate binding module (CBM) gene, and the GDH-linker-CBM fusion enzyme is prepared into a paper-based sensor through the modification effect of the carbohydrate binding module and a connecting peptide. The enzyme activity, the detection sensitivity and the anti-interference capability of the paper-based sensor are effectively improved, and a good market development prospect is realized.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method for carrying out reductive amination reaction by adopting microchannel reaction device
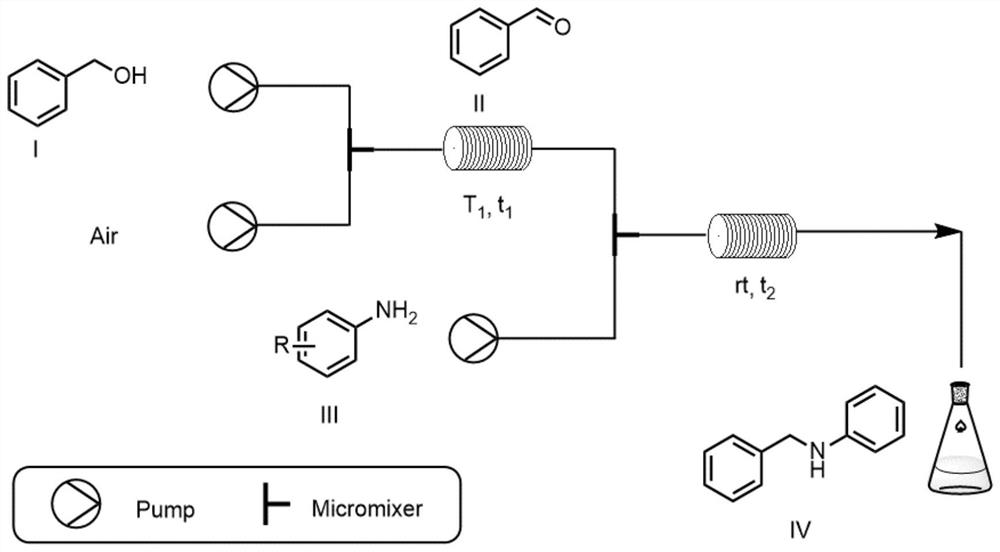
ActiveCN113801025AShort reaction timeHigh reaction conversion rateAmino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationFlavin adenine dinucleotideNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for carrying out reductive amination reaction by adopting a microchannel reaction device. The microchannel reaction device comprises a microreactor 1 and a microreactor 2 which are connected in series, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution containing benzyl alcohol, alcohol oxidase, flavin adenine dinucleotide and hydrogen peroxide reductase as a first homogeneous solution, and preparing a solution of an aniline compound III as a second homogeneous solution; (2) mixing the first homogeneous solution with air, and simultaneously pumping a formed mixture into a microreactor 1 for reaction; and (3) mixing the reaction solution obtained in the step (2) with the second homogeneous solution, and simultaneously pumping a formed mixture into a microreactor 2 for reaction to obtain the N-benzylaniline compound as shown in a formula IV. The microreactor disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high reaction safety, convenience in cleaning, easiness in amplification and the like. Meanwhile, compared with the prior art, the synthesis method has the advantages of simple, cheap and easily available initial materials, simple operation and high reaction efficiency, and is expected to be applied to industrial production.
Owner:NANJING ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS & PROCESS EQUIP INST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com