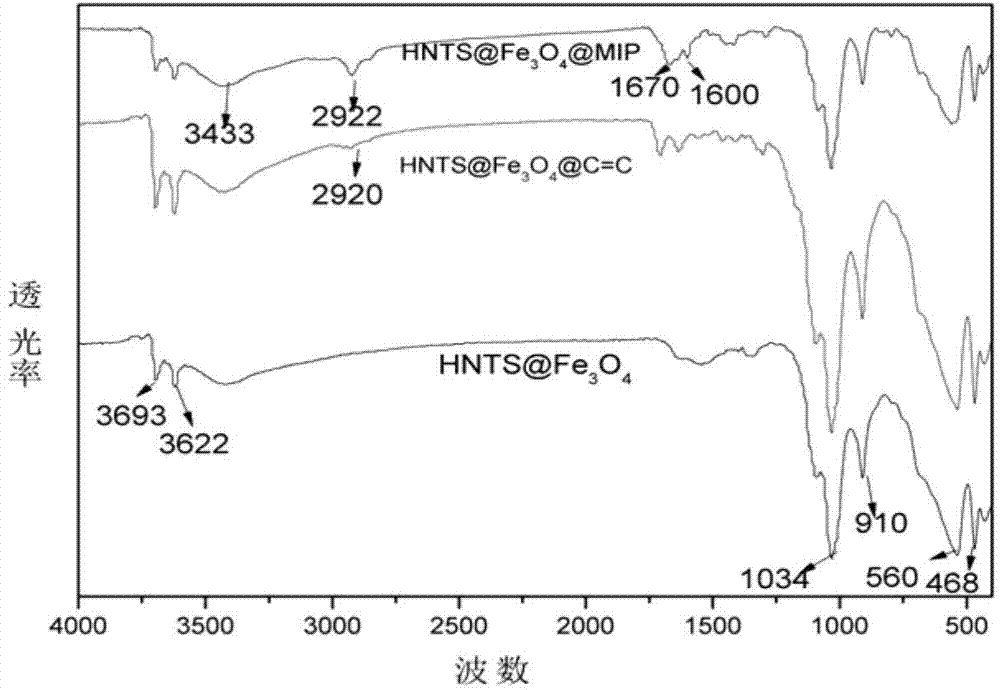
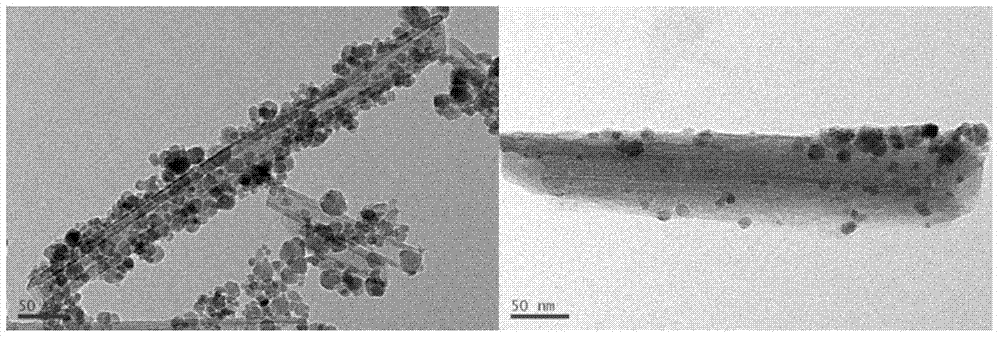
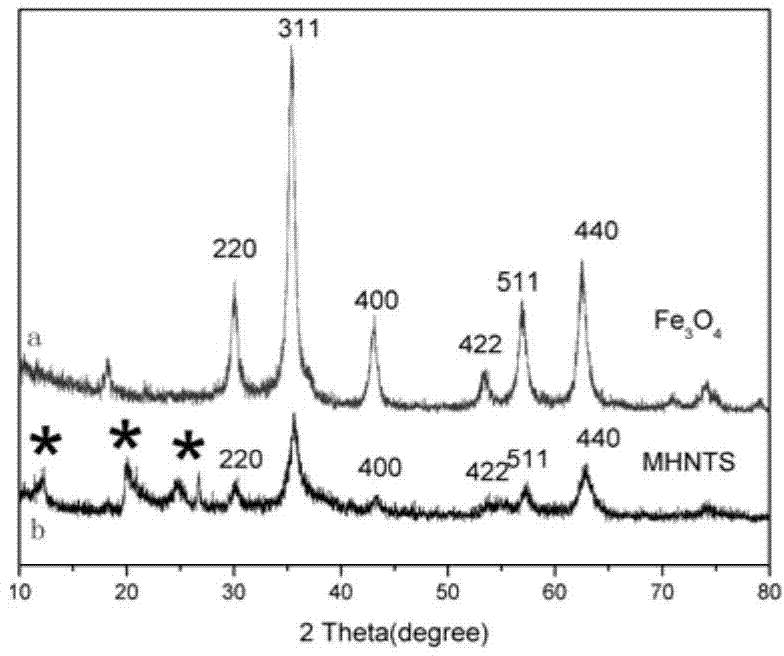
Method for preparing magnetic halloysite molecularly imprinted polymer with specific adsorption to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
A dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, molecular imprinting technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes and other directions, can solve the problems of time-consuming, laborious, and low removal efficiency of removal methods, achieve good reusability, and be conducive to repeated service life. , The effect of high-efficiency selective separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Co-precipitation method to prepare corroded magnetic halloysite nanotubes (HNTS-Fe 3 o 4 )
[0040] Disperse 2g of halloysite nanotube particles in 100mL of 2mol / L dilute sulfuric acid solution, stir magnetically in a 60°C water bath for 12h after ultrasonication, filter, wash with a large amount of distilled water until PH = 7, and dry under vacuum at 50°C to obtain a partially corroded inner wall Corroded halloysite nanotubes (HNTS) after expansion.
[0041] Corroded halloysite nanotubes, anhydrous ferric chloride, and ferrous chloride tetrahydrate were dissolved in 200mL deionized water according to the mass ratio of 0.2:0.69:0.51, and 5wt% (based on the total mass of the mixture) of polyethylene After the alcohol (PVA) is ultrasonically dispersed, under the protection of nitrogen, stir magnetically in a water bath at 60°C for 1 hour; add 12 mL of concentrated ammonia water to the above mixture dropwise, and control the dropping time for 30 minutes, then adjust...
Embodiment 2
[0051] (1) Co-precipitation method to prepare corroded magnetic halloysite nanotubes (HNTS-Fe 3 o 4 )
[0052] Disperse 2g of halloysite nanotube particles in 100mL of 2mol / L dilute sulfuric acid solution, ultrasonically stir in a water bath at 60°C for 12h, filter, wash with a large amount of distilled water until pH = 7, and dry under vacuum at 50°C to obtain the inner wall part Corroded halloysite nanotubes (HNTS) expanded after etching.
[0053] Corroded halloysite nanotubes, ferric chloride hexahydrate, and ferrous sulfate heptahydrate were dissolved in 200 mL of deionized water according to the mass ratio of 0.25:0.466:0.3, and 5 wt % (based on the total mass of the mixture) of polyethylene glycol was added. Alcohol 2000 (PEG-2000) was ultrasonically dispersed, and then magnetically stirred in a 50°C water bath for 1 h under nitrogen protection; 12 mL of concentrated ammonia water with a volume fraction of 28% was added dropwise to the above mixture, and the dropping t...
Embodiment 3
[0061] The adsorption amount detection of the magnetic halloysite nano-molecularly imprinted polymer of Example 1: the process is as follows: put 5 mg of the magnetic halloysite nano-molecularly imprinted polymer of Example 1 into 5 mL of substrate with a concentration of 80 mg / In the 2,4-D solution of L, put it on a rotary shaker and oscillate to mix well. During the oscillation process, use a magnet at different time intervals of 5min, 10min, 15min, 20min, 30min, 40min, 50min, 60min, and 80min. Separation, take the supernatant, test the absorbance to calculate the concentration after adsorption equilibrium, according to the concentration difference before and after according to the formula Q e =(C o -C e )×V / m, where C o and C e is the initial concentration of 2,4-D and the concentration after adsorption, V is the solution volume, and m is the mass of polymer adsorption material. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the adsorption time can reach the adsorption equil...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com