Heat-resistant steel for ultra-supercritical steam turbine rotor
A steam turbine rotor and ultra-supercritical technology, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve the problem that the ultra-supercritical steam turbine rotor cannot meet the 620 ℃ requirement of the ultra-supercritical steam turbine unit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
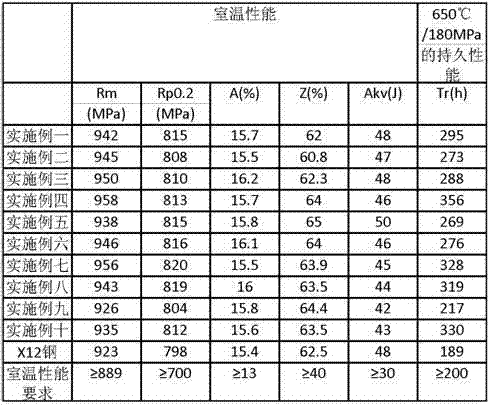
[0018] To process a heat-resistant steel for an ultra-supercritical steam turbine rotor, the raw material composition of the constituent elements is vacuum smelted and poured in sequence according to the following proportions, carbon (C): 0.1; manganese (Mn): 0.2; chromium (Cr): 11.00; cobalt (Co): 3.0; molybdenum (Mo): 0.75; tungsten (W): 1.7; nickel (Ni): 0.25; vanadium (V): 0.15; niobium (Nb): 0.072; ;The balance is Fe and impurity elements, of which impurity elements sulfur (S)≤0.010; phosphorus (P)≤0.012; copper (Cu)≤0.15; aluminum (Al)≤0.010; tin (Sn)≤0.010; )≤0.0015 parts; arsenic (As) ≤0.020; silicon (Si) ≤0.12; H ≤1.0ppm; For the mechanical property test, the mechanical properties of the tested material at room temperature and the durability of the material under the conditions of 650°C and 180Mpa in a short-term high-temperature endurance test are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0020] To process a heat-resistant steel for an ultra-supercritical steam turbine rotor, vacuum smelt and cast the raw material composition of the constituent elements in sequence according to the following proportions, carbon (C): 0.11; manganese (Mn): 0.2; chromium (Cr): 10.5; cobalt (Co): 2.4; molybdenum (Mo): 0.9; tungsten (W): 1.4; nickel (Ni): 0.23; vanadium (V): 0.2; niobium (Nb): 0.08; nitrogen (N): 0.03 ;The balance is Fe and impurity elements, of which impurity elements sulfur (S)≤0.010; phosphorus (P)≤0.012; copper (Cu)≤0.15; aluminum (Al)≤0.010; tin (Sn)≤0.010; ) ≤ 0.0015 parts; arsenic (As) ≤ 0.020; silicon (Si): 0.115; H ≤ 1.0ppm; Mechanical properties test; the tested mechanical properties of the material at room temperature and the durability of the material in the short-term high temperature endurance test under the conditions of 650°C and 180Mpa are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0022] To process a heat-resistant steel for an ultra-supercritical steam turbine rotor, the raw material composition of the constituent elements is vacuum smelted and poured in sequence according to the following proportions, carbon (C): 0.125; manganese (Mn): 0.2; chromium (Cr): 10.35; cobalt (Co): 3.1; molybdenum (Mo): 0.82; tungsten (W): 1.5; nickel (Ni): 0.24; vanadium (V): 0.2; niobium (Nb): 0.08; nitrogen (N): 0.03 ;The balance is Fe and impurity elements, of which impurity elements sulfur (S)≤0.010; phosphorus (P)≤0.012; copper (Cu)≤0.15; aluminum (Al)≤0.010; tin (Sn)≤0.010; ) ≤ 0.0015 parts; arsenic (As) ≤ 0.020; silicon (Si): 0.115; H ≤ 1.0ppm; Mechanical properties test; the tested mechanical properties of the material at room temperature and the durability of the material in the short-term high temperature endurance test under the conditions of 650°C and 180Mpa are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com