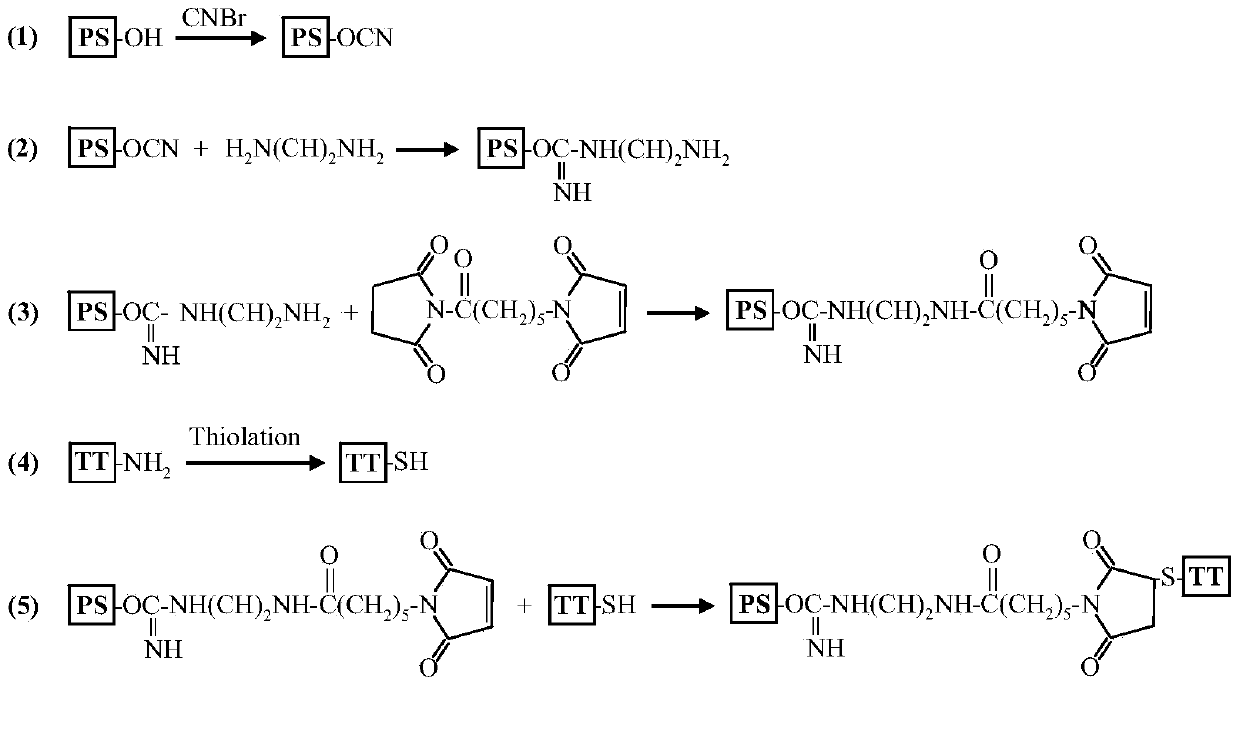
Meningitis polysaccharide conjugate vaccine and preparing method thereof
A combined vaccine and meningitis technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as restricting the development of polysaccharide conjugate vaccines, reducing polysaccharide-protein binding efficiency, and reducing polysaccharide immunogenicity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
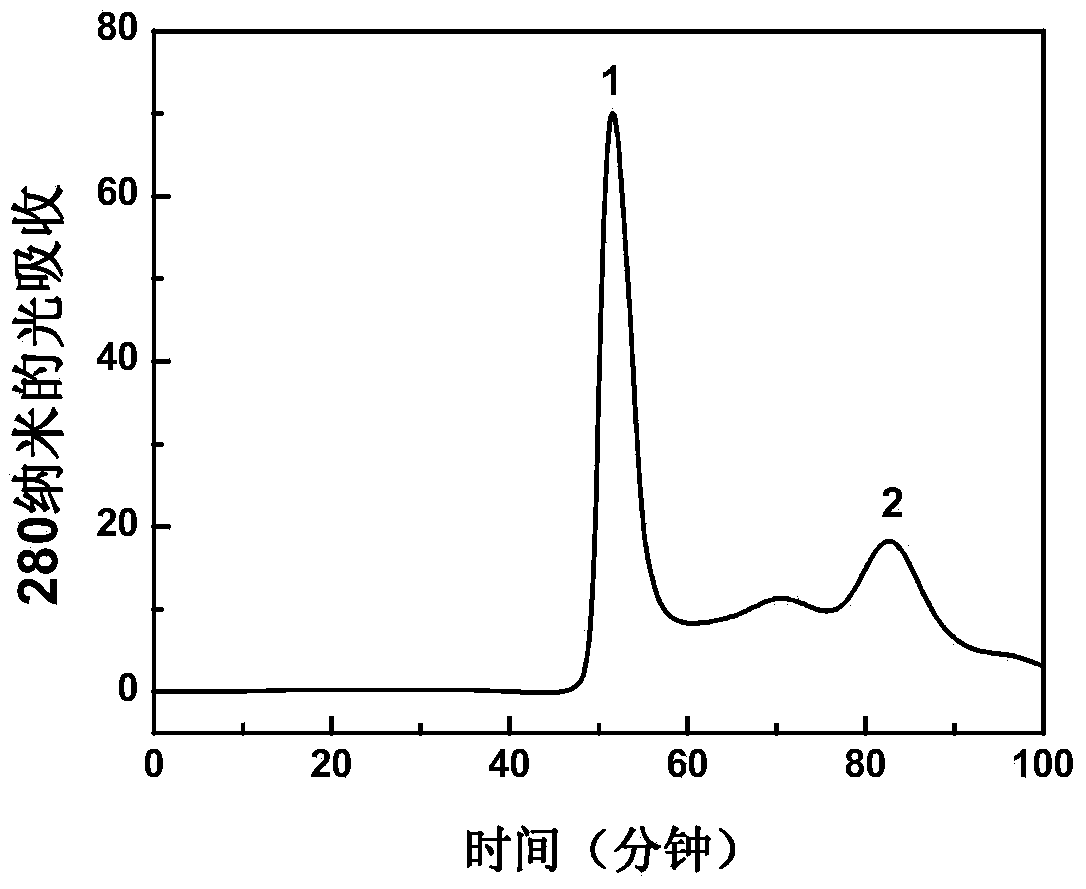
[0021] Example 1: Preparation and separation and purification of group A meningitis polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
[0022] (1) Activation and derivation of meningitis group A polysaccharides
[0023] The preparation reaction of group A meningitis polysaccharide conjugate vaccine is as follows: figure 1 shown. Dissolve 16 mg of group A meningococcal capsular polysaccharide in 4 ml of normal saline, and adjust the pH to 10.8 with 0.2 M NaOH. Add 32 microliters of 50% (w / v) cyanogen bromide solution for activation, and react at room temperature for 1 hour. During the activation process, the pH of the solution was maintained at 10.8 with 0.2M NaOH as the pH decreased continuously. After the activation, the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 8.5 with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, and 1 ml of ethylenediamine solution with a concentration of 32 mg / ml was added. The pH value of the solution was reduced to about 5.0, and then the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 8.0 wit...
Embodiment 2
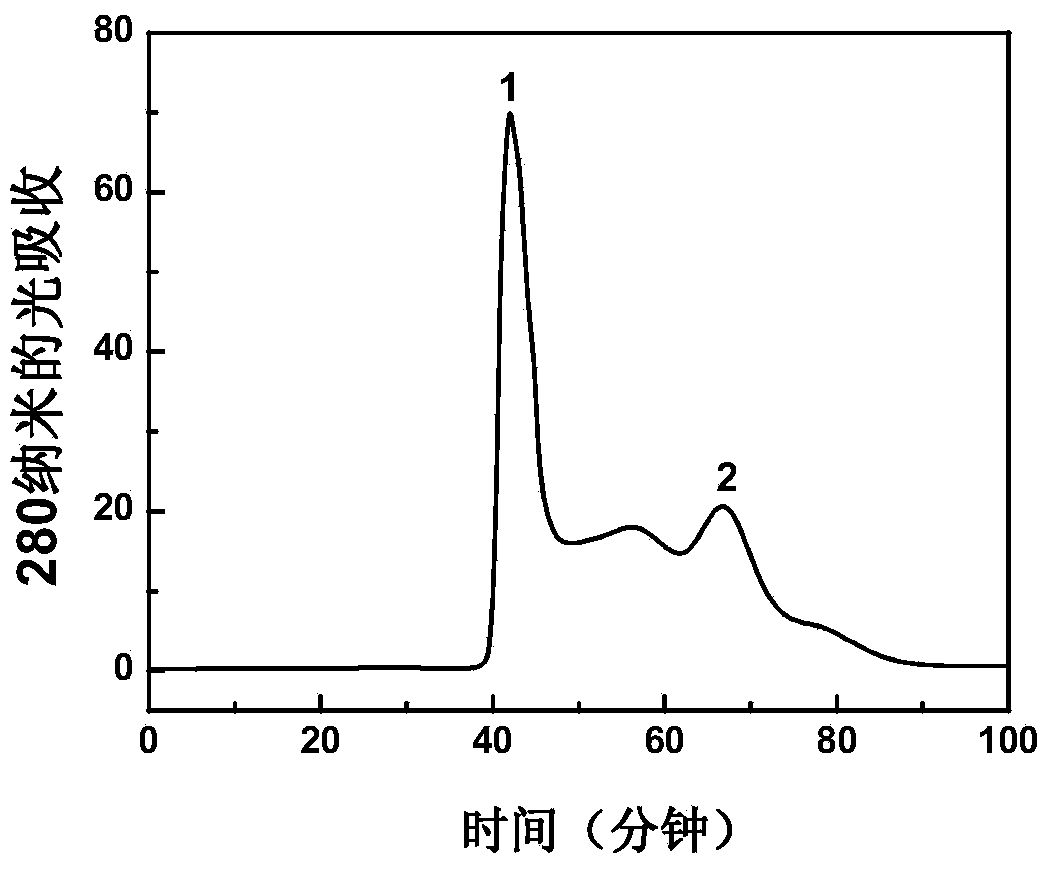
[0031] Example 2: Preparation and separation and purification of group C meningitis polysaccharide conjugate vaccine
[0032] (1) Activation and derivation of group C meningitis polysaccharides
[0033] The preparation reaction of group C meningitis polysaccharide conjugate vaccine is as follows: figure 1 shown. Dissolve 16 mg of group C meningococcal capsular polysaccharide in 4 ml of normal saline, and adjust the pH to 10.8 with 0.2 M NaOH. Add 32 microliters of 50% (w / v) cyanogen bromide solution for activation, and react at room temperature for 1 hour. During the activation process, the pH of the solution was maintained at 10.8 with 0.2M NaOH as the pH decreased continuously. After the activation, the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 8.5 with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, and 1 ml of ethylenediamine solution with a concentration of 48 mg / ml was added. The pH value of the solution was reduced to about 5.0, and then the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 8.0 wit...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: SD-PAGE electrophoresis identification polysaccharide conjugated vaccine
[0042] Group A and C polysaccharide conjugate vaccines were identified by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. like Figure 4 As shown, tetanus toxoid showed two main electrophoresis bands (lane 2) on the SDS-PAGE electrophoresis graph. Group A polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (lane 3) and group C polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (lane 4) also showed 2 major electrophoresis bands, but their migration rates were significantly slower than those corresponding to tetanus toxoid. This indicates that the group A and group C polysaccharide conjugate vaccines have very high molecular weight and are significantly larger than tetanus toxoid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com