Method for improving ionic rare earth extraction rate and mine tailing safety
An ionic rare earth, safe technology, applied in the fields of mine environmental protection, rare earth chemical beneficiation and hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of rare earth resource waste, achieve the effect of improving recycling rate, reducing ammonium consumption, and reducing landslide risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
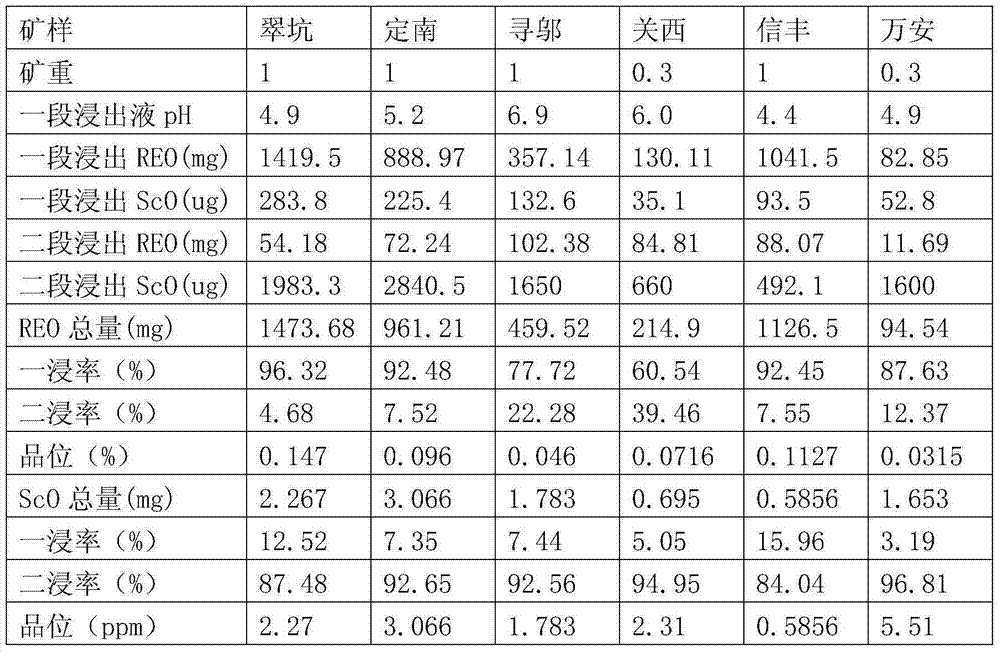
[0016] Take 1 kg of ore from 6 different origins (marked as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) respectively, put them into a glass column with a diameter of 50 mm, and first use 2% ammonium sulfate solution at a liquid-solid ratio of 0.8 :1 leaching, and then use 2% ammonium sulfate solution of pH 1 to leaching the ore with a liquid-solid ratio of 0.4:1. The leachate was collected separately, and the total amount of rare earth and scandium oxide content were analyzed. The results are listed in Table 1.
[0017] Table 1 Comparison of two-stage leaching effects of several representative ionic rare earth ores
[0018]
[0019]
[0020] It can be seen from the results in Table 1 that the content of rare earths in ores from different origins is different, and the proportion of rare earths leached from neutral salts to the total ionic phase is also different. Among them, by increasing the acid leaching process in Kanxi and Xunwu rare earth mines, the secondary leaching rates exceeded 20% a...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Naturally air-dry the rare earth raw ore samples at a depth of 1m in GX-S2 mine, and take samples under a 20-mesh sieve for rinsing experiments. According to the liquid-solid ratio of 0.2:1, it is ejected with water, which is the main content of the technology used in mines at present. Continue to fully rinse with water, which is equivalent to simulating the rainwater leaching process in mines. The analysis of the leachate can explain the situation of mine wastewater under natural rainwater leaching; finally, it is fully exchanged with 10% NaCl solution, and the analysis of the leachate can explain the residues in the mine. The ammonia nitrogen content in the ore and the residual rare earth content. The results obtained are shown in Table 1
[0023] Table 2 GX-S2 ionic rare earth ore ammonium sulfate leaching and sodium chloride washing exchange experiment results (mg / kg)
[0024]
[0025] The results in Table 2 show that the amount of rare earth leached according ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Naturally air-dry the rare earth raw ore samples at a depth of 1m in GX-S2 mine, and take samples under a 20-mesh sieve for rinsing experiments. With a liquid-solid ratio of 0.2:1, use a 2% ammonium sulfate solution of pH 2 to leaching out, and then push out with water according to a liquid-solid ratio of 0.2:1. The results obtained are shown in Table 3:
[0029] Table 3 GX-S2 ionic rare earth ore neutral-acidic salt two-stage leaching test results
[0030]
[0031] Comparing the results in Table 3 with the results in Table 2, when the last quarter of the original neutral ammonium sulfate leaching is replaced by acidic ammonium sulfate leaching, the amount of rare earth leached with a liquid-solid ratio of 1:1 can be increased. , but the leaching amount did not increase when the liquid-solid ratio was 0.8:1, but more rare earths were obtained in the subsequent water topping process. It shows that the increase of rare earth leaching caused by the addition of acid will ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com