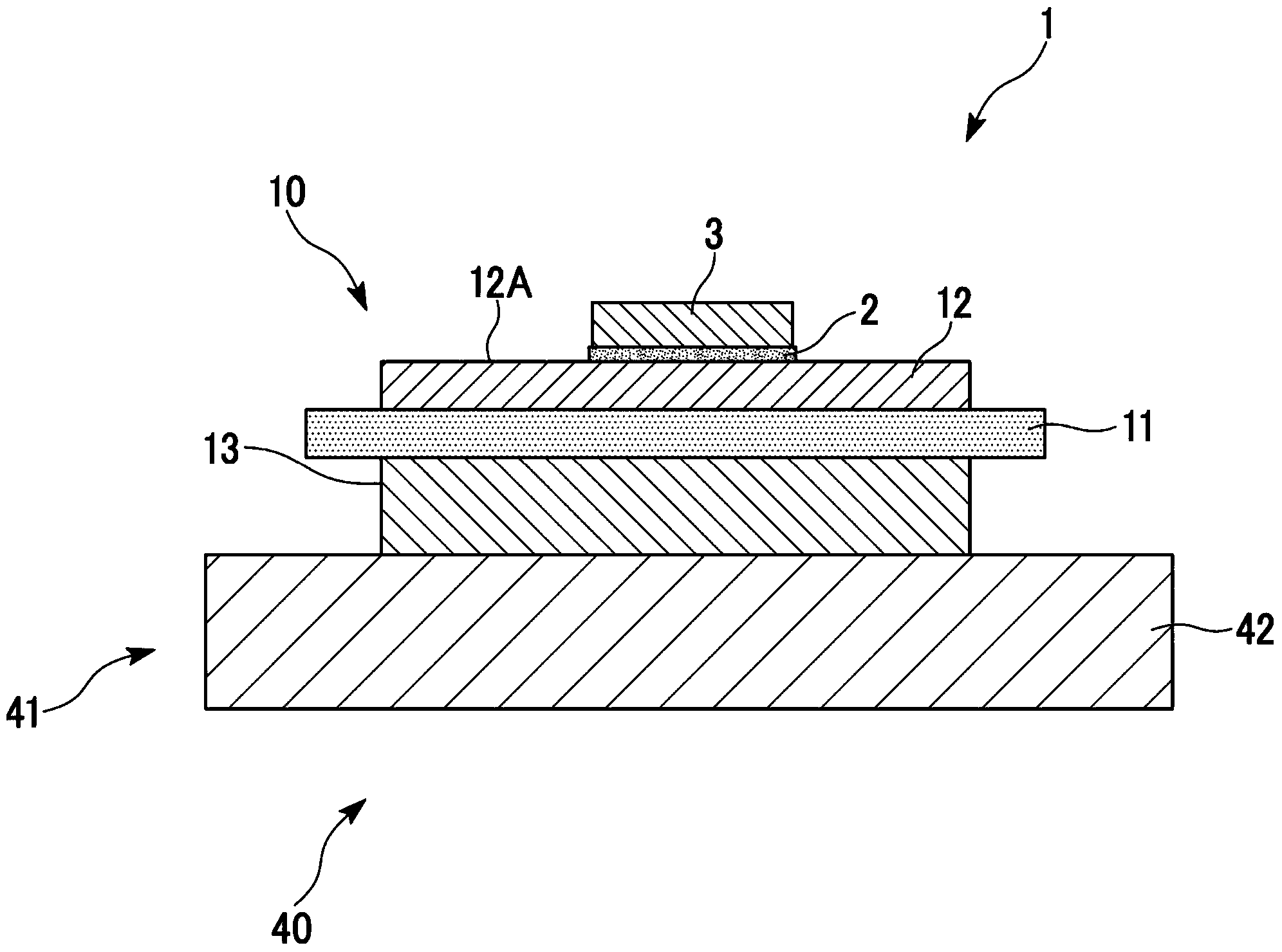
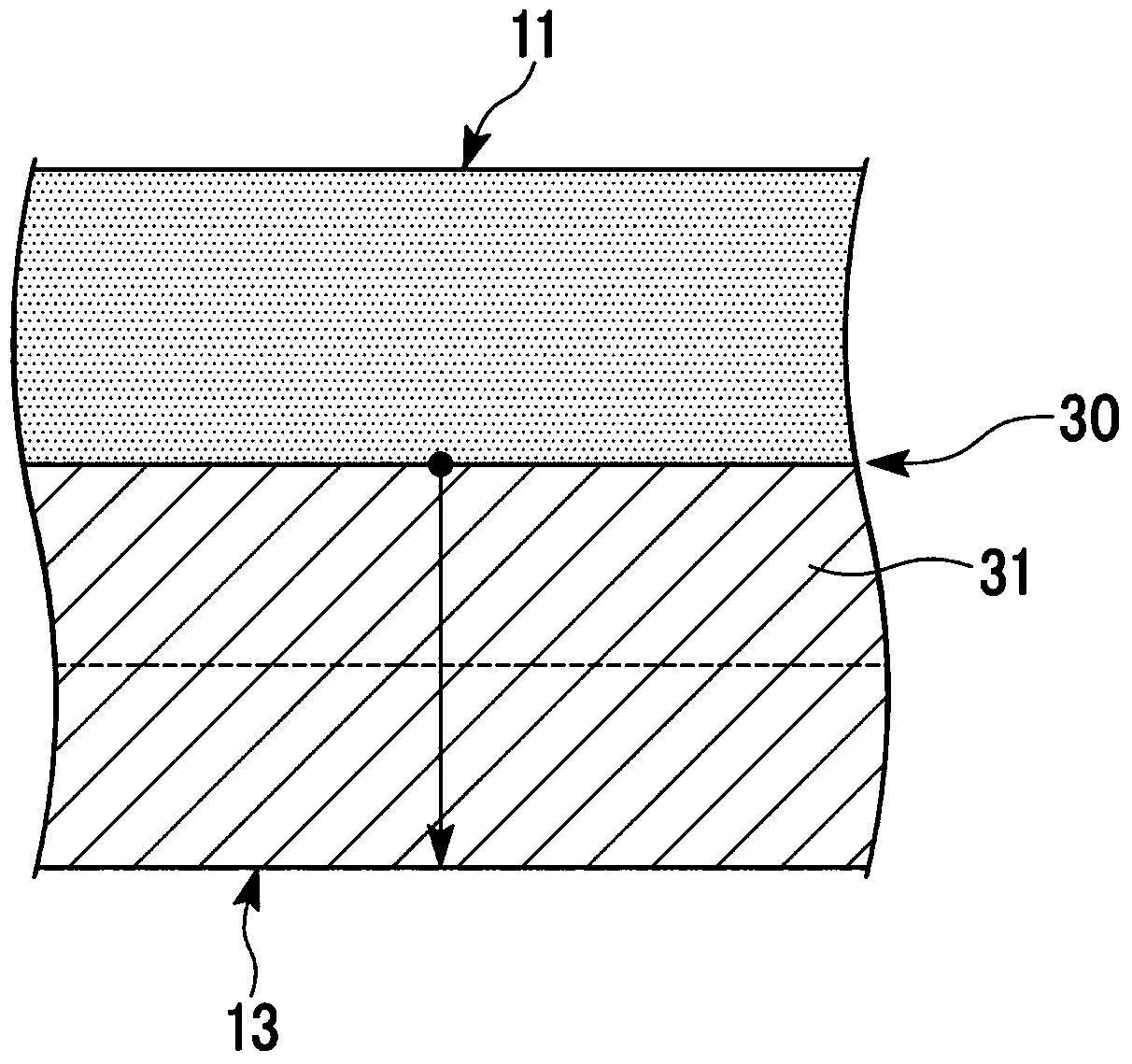
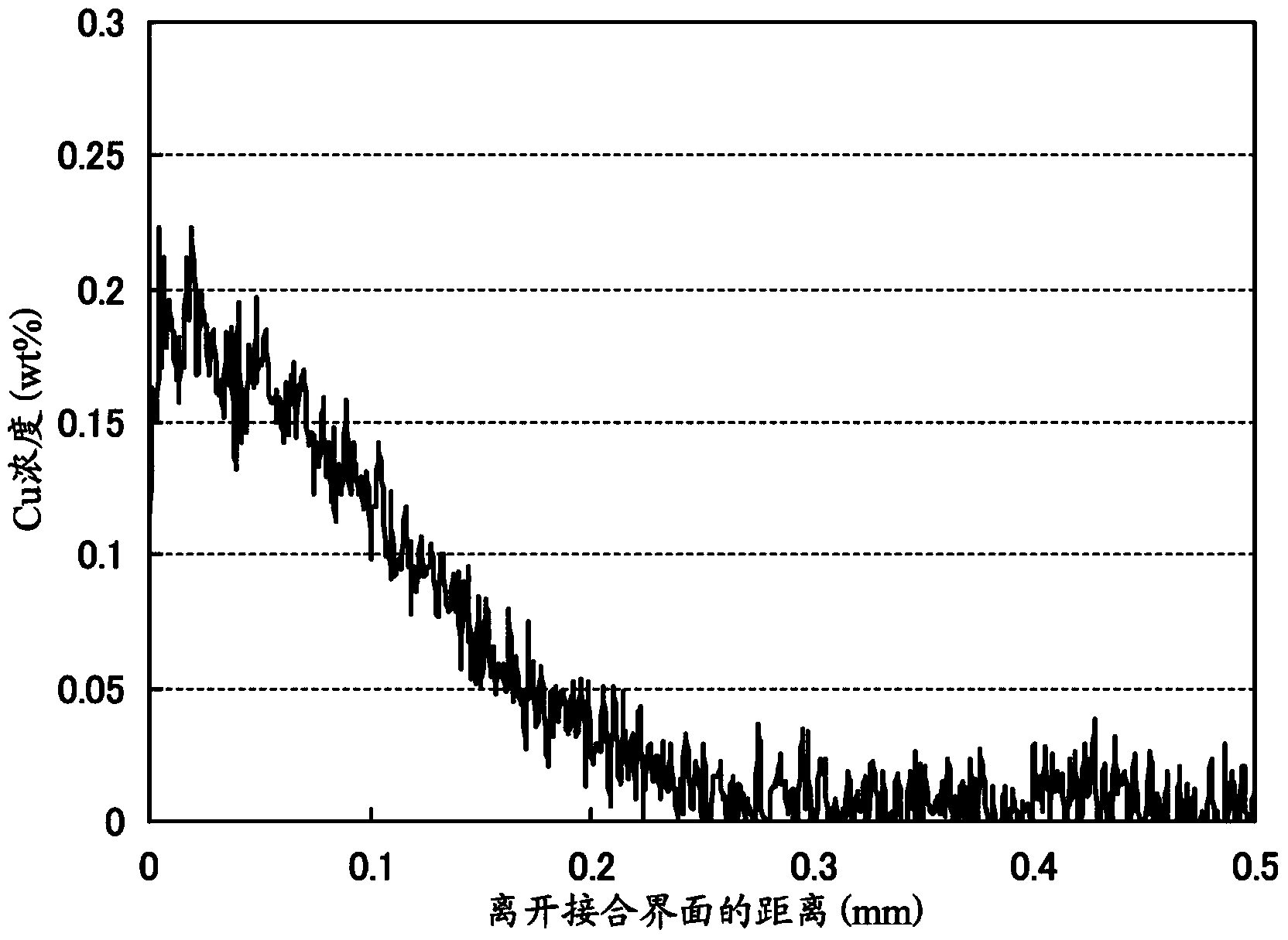
Substrate for power module, substrate for power module with heat sink, power module, and method for manufacturing substrate for power module
A technology for power modules and substrates, which is used in the improvement of metal adhesion of insulating substrates, manufacturing tools, circuit substrate materials, etc., and can solve the problems of cracking of insulating substrates and inability to fully alleviate thermal deformation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0248] A comparative experiment performed to confirm the effectiveness of the present invention will be described.
[0249] Prepare a ceramic substrate made of AlN with a thickness of 0.635mm, and a ceramic substrate with a thickness of 0.3mm made of doped copper, oxygen-free copper (OFC) and tough copper (TPC) with the composition shown in Table 1. A copper plate, and an aluminum plate with a thickness of 1.6 mm made of aluminum (4NAl) with a purity of 99.99% by mass.
[0250] These ceramic substrates, copper plates, and aluminum plates are joined by the method described in the third embodiment. Set the pressing pressure in the circuit layer forming step S201 to 0.5 gf / cm 2 , Set the heating temperature to 850°C. In addition, the pressing pressure in the first metal layer forming step S202 was set to 5 kgf / cm 2 , and set the heating temperature to 640°C.
[0251] These substrates for power modules were subjected to a predetermined number of cooling and heating cycles (-40...
Embodiment 2
[0258] A comparative experiment conducted to confirm the effectiveness of the present invention will be described.
[0259] Prepared by Al 2 o 3 A ceramic substrate with a thickness of 0.635 mm and a copper plate with a thickness of 0.3 mm composed of copper or a copper alloy having the compositions shown in Table 2 were used.
[0260] These copper plates, ceramic substrates, and copper plates are joined by the method described in the seventh embodiment. The pressing pressure in the circuit layer forming step S601 and the second metal layer forming step S602 is set to 0.5kgf / cm 2 , and set the heating temperature to 850°C.
[0261] These substrates for power modules were subjected to a predetermined number of cooling and heating cycles (-40°C to 110°C and 110°C to -40°C) to check for cracks in the ceramic substrate.
[0262] [Table 2]
[0263]
[0264] In the conventional example B1 using ductile copper and the conventional example B2 using oxygen-free copper (OFC), crac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com