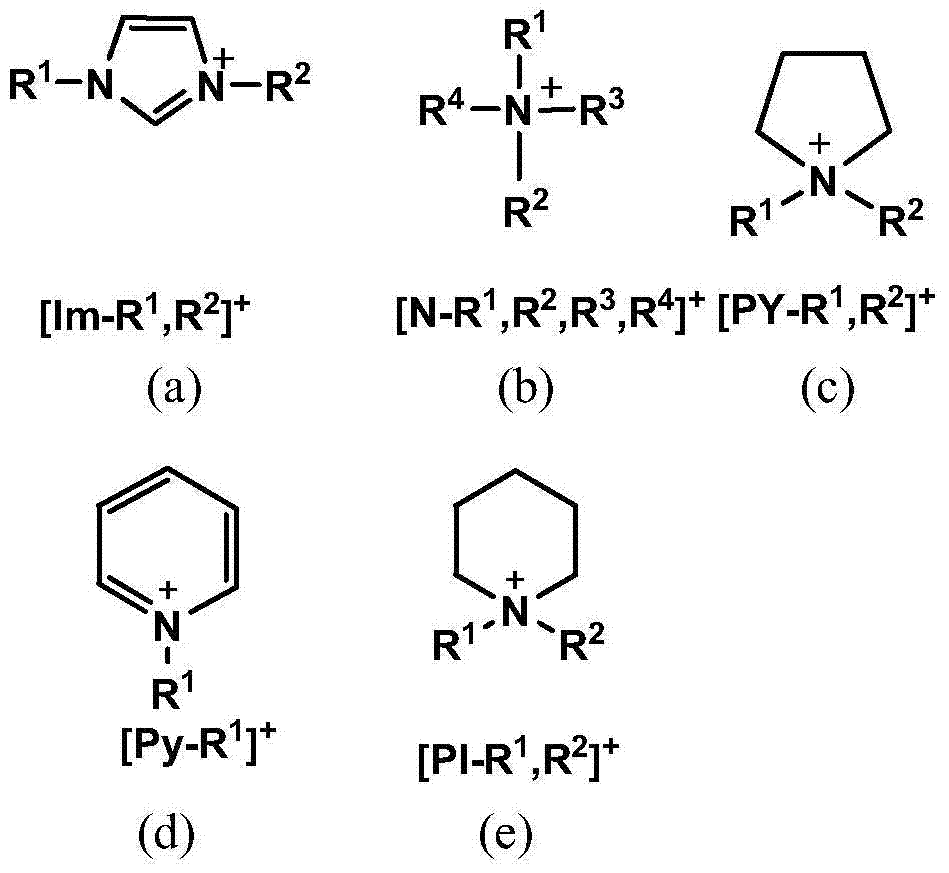Preparation method of fluoroethylene carbonate
A technology of fluoroethylene carbonate and chloroethylene carbonate, which is applied in the field of preparation of fluoroethylene carbonate, can solve the problems of increased reaction operation complexity, long time, high reaction temperature, etc., and achieve enhanced nucleophilicity and room temperature reaction The effect of mild conditions and high reaction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] In a 250ml three-necked flask, add 24.5g (0.2mol) of chloroethylene carbonate (Cl-EC), then add successively relative to 1.3 times the fluorinating reagent KF of chloroethylene carbonate consumption, 10mol% bis(tri-EC) Fluoromethylsulfonyl) imidized 1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolium (Im-1,2-TFSI, 7.8g) ionic liquid catalyst, and 60ml of acetonitrile. Stir magnetically and react at 25°C for 12h. Filter off the solid, collect the filtrate, remove the organic solvent in the filtrate by rotary evaporation, and carry out vacuum distillation on the remaining liquid, collect 18g of 70~72℃ / 2~3mm Hg fraction, the yield is 85%; the water content is 15ppm (measured by coulometric method) . The light yellow residue remaining in the bottle after distillation is ionic liquid (ionic liquid cannot be distilled out by ordinary distillation methods due to its extremely low volatility), weighing about 8g. The recovered ionic liquid is directly used in the next cycle reaction.
[0024] The ch...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The ionic liquid recovered in Example 1 was directly used in the catalytic reaction to prepare fluoroethylene carbonate (F-EC). Except using the recovered ionic liquid of Example 1 for the catalytic reaction, the remaining reaction steps and reagent consumption were the same as in Example 1 to obtain 18 g of fluoroethylene carbonate (F-EC) with a yield of 85%. Following examples 1 and 2, the ionic liquid recovered after each reaction was used for the next reaction to catalyze the preparation of fluoroethylene carbonate, and 10 consecutive reactions were carried out like this. As a result, the yield of fluoroethylene carbonate (F-EC) was 82 to 85%. After ten reactions, the ionic liquid was yellow, washed with water, dried and weighed, and the weight of the ionic liquid was 6.5 g. Therefore, the recovery of the ionic liquid was 83% after 10 catalytic reactions. It was confirmed by nuclear magnetic characterization that the ionic liquid did not decompose after 10 reactio...
Embodiment 3-24
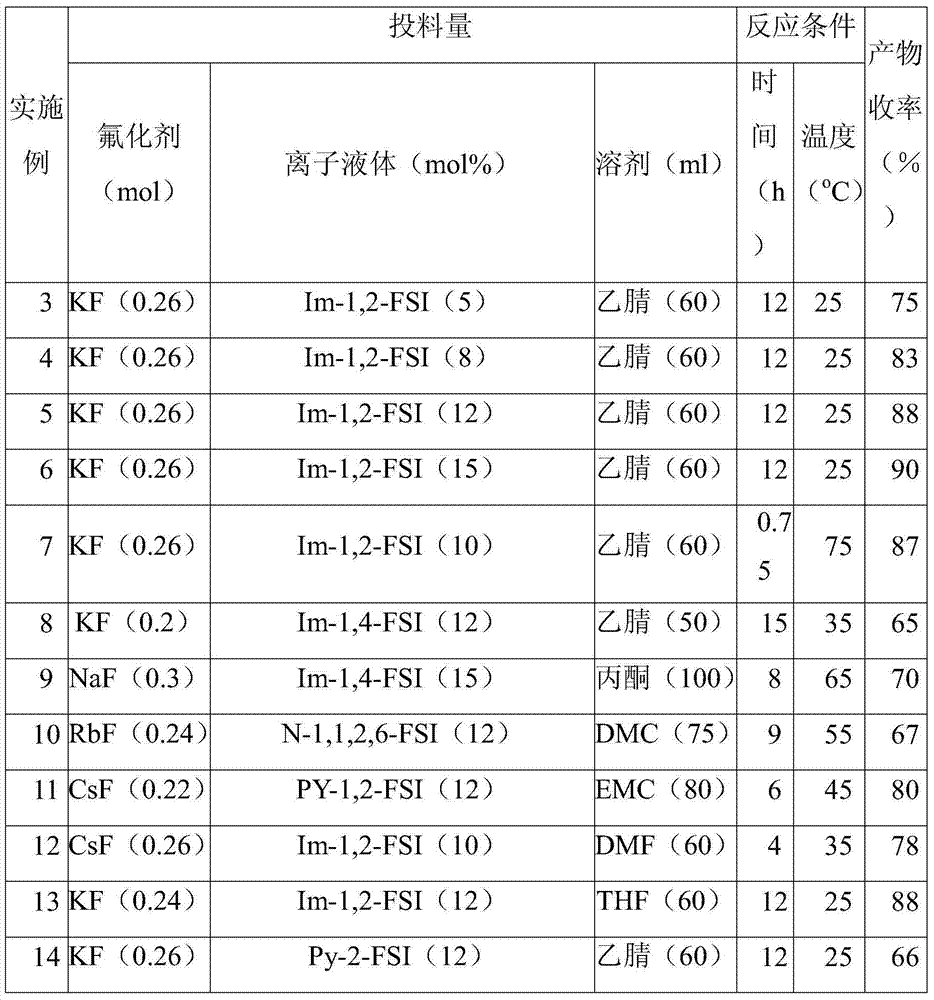
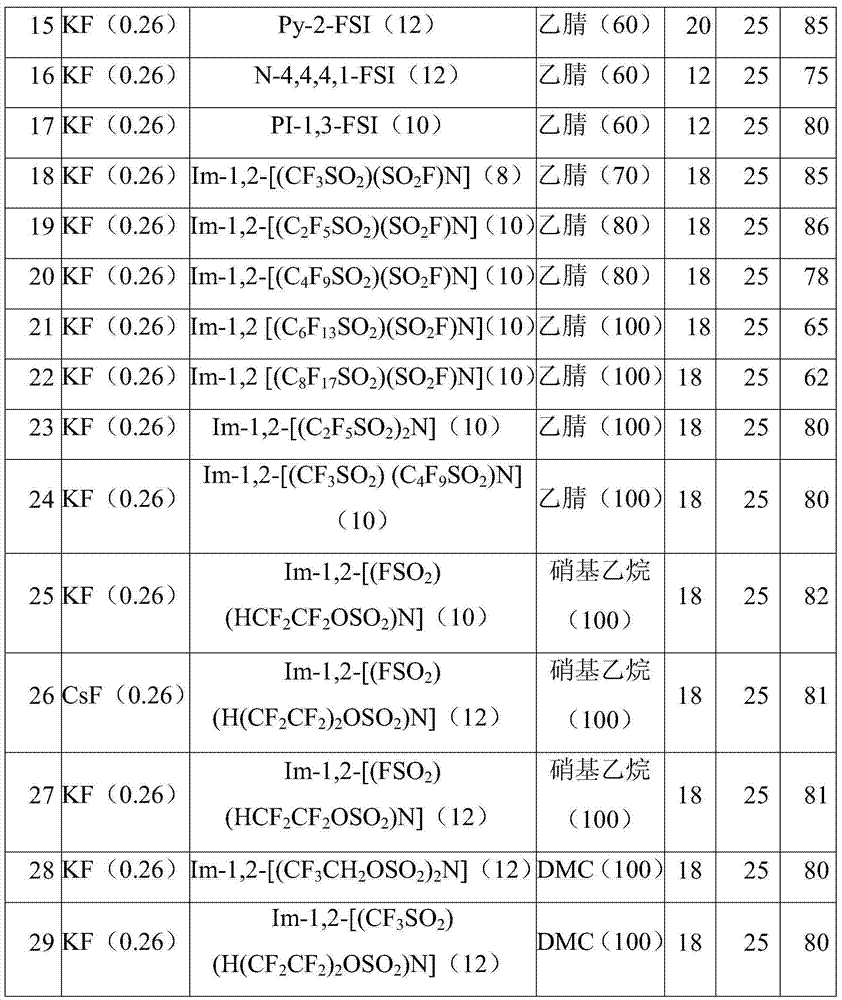
[0036] Examples 3-29 show the preparation methods and yields of F-EC under different reaction conditions. In all the examples, the amount of Cl-EC is 24.5g (0.2mol), and the amount of the catalyst ionic liquid is calculated according to the percentage molar ratio of the amount of Cl-EC.
[0037] Table 1 Preparation methods and results of F-EC under different reaction conditions
[0038]
[0039]
[0040] Explanation: Im, N, PY, Py and Pl represent (a) imidazole, (b) tetraalkyl quaternary ammonium, (c) tetrahydropyrrole, (d) pyridine and piperidine (e) in formula 1 respectively in the table ) parent structure. The substituents methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl, n-pentyl and n-hexyl on the nitrogen atom are represented by numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 respectively (such as PY-12 represents N- methyl-N-ethyltetrahydropyridinium cation).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com