Graphene-sulfur composite electrode material, preparation method and application thereof
A composite electrode and electrode material technology, which is applied in the field of electrochemical batteries, can solve problems such as poor cycle performance and difficult capacity of electrode materials, and achieve the effects of strong adsorption capacity, good electrochemical performance, superior flexibility and conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
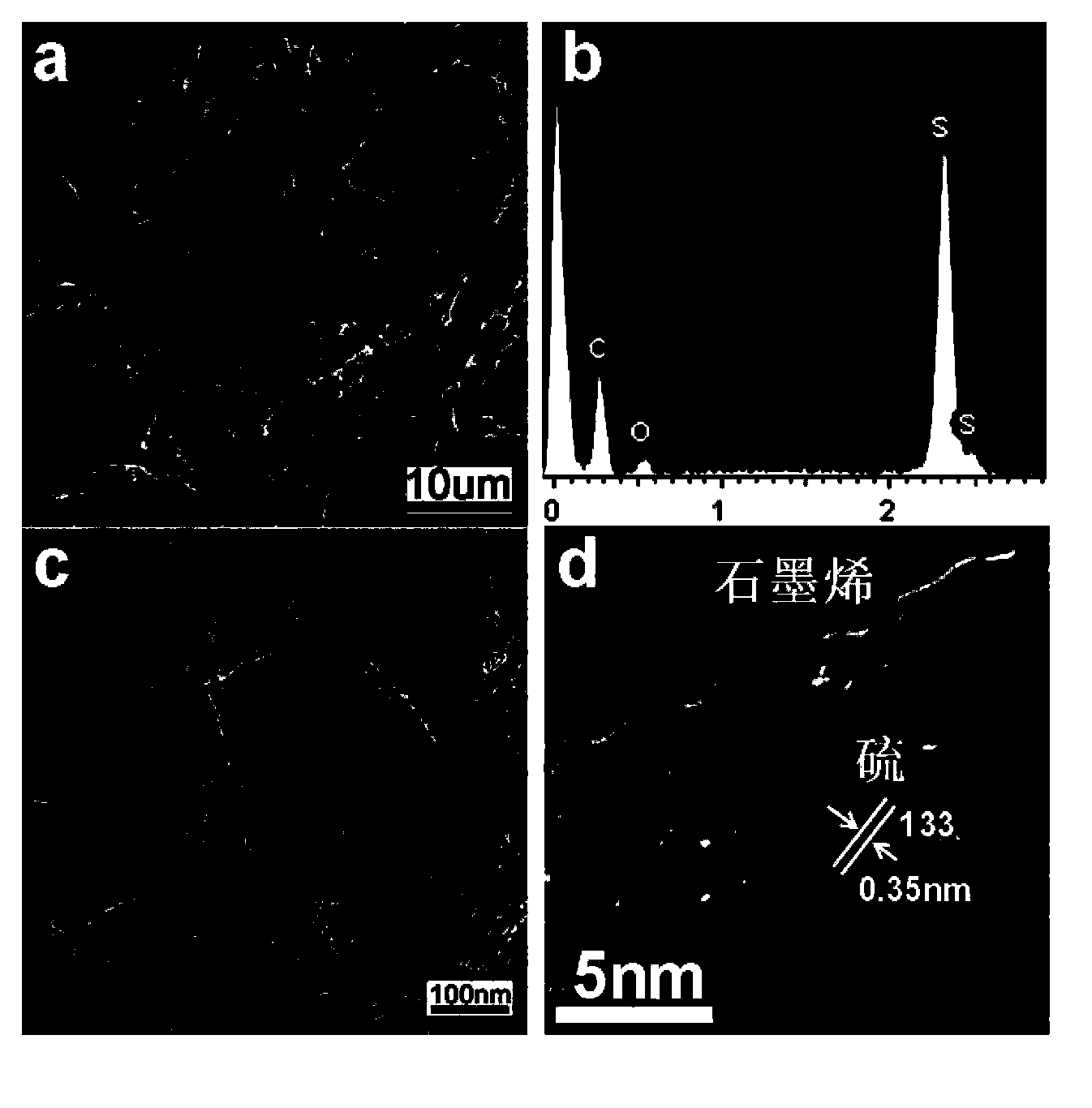
[0036] Graphene oxide aqueous solution (50mL) with a graphene oxide content of 2mg / mL was mixed with 3mL sulfur carbon disulfide solution (containing 150mg sulfur), and 15mL ethanol was added and stirred for 2h, then put into a hydrothermal kettle for hydrothermal reaction; hydrothermal reaction The temperature is 180°C, and the reaction time is 12h. During the hydrothermal process, the in-situ reduction self-assembles to form a three-dimensional macroscopic structure of sulfur particles (5-10nm) uniformly distributed and anchored on the graphene surface. See figure 1(III), obtain the graphene-sulfur macroscopic body composite material after freeze-drying at low temperature-70 ℃ for 24h, the elemental sulfur content is 63wt%; Gained graphene-sulfur macroscopic body composite material section, material thickness after pressing under 2MPa pressure It is about 40 μm, and it can be used as an electrode material without metal current collectors, conductive agents and binders for lit...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The difference from Example 1 is:
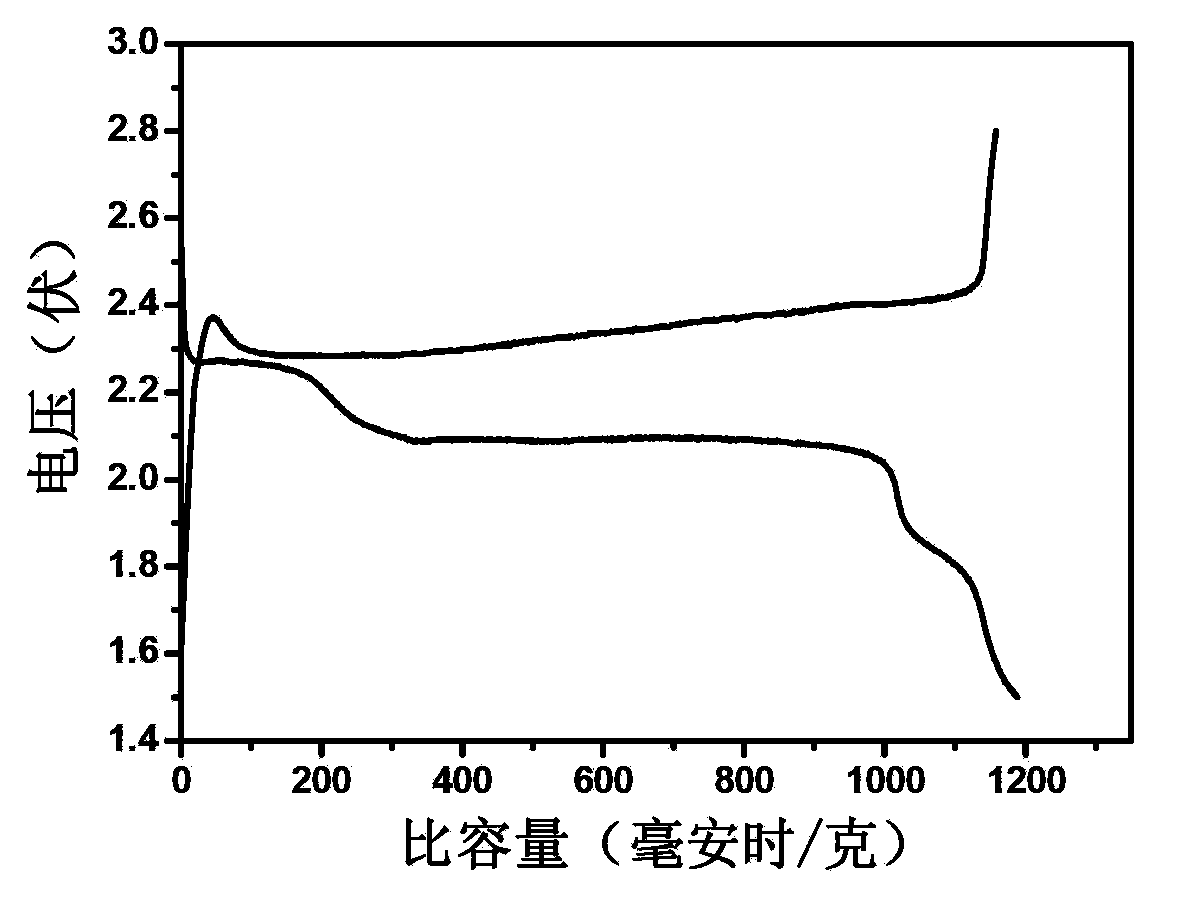
[0040] The preparation process is based on Example 1, changing the content of sulfur in the hydrothermal reaction solution, using 3mL of sulfur in carbon disulfide solution (containing 100mg of sulfur); the temperature of the hydrothermal reaction is 180 ° C, the reaction time is 12h, in water In situ reduction self-assembly during the thermal process to form a three-dimensional macroscopic structure of sulfur particles (510nm) uniformly distributed and anchored on the graphene surface see figure 1 (IV), and then freeze-dried at -70°C for 24 hours to obtain a graphene-sulfur macroscopic composite material; the content of elemental sulfur in the composite material was 55wt%. The graphene-sulfur composite film is used as the cathode material, and at 300mA·g -1 Under the highest current density, the initial discharge capacity can reach 1240mAh·g -1 , the discharge capacity of the graphene-sulfur composite electrode at various current d...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The difference from Example 2 is:
[0043] The preparation process is based on Example 1. In this example, the content of sulfur in the hydrothermal reaction solution is changed, and 3 mL of sulfur carbon disulfide solution (containing 200 mg of sulfur) is used; the temperature of the hydrothermal reaction is 180 ° C, and the reaction time is 12h, in situ reduction self-assembly in the hydrothermal process to form a three-dimensional macroscopic structure of sulfur particles (5-10nm) uniformly distributed and anchored on the graphene surface see figure 1 (V), and then freeze-dried at -70°C for 24 hours to obtain a graphene-sulfur macroscopic composite material; the content of elemental sulfur in the composite material was 71wt%. The graphene-sulfur composite film is used as the cathode material, and at 300mA·g -1 Under the highest current density, the first discharge capacity can reach 1115mAh·g -1 , the discharge capacity of the graphene-sulfur composite electrode at...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com