Method for treating spiramycin zymophyte dreg
A technology of spiramycin and bacterial residue, which is applied in the field of processing spiramycin fermentation waste residue, can solve problems such as unbalanced ratio of antibiotic waste residue, failure to remove antibiotics, hidden dangers in the treatment or application of biogas slurry and biogas residue, and achieve resource utilization. The effect of maximizing utilization, avoiding waste, and reducing the cost of disposal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
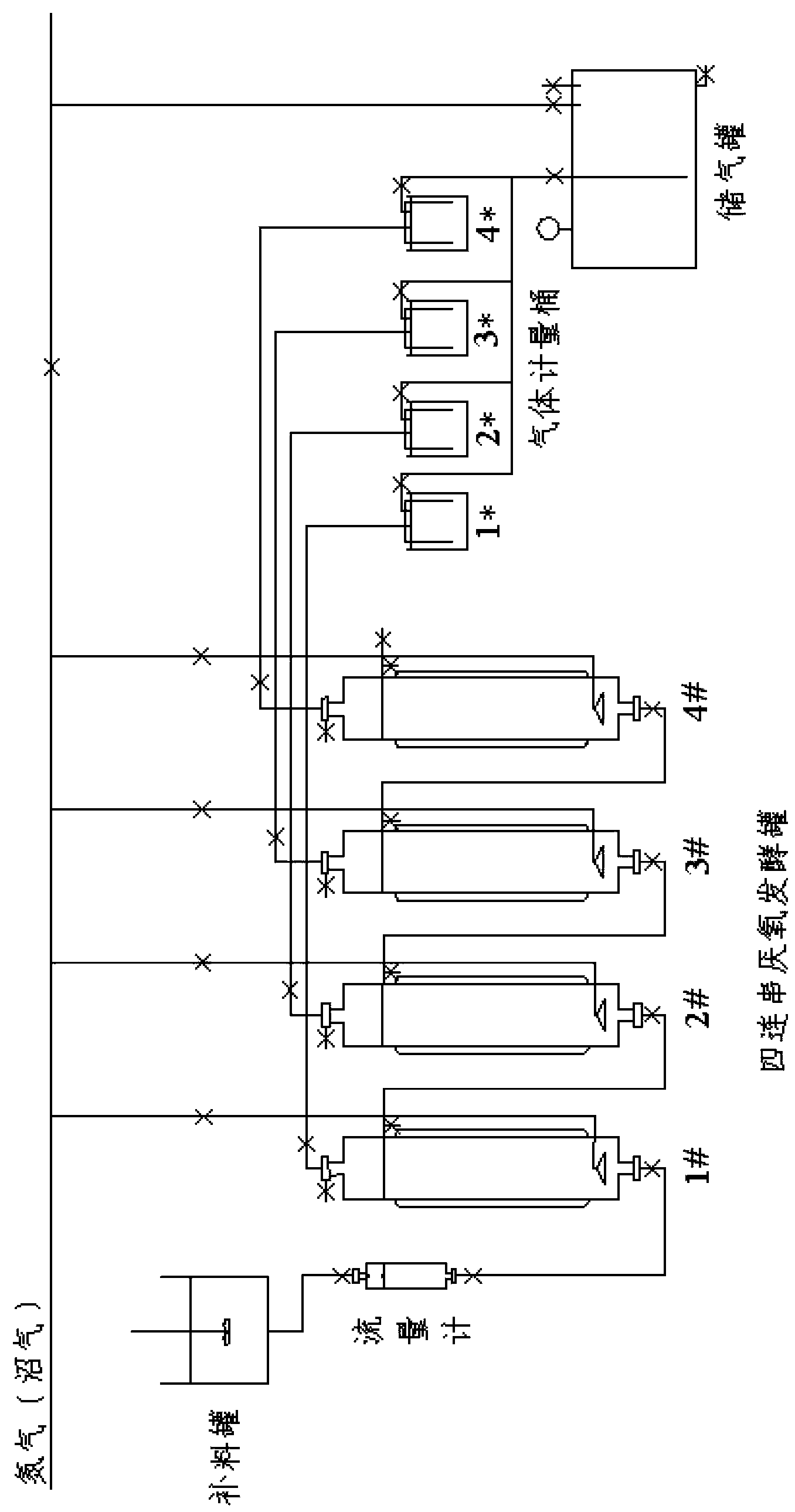
[0062] Take 1600g of spiramycin residue with a water content of 75%, add water to dilute to 20L, crush the residue with a mixer to form a residue liquid with a solid content of 2%, add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7.5, and then pour it into In glass jars with a total volume of 40L. Add 13.3L of swamp mud to the fungus residue liquid at an inoculation ratio of 40%, fill it with nitrogen to drive out the air, seal it with a cover, and mix well. Open a small opening from the cork to insert the airway tube, and put the other end of the airway tube into the water for exhaust. The whole device was cultured in an environment with a temperature of 37° C., shaken twice a day, and activated for a total of 15 days.
[0063] According to 1 / 3 of the total volume of 11L in a single tank of the multi-stage anaerobic device, take 3.6L of the mixed biogas slurry from the activated bacteria residue liquid and biogas slurry in the glass tank and add them to the tanks of all levels of th...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Take 1600g of spiramycin residue with a water content of 75%, add water to dilute to 20L, crush the residue with a mixer to form a residue liquid with a solid content of 2%, add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7.5, and then pour it into In glass jars with a total volume of 40L. Add 13.3L of swamp mud to the fungus residue liquid at an inoculation ratio of 40%, fill it with nitrogen to drive out the air, seal it with a cover, and mix well. Open a small opening from the cork to insert the airway tube, and put the other end of the airway tube into the water for exhaust. The whole device was cultured in an environment with a temperature of 34° C., shaken twice a day, and activated for a total of 15 days.
[0068] According to 1 / 3 of the total volume of 11L in a single tank of the multi-stage anaerobic device, take 3.6L of the mixed biogas slurry from the activated bacteria residue liquid and biogas slurry in the glass tank and add them to the tanks of all levels of th...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Take 1600g of spiramycin residue with a water content of 75%, add water to dilute to 20L, crush the residue with a mixer to form a residue liquid with a solid content of 2%, add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7.5, and then pour it into In glass jars with a total volume of 40L. Add 13.3 L of swamp mud to the fungus residue liquid at an inoculation ratio of 40%, fill it with carbon dioxide to drive out the air, seal it with a cover, and mix well. Open a small opening from the cork to insert the airway tube, and put the other end of the airway tube into the water for exhaust. The whole device was cultured in an environment with a temperature of 38° C., shaken twice a day, and activated for a total of 15 days.
[0073] According to 1 / 3 of the total volume of 11L in a single tank of the multi-stage anaerobic device, take 3.6L of the mixed biogas slurry from the activated bacteria residue liquid and biogas slurry in the glass tank and add them to the tanks of all level...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com