Method for removing rhodamine B dye from wastewater by walnut shell biomass charcoal adsorbent
A biochar and walnut shell technology, applied in the direction of adsorption of water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve the problems of resource waste, pollution, incineration or discarding, etc., and achieve good adsorption performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] Sorbent preparation
[0024] Take a certain amount of commercially available common walnut shells, wash them with tap water, dry them, crush them, and sieve them to 300-600 μm, mix the crushed walnut shells and zinc chloride solution according to the mass of walnut shells (g): the mass of zinc chloride solution (g) mixed and impregnated in a conical flask with a ratio of 1:6, in which the concentration of zinc chloride solution was 30%, and then heated by 560W microwave for 15 minutes, and the obtained walnut shell biochar was pickled with 10% hydrochloric acid, Wash with distilled water until the pH is neutral, and dry to obtain adsorbent A.
[0025] Take a certain amount of commercially available common walnut shells, wash them with tap water, dry them, crush them, and sieve them to 300-600 μm, mix the crushed walnut shells and zinc chloride solution according to the mass of walnut shells (g): the mass of zinc chloride solution (g) mixed and impregnated in a conical ...
Embodiment 1
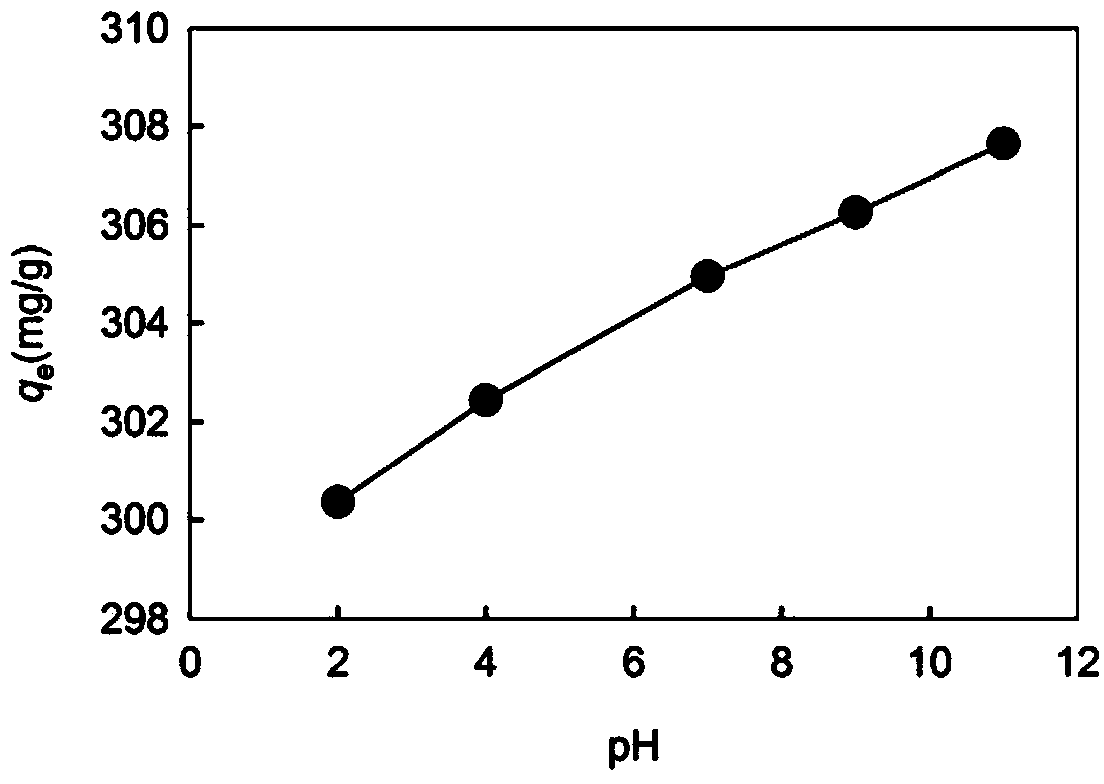
[0030] Take adsorbent B and sodium chloride and add the pH value of the solution to 2, 4, 7, 9, respectively, in the rhodamine B solution of 650mg / L, wherein every 0.05g of adsorbent B corresponds to 2.5g of sodium chloride and 50mL of rhodamine B After the solution was stirred or shaken at 25°C for 6 hours, it was separated by filtration, and the filtrate was adjusted to neutrality before being discharged.
[0031] The effect of different initial pH on the removal effect of rhodamine B is as follows: figure 1 Shown, along with the raising of pH, the adsorption value of adsorbent B to rhodamine B increases thereupon, illustrate that the method for removing rhodamine B of the present invention is applicable to the treatment of alkaline wastewater, and the higher the pH, the better the treatment effect it is good.
Embodiment 2
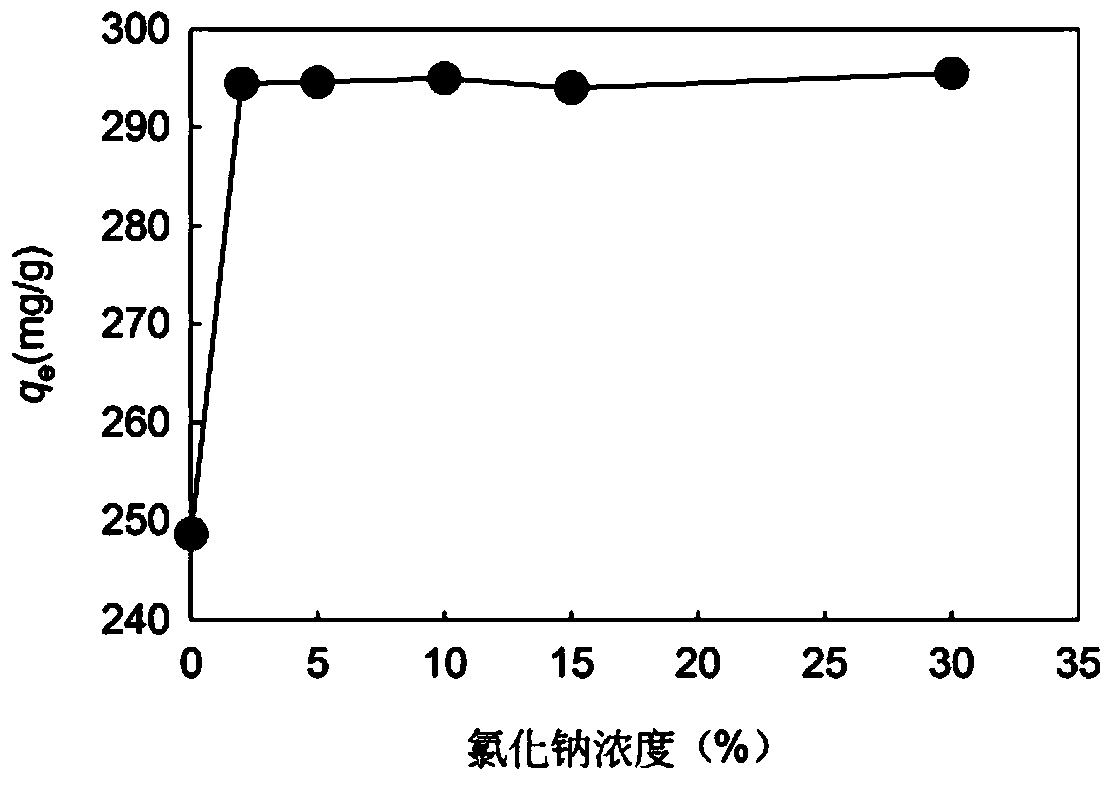
[0033] Take adsorbent C and add it to pH=4.0, 600mg / L rhodamine B solution, wherein every 0.15g of adsorbent C corresponds to 50mL rhodamine B solution, and add sodium chloride at the same time so that the percentage mass concentration is 0%, 2%, respectively. 5%, 10%, 15%, 30%, after stirring or shaking at 45°C for 8 hours, filter and separate, adjust the filtrate to neutral and discharge.
[0034] The effect of sodium chloride concentration on the removal effect of rhodamine B is as follows: figure 2 shown. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the presence of sodium chloride is very beneficial to the removal of Rhodamine B. from figure 2 It can also be found that when the concentration of sodium chloride is between 2% and 30%, there is basically no difference in the adsorption amount of rhodamine B by adsorbent C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap