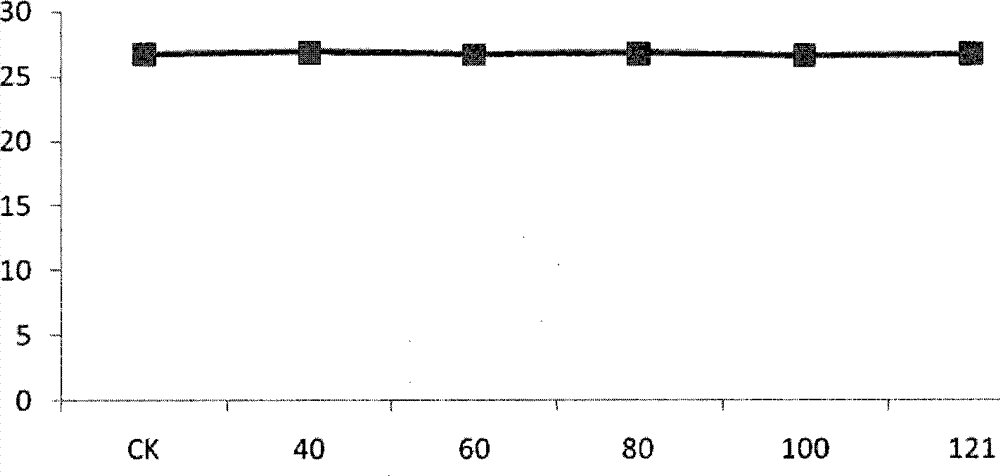
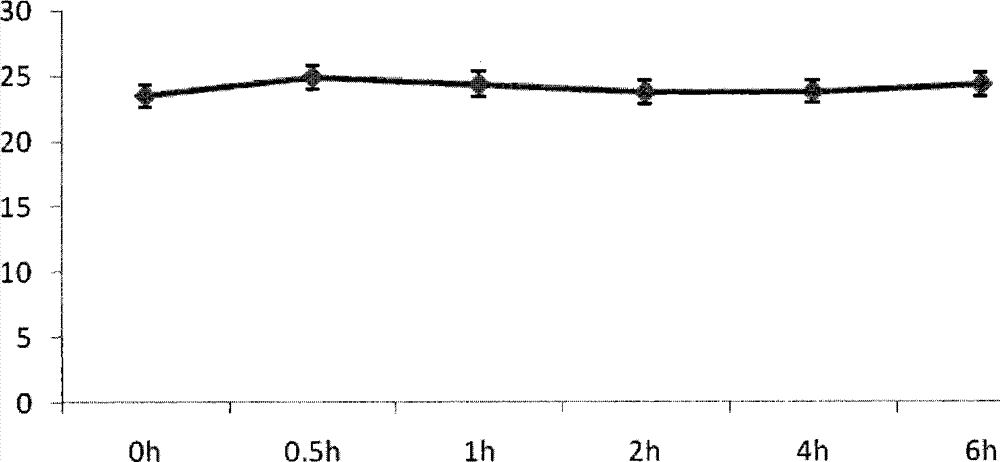
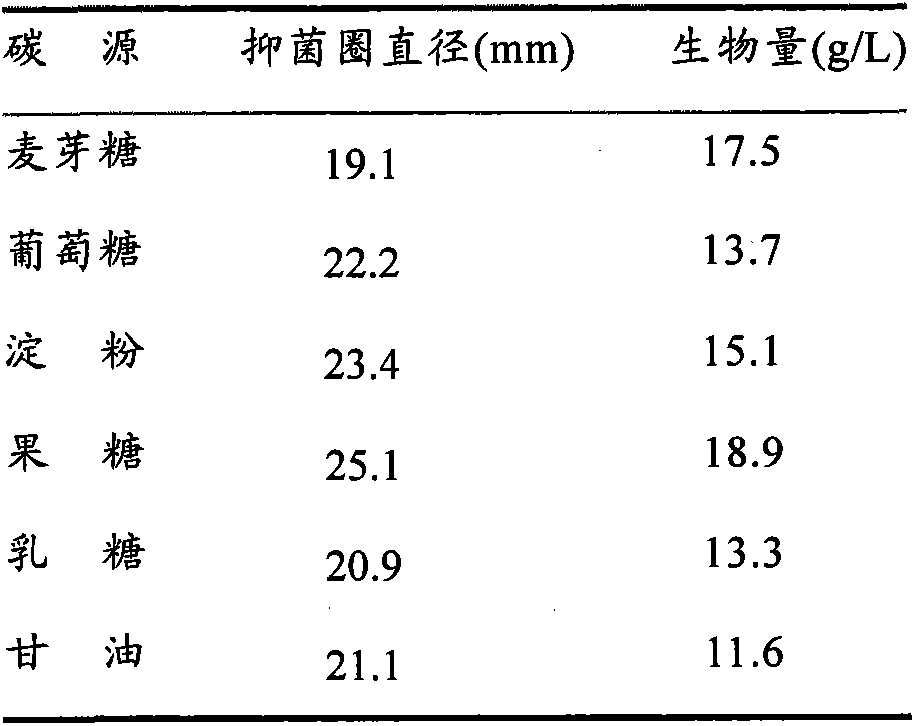
Application of fermented Aspergillus niger xj for inhibiting Ralstonia solannacearum of tobacco
A strain of Aspergillus niger, the technology of Aspergillus niger, applied in the application field of Aspergillus niger in inhibiting tobacco bacterial wilt, can solve problems such as deterioration and mold of flue-cured tobacco, increased risk in the field, and danger of post-production of flue-cured tobacco.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: the isolation of pathogenic bacteria
[0025] The isolated strains were artificially cultivated on NA medium and TTC medium respectively, and the bacterial morphology was observed. Among them, several isolated strains had a single colony on NA medium, which was small round, slightly raised, white soup-like and shiny , which is consistent with the description of the growth morphology of R. solanacearum on NA medium; the center of the colony of some isolates on TTC medium is pink, and the surrounding white is more fluid, which is consistent with the description of the growth morphology of R. solanacearum on TTC medium .
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Identification of pathogenicity
[0027] The strain was transferred from sterile water to NA slant medium, cultured for 48 hours, added sterile water to suspend, poured into a triangular flask containing NA culture medium, and cultured for 48 hours on a constant temperature shaker at 30°C at 180r / min. Bacterial water diluted to 1x10 8 cfu / mL of bacterial suspension.
[0028] Use the leaf axil acupuncture inoculation method: use a sterile injection needle to pierce the vascular bundle in the stem from the leaf axil of the third fully expanded leaf downwards from the top of the tobacco plant with a sterile injection needle, inject 0.2mL of bacterial suspension, then draw out the injection needle, and use Cover the injection site with sterilized and degreased cotton, and then wrap it with a piece of sterilized absorbent cotton to keep it moist for 48 hours. Set up 5 replicates, with 5 plants in each replicate. Use sterile water as a control, and induce the di...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Embodiment 3: antibacterial action assay:
[0030] Training method:
[0031] Experimental strains: Aspergillus niger (Aspergillus niger xj): isolated from the Institute of Fungal Resources, Guizhou University, and is now preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (Address: Wuhan University, Wuhan, China), and the preservation number is CCTCCNO: M206021.
[0032] Tobacco Ralstonia solanacearum: preserved in the Microbiology Laboratory of the College of Life Sciences, Guizhou University.
[0033] PDA slant medium: cut 200g of potatoes into pieces, boil in water for 30min, filter the juice, add 20g of glucose, 20g of agar, make up 1000mL of water, the pH is natural. Sterilization conditions: 121°C, 30min (the following sterilization conditions are the same).
[0034] LB medium (Luria-Bertan medium): tryptone 1%, NaC 10.5%, yeast extract 1%, pH 7.2. Sterilize.
[0035]Tobacco R. solanacearum cultivation method: under aseptic conditions, inoculate tobacc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com