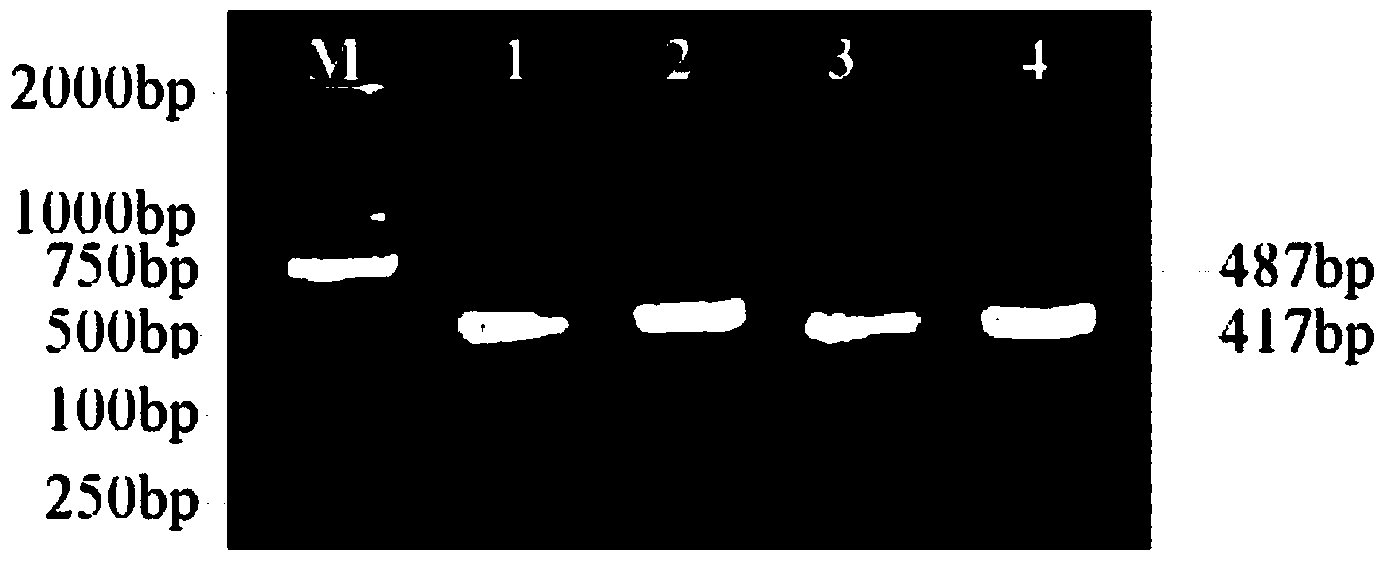
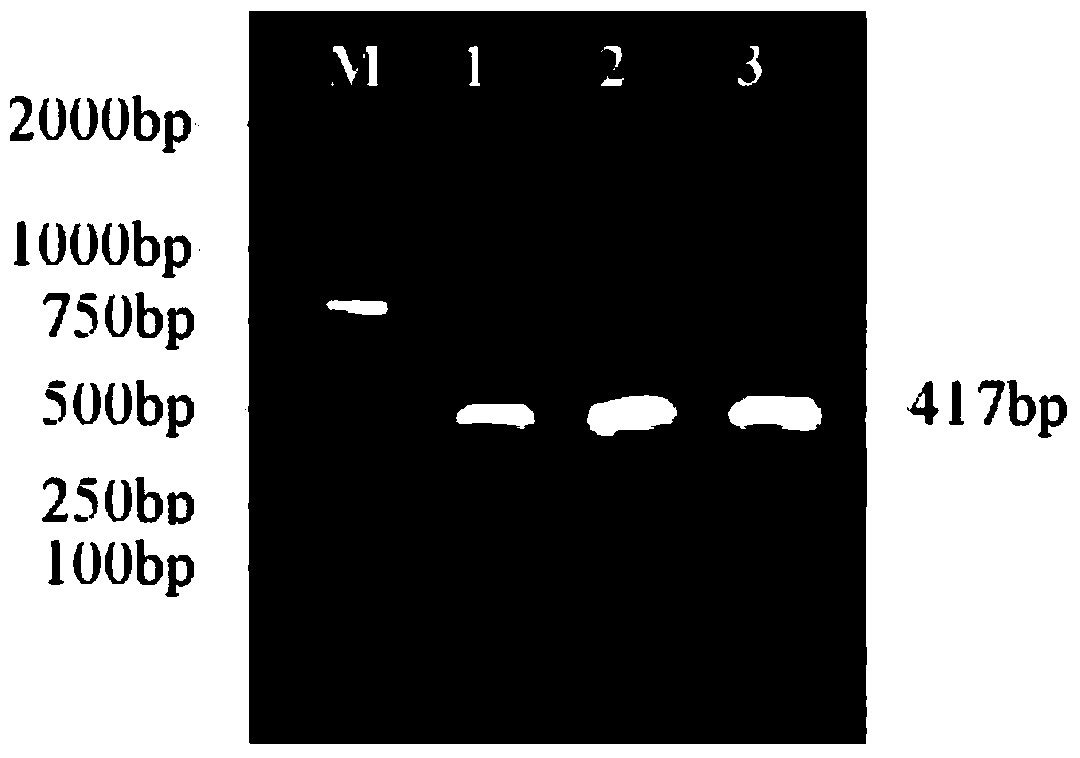Escherichia coli engineering bacterium containing gene of Epl1 (eliciting plant response protein1) and construction method of escherichia coli engineering bacteria
A technology of Escherichia coli and construction methods, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to directly separate Epl1 protein, many proteins and metabolites, and heavy workload, and achieve an improvement Defense ability, wide application prospect, growth-promoting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0031] Specific embodiment one: In this embodiment, an Escherichia coli engineering bacterium BL21-Epl1 containing the plant-stimulating response protein Epl1 gene is a Gram-negative short bacillus, a facultative anaerobic bacterium, and the colonies are round, smooth, colorless, and transparent .
[0032]The Escherichia coli engineered bacteria containing the stimulatory plant response protein Epl1 gene of this embodiment can inhibit the salicylic acid, jasmine Acid and auxin signaling pathway related gene expression can be significantly stimulated, and can cause significant changes in the activity of physiological enzymes in Populus japonicus. Therefore, the recombinant protein rEpl1 can not only induce the resistance of Populus japonicus, improve the defense ability of Populus japonicus, but also effectively promote the growth of Populus japonicus.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Specific embodiment two: the construction method of the Escherichia coli engineering bacterium that contains the stimulatory plant response protein Epl1 gene of this embodiment is carried out by the following steps:
[0034] 1. Extract the mycelium cDNA of Trichoderma dark green: at 28 ℃, under the condition of 200 rpm, culture the mycelium of Trichoderma dark green in 1 / 4PD medium for 48 hours, collect the mycelium, and then extract the total RNA, and reverse transcription of total RNA into cDNA;
[0035] Two, the construction of the prokaryotic expression vector pGEX-Epl1: the mycelia cDNA of Trichoderma dark green obtained in step 1 is used as a template, and Ep1e and Ep2e are primers for PCR amplification and purification to obtain a PCR product; then from Escherichia coli TOP10- Plasmid pGEX-4T-2 was extracted from pGEX-4T-2, and then the plasmid pGEX-4T-2 and the PCR product were first digested with BamHI, and the digested products were recovered, and then the dig...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 2 is that the PCR amplification reaction system described in step 2 is: 10×buffer 2 μL, dNTP 0.8 μL, template 2 μL, primer Ep1e1 μL, primer Ep2e1 μL, deionized water 12.8 μL, EXTaq 0.4 μL, total volume 20 μL. Reaction program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 94°C for 30s, annealing at 58°C for 40s, extension at 72°C for 80s, 35 cycles; fill-in at 72°C for 20 minutes, and storage at 4°C, where the template is cDNA, primer Ep1e and primer Ep2e The concentration is 20 μM. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com