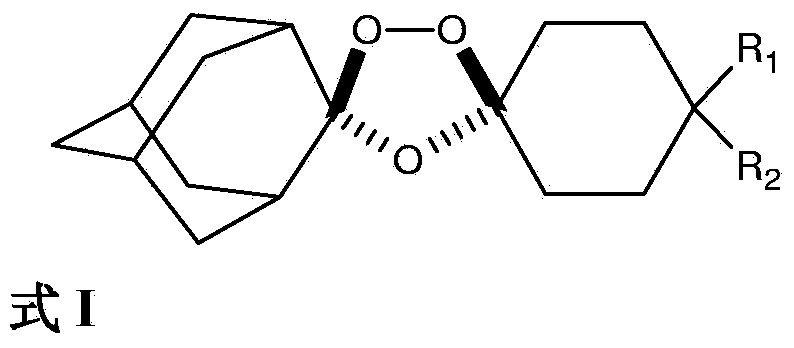
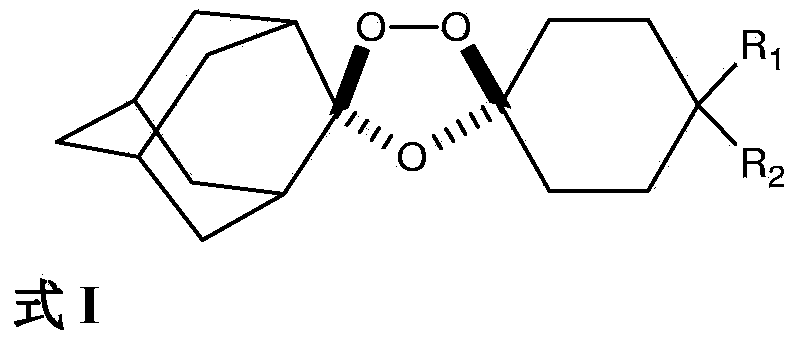
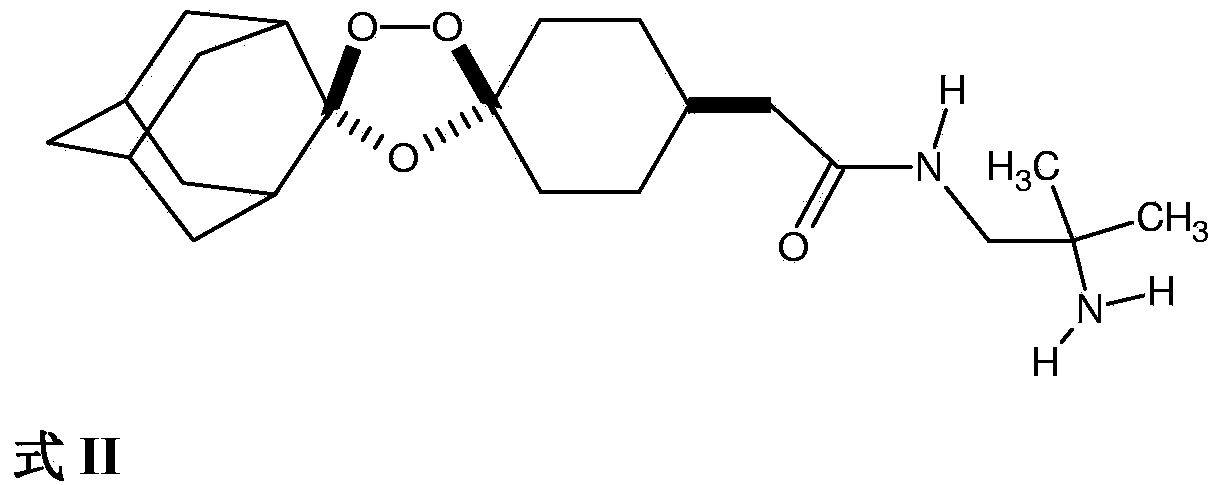
Stable dosage forms of arterolane and piperaquine
A stable, dosage-form technology, applied in the field of stable dosage forms of artemisinin and piperaquine, which can solve problems such as poor efficacy, reduced efficacy, and poor compliance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0162]
[0163] process:
[0164] 1. Sieve Active Compound I with the intragranular portion of microcrystalline cellulose through a sieve BSS #44 and mix in a double cone mixer to form a homogeneous mixture.
[0165] 2. Add the sieved intragranular portion of the magnesium stearate to the mixture of step 1 and mix for about 5 minutes.
[0166] 3. Compact the mixture from step 2 in a roller compactor, then sieve through a BSS #22 sieve to form granules.
[0167] 4. Sieve the microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate of the extragranular fraction through a sieve BSS#44 and blend with the granules from step 3.
[0168] 5. The mixture of step 4 is compressed using a punching machine of appropriate size to obtain compressed tablets.
[0169] 6. The tablets obtained in step 5 are coated with Perform coating.
[0170] The tablets prepared in Example 1 were subjected to a stability study for 6 months at 25°C / 60% relative humidity, 30°C / 65% rela...
Embodiment 2
[0179]
[0180] process:
[0181] 1. Sieve Active Compound I, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate through sieve BSS #44.
[0182] 2. Mix the sieved Active Compound I, microcrystalline cellulose and croscarmellose sodium in a double cone mixer for about 15 minutes to form a homogeneous mixture.
[0183] 3. Add the sieved magnesium stearate to the mixture from step 2 and mix for approximately 5 minutes.
[0184] 4. The mixture obtained in step 3 is directly compressed using capsule-shaped punches of appropriate size to obtain compressed tablets.
Embodiment 3 and 4
[0186]
[0187]
[0188] process:
[0189] 1. Sieve the intragranular fraction of Active Compound I, piperaquine phosphate and microcrystalline cellulose and cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone through a sieve BSS #44, then mix in a double cone mixer to form a homogeneous mixture.
[0190] 2. Add the intragranular portion of the sieved magnesium stearate to the mixture of step 1 and mix for about 5 minutes.
[0191] 3. The mixture from step 2 was compacted in a roller compactor, then sieved through a BSS #18 sieve to form granules.
[0192] 4. Sieve the microcrystalline cellulose and cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone in the extragranular portion through a sieve BSS#44, then mix with the granules from step 3.
[0193] 5. Sieve the magnesium stearate extragranular portion through a sieve BSS #44 and blend with the mixture from step 4 in a double cone blender for about 5 minutes.
[0194] 6. The blend of step 5 is compressed using appropriate sized punches to obtain compr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com