Micro nano structure solar battery and preparation method of back light trapping structure thereof
A technology of a solar cell and a light trapping structure, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of uneven deposition in a deposition process, and achieve the effects of improving short-circuit current and conversion efficiency, increasing optical path, and realizing light scattering.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The invention provides a method for preparing a light-trapping structure on the back of a micro-nano structured solar cell, which specifically includes the following steps:
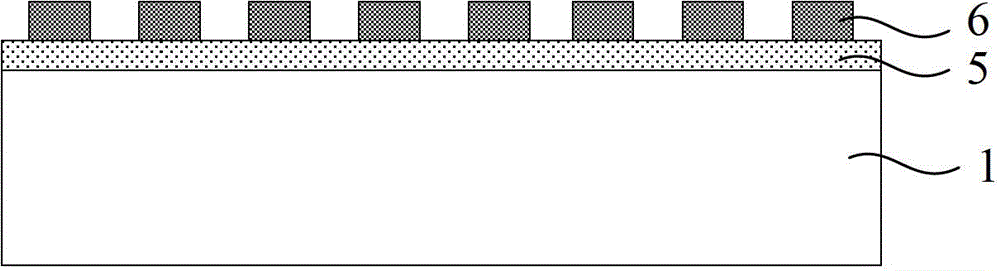
[0039] (1) A glass substrate 1 is provided.
[0040] see figure 1 . Before performing subsequent processes, the provided glass substrate 1 can be cleaned to remove impurities on the glass substrate 1 and avoid affecting the photoelectric conversion performance of the solar cell.
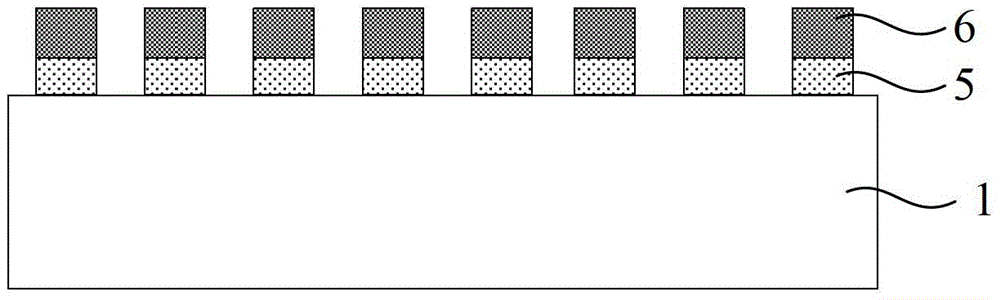
[0041] (2) Etching the glass substrate 1 by using an etching process, so that the surface of the glass substrate 1 is a columnar array structure 11;
[0042]This step includes the following steps: first prepare and form a metal layer 5 on the glass substrate 1; then apply a photoresist layer 6 on the metal layer 5, and obtain the required photoresist pattern by photolithography; The metal layer 5 and the glass substrate 1 are etched by an etching process; after the metal layer is removed, the glass substrate 1 with a c...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the process parameters for preparing the light-trapping structure are different, as follows:
[0058] 1) A glass substrate is used as a substrate, and a metal layer is deposited on the glass substrate as a mask layer. The metal layer is metal such as Cr with a thickness of 70nm.
[0059] 2) The desired photoresist pattern is obtained on the glass substrate by using photolithography technology of contact ultraviolet exposure, and the line width of the photoresist pattern is 700 nm.
[0060] 3) Use the photoresist as a mask to wet-etch the window of the metal layer. The composition ratio of the mixed solution used is: in every 100ml of etching solution, cerium ammonium nitrate is 11g, perchloric acid is 4.4ml, The balance is water.
[0061] 4) Using reactive ion etching technology to etch the glass substrate, the reaction gas is CHF 3 , the flow rate is 30 sccm, and the aspect ratio of the pattern etched i...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiments 1 and 2 is that the process parameters for preparing the light-trapping structure are different, as follows:
[0067] 1) A glass substrate is used as a substrate, and a metal layer is deposited on the glass substrate as a mask layer. The metal layer is metal such as Cr with a thickness of 80nm.
[0068] 2) The required photoresist pattern is obtained on the glass substrate by using the photolithography technology of contact ultraviolet exposure, and the line width of the photoresist pattern is 800nm.
[0069] 3) Use the photoresist as a mask to wet-etch the window of the metal layer. The composition ratio of the mixed solution used is: in every 100ml of etching solution, cerium ammonium nitrate is 14g, perchloric acid is 5.6ml, The balance is water.
[0070] 4) Using reactive ion etching technology to etch the glass substrate, the reaction gas is CHF 3 , the flow rate is 30 sccm, and the aspect ratio of the patte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com